Arrays
Array is a type of linear data structure that is defined as a collection of elements with same or different data types. They exist in both single dimension and multiple dimensions. These data structures come into picture when there is a necessity to store multiple elements of similar nature together at one place.
배열은 동일하거나, 다른 데이터 타입 유형을 가진 요소의 모음(?)으로 정의되는 선형 데이터 구조임. 단일/다중 범위 내에 존재한다. 배열은 비슷한 다중 요소를 한 곳에 저장할 때 필요하다.
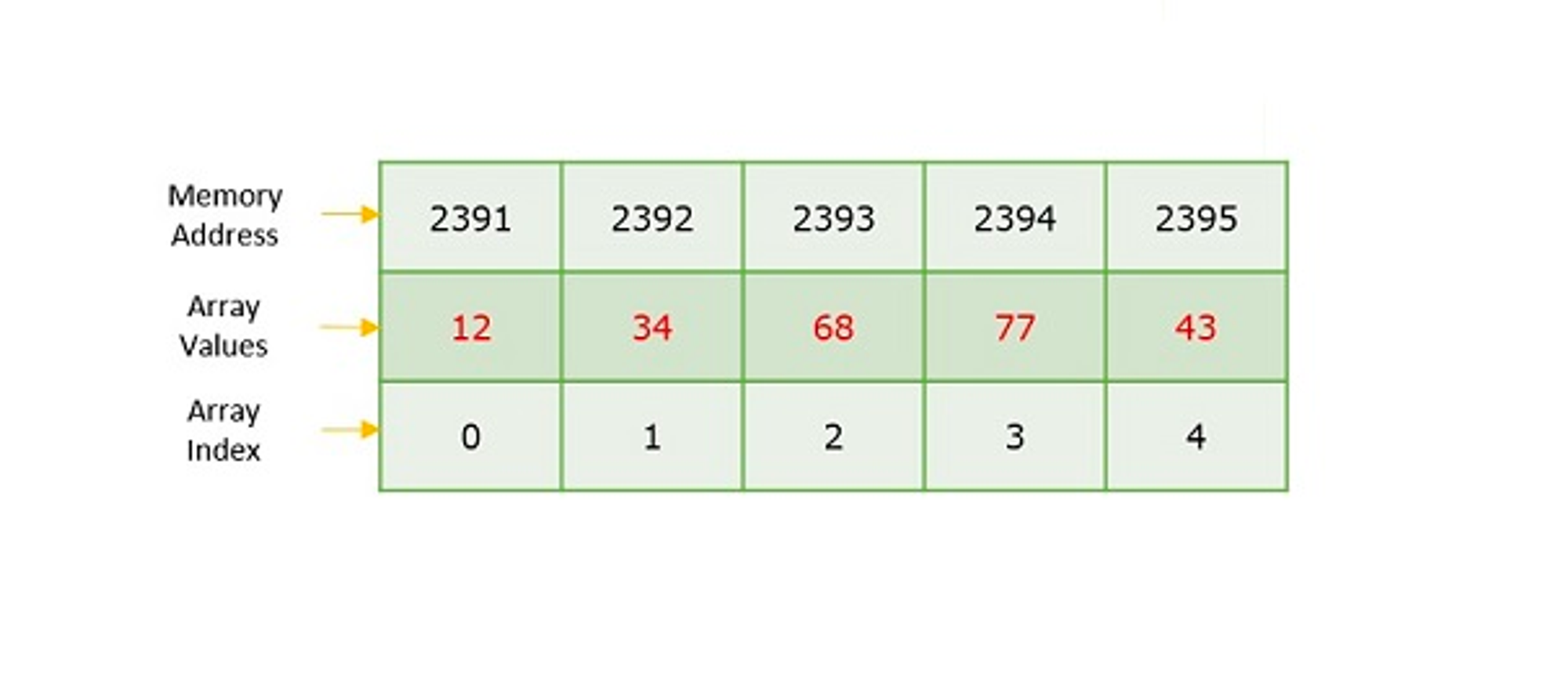
The difference between an array index and a memory address is that the array index acts like a key value to label the elements in the array. However, a memory address is the starting address of free memory available.
