💡 java.io.File
-
File 클래스는 파일 또는 폴더에 대한 정보를 제공하는 클래스이다.
-
파일 클래스의 객체는 정보를 조회하고자 하는 파일이나 폴더의 경로에 대한 문자열을
생성자 파라미터로 전달하는 형태로 만들 수 있다.
이 때, 파라미터로 전달되는 경로가 실제로 존재하지 않더라도 File객체의 생성이 가능하다.
- ex) C:\photo\food.jpg 파일에 대한 객체생성.
1) File file = new File("C:\photo\food.jpg");
2) File file = new File("c:\photo", "food.jpg");💡 경로 설정하기
- 운영체제간의 호환성 유지를 위해 "/"를 사용한다.
-> 경로 문자열을 설정할 때, 윈도우 기반에서는 역슬래시 '\' 를 사용하지만
이 경우 이스케이프문자를 사용하여 '\\'의 형식으로 사용해아한다.
따라서, 가급적 다른 운영체제와읭 호환성을 위해 슬래시 '/' 를 사용하는 것이 좋다.💡 절대 경로
-> 작업 디렉토리와 관계없이 절대적인 위치를 의미하는 경로.
-> 리눅스 : /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
-> 윈도우 : C:/Windows/System32/drivers/etc/hosts💡 상대 경로
-> 작업 디렉토리를 기준으로 상대적인 위치를 의미하는 경로
-> 리눅스 : ./conf/httpd.conf
-> 윈도우 : ..drivers/etc/hosts💡 문자 인코딩이란? (Character encoding)
-> 문자나 기호들의 집합을 컴퓨터에서 저장하거나 통신에 사용할 목적으로 부호화하는 방법.
-> 모스부호.
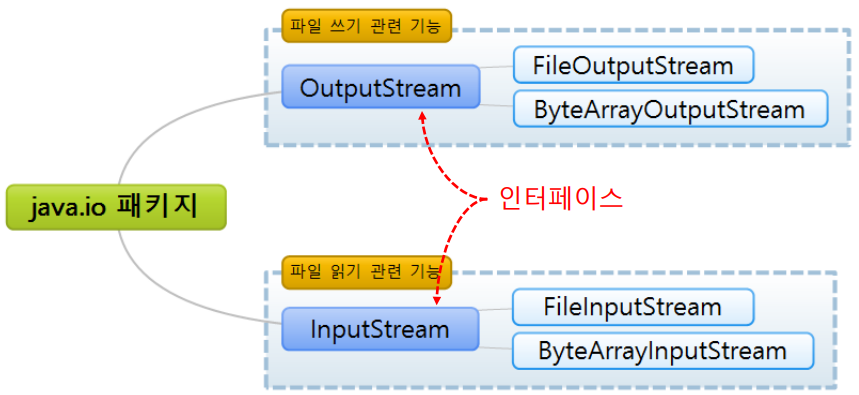
-> UTF-8. (8비트 2진수로 표현하는 방법.)💡 스트림이란?
-> 입출력에서 stream이란,
디바이스의 입출력 방식이 Character단위이던 block단위이던 관계없이 '1byte'씩 '연속'적으로 전달되는 형태로, 추상화된 상태를 의미한다.
-> 입출력장치는 개별적인 특성이 있으므로, 읽고쓰는 단위가 각각 다르지만,
스트림은 이러한 일련의 과정을 추상화하여 사용하고있다.
즉, 입출력 디바이스의 특성을 무시하고 하나의 단일한 입출력 인터페이스로 다룰 수 있도록 하는 것이 stream이라고 한다.
💡 Java 스트림 관련 클래스
- stram관련 클래스들은 각각
'InputStream(입력/읽기)', 'OutputStream(출력/저장)'과 관련된 인터페이스를 상속받기 때문에,
모두 동일한 메소드를 가지고 있다.💡 파일 저장 과정
- 저장을 위한 빈 파일 생성
-> OutputStram의 객체를 생성
- 파일에 내용 쓰기
-> 저장할 내용을 byte배열로 변환한다.
-> 변환된 배열을 OutputStream의 write()메소드에게 파라미터로 전달한다.
- 파일 닫기
-> OutputStream 객체로 close() 메소드를 호출하여 스트림을 닫는다.💡 파일 저장시 유의사항
- OutputStream은 각각의 단계마다 예외처리를 강제적으로 요구한다.
- try ~ catch 블록이 형성되는 과정에서 변수의 유효성 범위에 대한 처리에 유의해야한다.
💡 파일 저장 예시
package file;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class Main02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
* 문자열을 파일로 저장
-> 문자열을 파일로 저장하기 위해서는 byte배열로 변환해야 한다.
-> 문자열을 byte배열로 변환하기 위해서는 getBytes() 메소드를 사용하는데,
이 때 변환 과정에서 사용할 인코딩 형식을 지정해 주어야한다.
