
상속이란?
객체는 연관된 로직들로 이루어진 작은 프로그램이라고 할 수 있다.
상속은 객체의 로직을 그대로 물려 받는 또 다른 객체를 만들 수 있는 기능을 의미한다.
단순히 물려받는 것이라면 의미가 없을 것이다.
기존의 로직을 수정하고 변경해서 파생된 새로운 객체를 만들 수 있게 해준다.
상속의 사용 방법
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
this.introduce = function(){
return 'My name is ' + this.name;
}
}
var p1 = new Person('sehwan');
console.log(p1.introduce());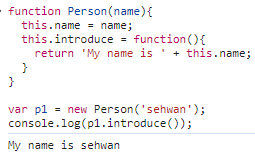
위의 코드를 아래와 같이 바꿔보자.
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.name=null;
Person.prototype.introduce = function(){
return 'My name is ' + this.name;
}
function Programmer(name){
this.name = name;
}
Programmer.prototype = new Person();
var p1 = new Programmer('sehwan'); // 객체 생성
console.log(p1.introduce());p1에 Programmer을 담고 호출하였다.
Programmer의 introduce는 정의하지 않았다.
Person이라는 객체에 prototype으로 introduce라는 메소드를 정의하였다.
그런데 Programmer 객체에서 introduce를 사용할 수 있었던 이유는 Programmer가 introduce를 상속하기 때문이다.
어떻게 가능했을까?
Programmer.prototype = new Person();생성자 Programmer의 prototype이라는 특수한 property의 값으로
new Person()을 한 것이다.
function Person(name){에 의해 객체가 생성이 되는데, 그 객체를 생성할 때 Javascript는 prototype이라고 하는 property를 생성자 함수 안에 들어있는 객체와 똑같은 객체를 만들어서 생성자의 결과로 return한다.
name이라는 property와 introduce라고 하는 메소드를 가지고 있는 객체가 prototype 안에 들어가있기 때문에 new Person();을 통해 만든 객체는 name과 introduce를 가지고 있는 객체가 된다.
그 객체가 prototype이라고 하는 property의 값이 된다.
그 상태에서 new Programmer로
function Programmer를 객체화 시키고 있다.
정리하자면, p1은 prototype이라고 하는 생성자의 property에 들어있는 객체와 같은데, 그 객체는 new Person(). 즉,
function Person(name){생성자로 만든 객체이기 때문에 introduce라는 메소드도 가지고 있다.
기능 추가
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.name = null;
Person.prototype.introduce = function(){
return 'My name is ' + this.name;
}
function Programmer(name){
this.name = name;
}
Programmer.prototype = new Person(); // 추가된 부분
Programmer.prototype.coding = function(){
return "hello world";
}
var p1 = new Programmer('sehwan');
console.log(p1.introduce());
console.log(p1.coding());기능을 추가해보자.
new Programmer를 통해 p1이라는 객체를 만들었다.
그 객체를 introduce 하게되면 이 객체의 메소드가 실행된다.
이 메소드는 Programmer라는 생성자를 통해 정의하지 않았다.
Person을 통해 정의되어있는 introduce가 실행이 된다.
Programmer에는 coding이라는 기능을 가지고 있어야하고, Person에는 coding이라는 기능을 가지고 있지 않아야 한다.
Programmer를 기준으로, introduce는 부모인 Person에서 가져오고, coding은 Programmer에만 있어야 하니 Programmer에 정의한 것이다.
function Person(name){
this.name = name;
}
Person.prototype.name = null;
Person.prototype.introduce = function(){
return 'My name is ' + this.name;
}
function Programmer(name){ // Programmer
this.name = name;
}
Programmer.prototype = new Person();
Programmer.prototype.coding = function(){
return "hello world";
}
function Designer(name){ // Designer
this.name = name;
}
Designer.prototype = new Person();
Designer.prototype.design = function(){
return "beautiful!";
}
var p1 = new Programmer('sehwan');
console.log(p1.introduce());
console.log(p1.coding());
var p2 = new Designer('designer');
console.log(p2.introduce());
console.log(p2.design());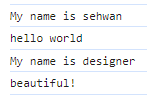
결과값
Programmer과 Designer는 Person으로부터 상속받았다.
Person의 기능인 introduce를 Programmer과 Designer 둘 다 가지고 있다.
Programmer는 coding, Designer는 design이라고 하는 메소드를 부여하였다.
Person.prototype.introduce = function(){
return 'My nickname is ' + this.name;
}부모인 Person의 introduce 기능을 변경해보자.
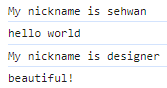
부모가 수정되면 상속된 Programmer와 Designer의 기능 모두 수정되었다.