배열의 index와 메모리 주소의 차이점: 배열의 index는 배열의 요소에 레이블을 지정하는 키값으로 작동한다. 그러나, 메모리 주소는 사용 가능한 메모리의 시작 주소이다.
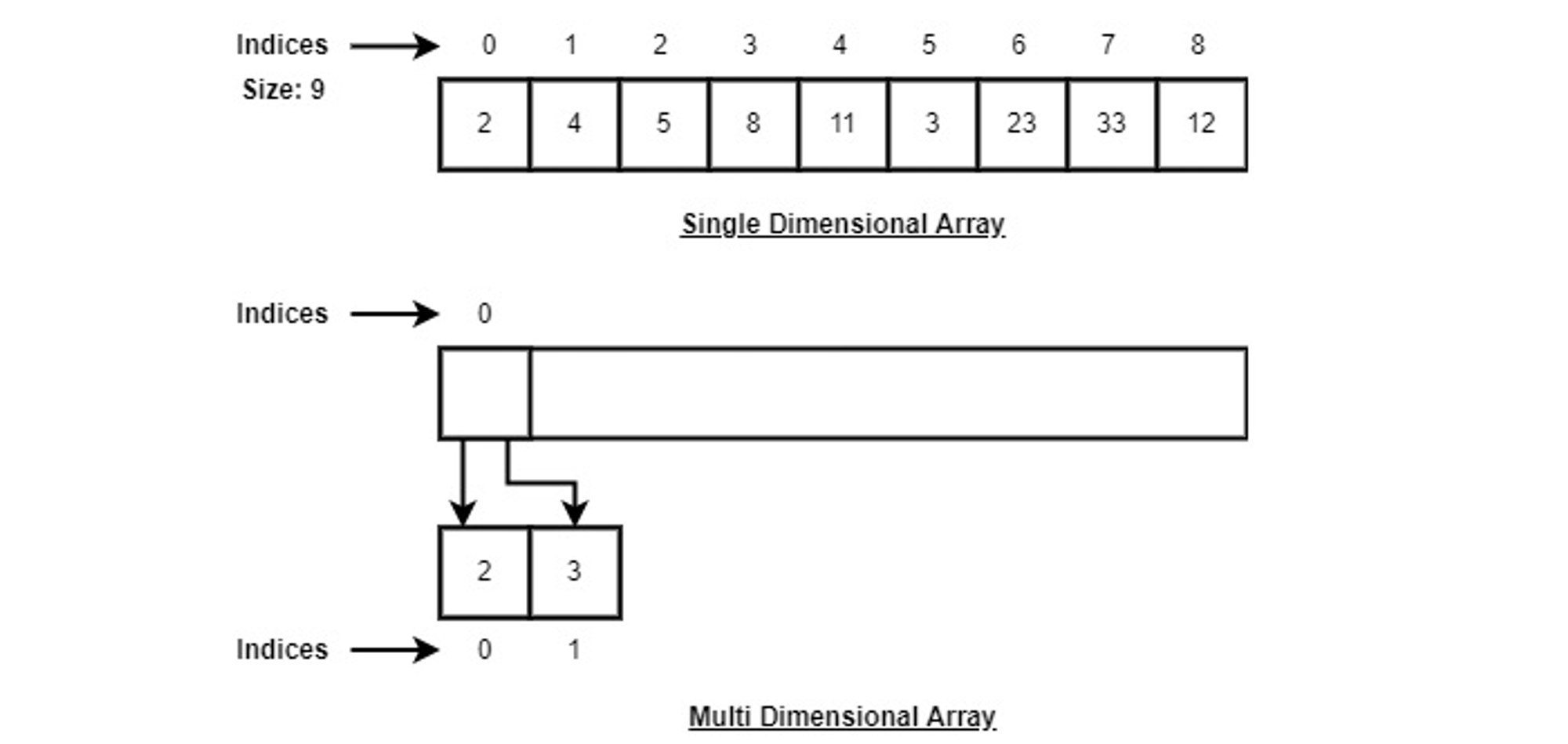
But I've always wondered, why do array indexes start at 0?