*/
// 저장할 파일의 경로
String path = "text.txt";
// 파일에 저장할 내용
String write_string = "가나다라마바사abcdefg";
// 특정 인코딩 방식 적용
// 객체나 배열이 선언과 할당에 대한 블록이 서로 분리되어 있을 경우
// 명시적으로 빈 영역임을 알리기 위하여 null로 초기화.
byte[] buffer = null;
try {
buffer = write_string.getBytes("utf-8");
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR]알수 없는 인코딩 정보 >> " + path);
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 파일 저장 절차 시작
// finally 블록에서 인식하기 위해서 선언부를 위로 이동시킨다.
OutputStream out = null;
try {
out = new FileOutputStream(path);
// 파일 쓰기
out.write(buffer);
System.out.println("[INFO]파일 저장 성공 >> " + path);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR]지정된 경로를 찾을 수 없음 >> " + path);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR]파일 저장 실패 >> " + path);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR]알 수 없는 예러 발생 >> " + path);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 저장의 성공여부 상관없이 스트림은 무조건 닫아야한다.
try {
out.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}💡 파일 읽기 과정
- 파일 읽기를 위한 InputStream 객체 생성하기
- 읽은 내용을 담기 위한 빈 byte 배열 생성하기
-> 파일의 용량 크기만큼 배열의 사이즈를 지정해야한다.
- 파일의 내용 읽기
-> 읽은 내용을 담기 위한 byte배열을
InputStream 객체의 read() 메소드에게 파라미터로 전달한다.
- 사용이 완료된 스트림 닫기
-> InputStream 객체의 close() 메소드를 호출하여 스트림을 닫느다.
- 읽은 내용을 문자열로 변환하기
-> byte배열을 String클래스의 생성자에게 전달하여 문자열로 변환한다.
-> 이 과정에서 어떤 인코딩을 사용할지를 함께 설정해야한다.💡 파일 읽기 예시
package file;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
public class Main03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 읽을 파일 경로
String path = "text.txt";
// 읽은 내용이 담겨질 스트림
byte[] data = null;
// 읽은 내용이 변환될 문자열
String read_string = null;
// 파일 읽기
InputStream in = null;
try {
in = new FileInputStream(path);
// 읽은 내용을 담기 위한 배열은 파일의 용량만큼 사이즈를 할당한다.
// in.available(); -> 열고 있는 파일의 크기
data = new byte[in.available()];
// 파일 읽기 - 파라미터로 전달된 배열 안에, 파일의 내용을 담아준다.
in.read(data);
System.out.println("[INFO] 파일 읽어오기 성공 >> " + path);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR] 지정된 경로를 찾을 수 없음 >> " + path);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR] 파일 읽기 실패 >> " + path);
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR] 알 수 없는 에러 >> " + path);
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (in != null) {
try {
in.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// data 배열에 내용이 있다면, 문자열로 변환하여 출력
if (data != null) {
// 문자열로 변환시에는 저장된 인코딩으로 지정해준다.
try {
read_string = new String(data, "utf-8");
System.out.println(read_string);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
System.out.println("[ERROR] 인코딩 지정 에러");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}💡 File 클래스의 유용한 메소드
package file;
import java.io.File;
public class Main01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// File클래스는 절대경로나, 상대경로를 생성자 파라미터로 전달한다.
// 이클립스에서 상대경로를 사용할 경우, 현재 프로젝트가 기준점.
// Workspace가 C:/java 이고, 프로젝트가 'day20'인 경우의 작업위치는
// C:/java/day20
File file = new File("src/file/Main01.java");
// 전달된 경로가 파일인지 검사
// -> 존재하지 않는 파일로 검사할 경우, 무조건 false.
boolean is_file = file.isFile();
System.out.println("is_file : " + is_file);
// 전달된 경로가 디렉토리인지 검사
// -> 존재하지 않은 디렉토리로 검사할 경우 무조건 false.
boolean is_dir = file.isDirectory();
System.out.println("is_dir : " + is_dir);
// 전달된 경로가 숨김형태인지 검사
// -> 존재하지 않는 파일로 검사할 경우 무조건 false
boolean is_hidden = file.isHidden();
System.out.println("is_hidden : " + is_hidden);
// 절대경로 값을 추출하기
String abs = file.getAbsolutePath();
System.out.println("절대경로 : " + abs);
// 생성자에 전달된 파일이나 디렉토리가 물리적으로 존재하는지를 검사.
boolean is_exist = file.exists();
System.out.println("존재여부 : " + is_exist);
// 디렉토리 정보 객체 생성
File file2 = new File("a/b/c/target");
System.out.println("isFile : " + file2.isFile());
System.out.println("isDirectory : " + file2.isDirectory());
System.out.println("isHidden : " + file2.isHidden());
System.out.println("절대경로 : " + file2.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("존재여부 : " + file2.exists());
// 경로에 따른 디렉토리 생성
file2.mkdirs();
// 마지막 "/" 경로 이후 단어를 리턴
System.out.println(file.getName());
System.out.println(file2.getName());
// 처음부터 마지막 "/" 직전까지 리턴
System.out.println(file.getParent());
System.out.println(file2.getParent());
// 삭제 시도 -> 성공시 true, 실패시 false
boolean del_ok = file2.delete();
System.out.println("삭제성공여부 : " + del_ok);
}
}