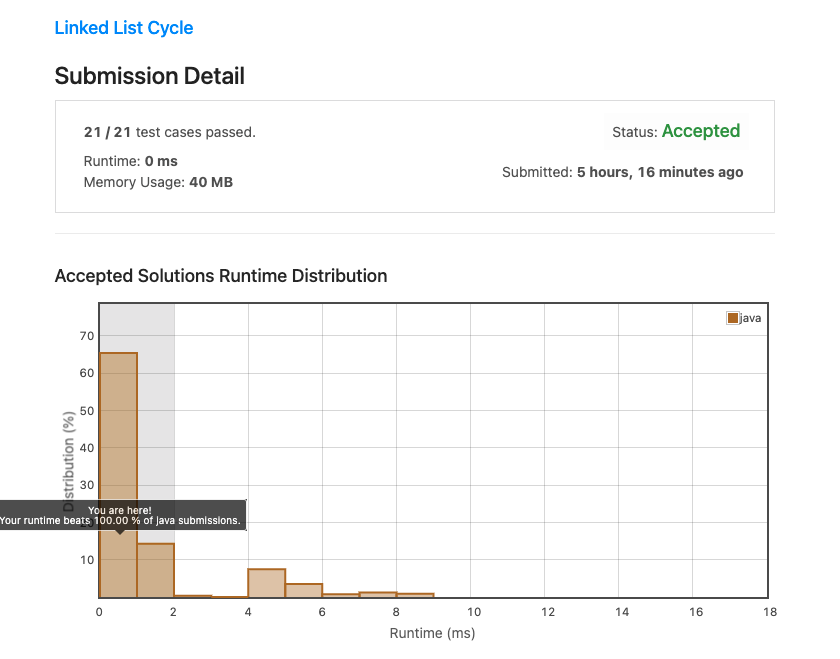
Linked List Cycle
Link : Linked List Cycle
Given head, the head of a linked list, determine if the linked list has a cycle in it.
There is a cycle in a linked list if there is some node in the list that can be reached again by continuously following the next pointer. Internally, pos is used to denote the index of the node that tail's next pointer is connected to. Note that pos is not passed as a parameter.
Return true if there is a cycle in the linked list. Otherwise, return false.
Ex 1:
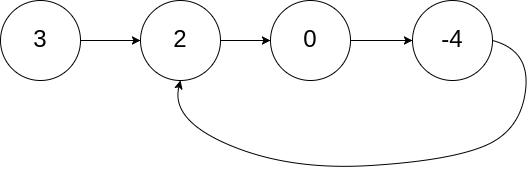
- Input: head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
- Output: true
- Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 1st node (0-indexed).
Ex 2:
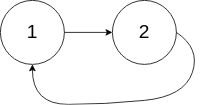
- Input: head = [1,2], pos = 0
- Output: true
- Explanation: There is a cycle in the linked list, where the tail connects to the 0th node.
Ex 3:

- Input: head = [1], pos = -1
- Output: false
- Explanation: There is no cycle in the linked list.
Constraints
- The number of the nodes in the list is in the range [0, 104].
- -10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5
posis -1 or a valid index in the linked-list.
Java code
import java.util.HashSet;
// Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode2 {
int val;
ListNode2 next;
ListNode2(int x) {
val = x;
next = null;
}
}
public class LC6 {
// public boolean hasCycle(ListNode2 head) {
// HashSet<ListNode2> indices = new HashSet<>();
// ListNode2 now = head;
// while (now!=null){
// if (indices.contains(now))){
// return true;
// }
// indices.add(now);
// now = now.next;
// }
// return false;
// }
public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
while (head != null) {
if (head.val > 100000) {
return true;
}
head.val = 100001;
head = head.next;
}
return false;
}
}풀이
- 콜렉션을 쓰면 복잡도가 엄청나게 늘었던 예시를 보여준다.
- 처음에는 주석 풀이대로 풀었으나 문제의 조건을 확인해보니,
-10^5 <= Node.val <= 10^5라는 부분이 있어 값을Node.val이 가질 수 있는 값보다 1만큼 큰 값으로 변경하여 이미 지나온 노드를 표기하였다. - 이렇게 하니 시간 복잡도가 미친 수준으로 줄었다. Java로 알고리즘 문제를 풀때는 최대한 컬렉션 사용을 자제해야 하나보다.