근데 예전부터 궁금했던 건데 왜 배열의 인덱스는 0부터 시작하지?
I immediately search on Google and understood.
바로 구글링해서 이해했다.
- Efficiency: the first element is at address 100 and each element is 4 bytes, the second element will be at address 104, the third at 108, and so on. If the index started at 1, the computer would need to add 1 to each address before using it, which would be less efficient.
효율성: 배열의 첫 번째 요소의 주소가 100이고, 각 요소가 4바이트라면 두 번째 요소의 주소는 104일 것. 세 번째는 108.
만약, 배열의 index가 1부터 시작한다면 컴퓨터는 배열을 사용하기 전에 1씩 더해줘야 할 것 ⇒ which would be less efficient !!
Two-Dimensional Arrays (이차원배열)
A 2D array is also known as a matrix (a table of rows and columns).
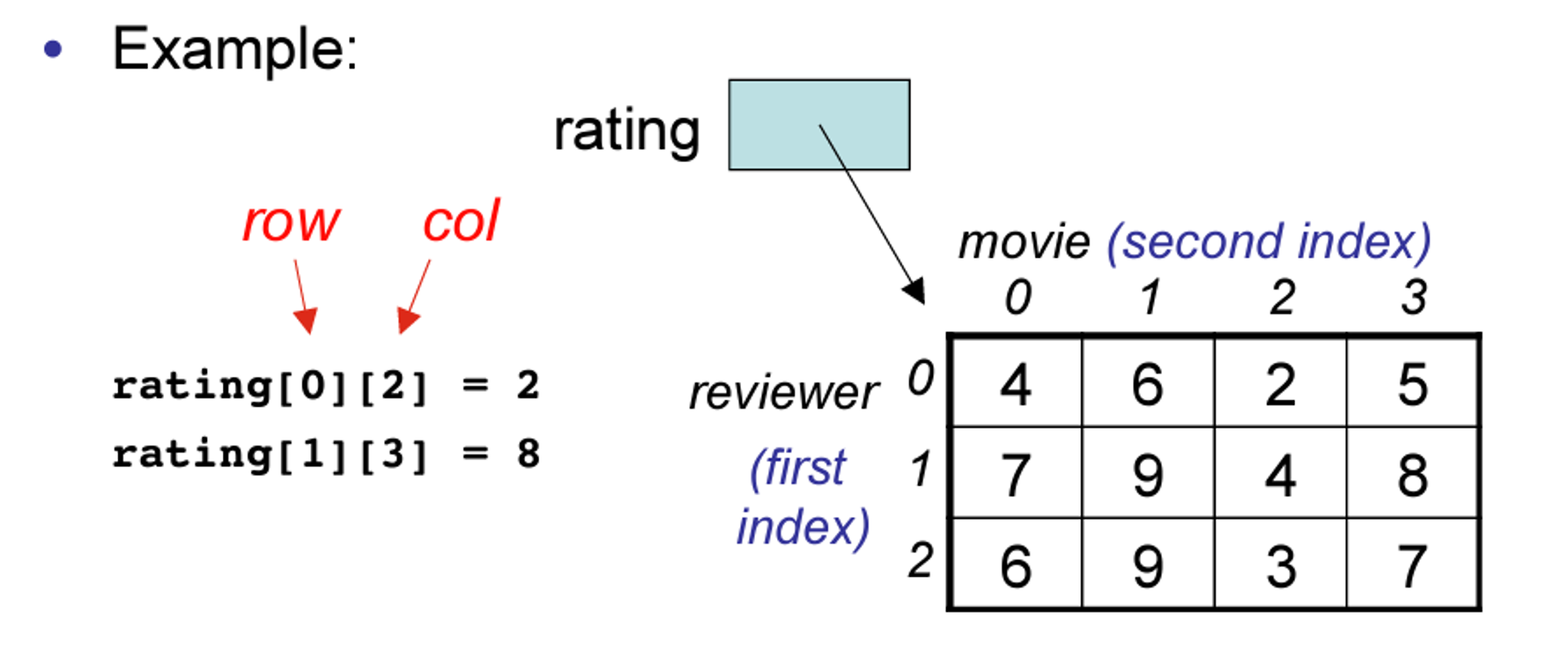
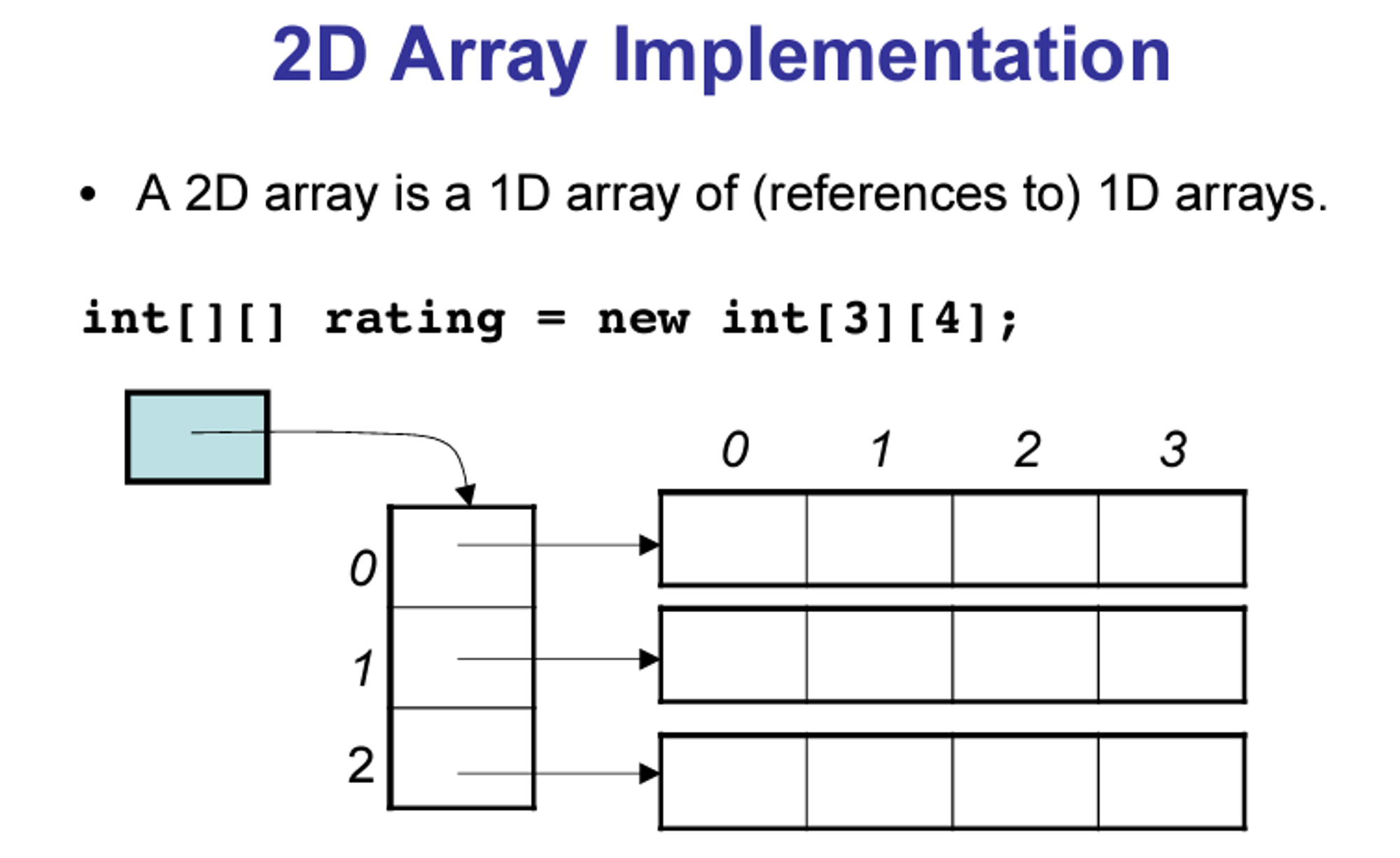
Size of 2D Arrays (이차원 배열의 길이)
#Output
the number of rows : 3
the number of columns : 4Understood through code.
코드로 이해 완료.........
