스프링 SPRING
자바 기반의 웹 어플리케이션을 만들 수 있는 프레임워크
스프링 프레임워크는 현대 자바 기반의 엔터프라이즈 어플리케이션을 위한 프로그래밍 및 Configuration Model을 제공한다.
- 자바 객체와 라이브러리들을 관리해주며 톰캣과 같은 WAS가 내장되어 있어 자바 웹 어플리케이션을 구동할 수 있다.
- 객체 생성 및 소멸과 같은 Life Cycle을 관리하며 Spring 컨테이너에서 필요한 객체를 가져와서 사용한다.
스프링 BEAN
Spring IOC 컨테이너가 관리하는 자바 객체를 Bean 이라고 한다.
스프링에서는 직접 new를 이용하여 생성한 객체가 아닌 Spring에 의해 관리당하는 자바 객체 Bean을 사용
Annotation
자바 소스 코드에 추가하여 사용할 수 있는 메타데이터의 일종
클래스와 메소드에 추가하여 다양한 기능을 부여하는 역할
annotation을 사용하면 코드량이 감소하고 유지보수하기 쉬우며, 생산성이 증가한다.
- Spring에서 자주 사용하는 Annotation
| Annotation | 역할 |
|---|---|
| @Component | 개발자가 생성한 Class를 Bean으로 등록할때 사용 |
| @Bean | 개발자가 제어가 불가능한 외부 라이브러리와 같은 것들을 Bean으로 만들 때 사용 |
| @Controller | 해당 Class가 컨트롤러의 역할을 한다고 명시할 때 사용 |
| @RequestHeader | request의 header값을 가져와 해당 애너테이션을 쓴 메소드의 파라미터에 사용 |
| @RequestMapping | @RequestMapping(value="")와 같은 형식으로 작성하며 요청 들어온 URI의 요청과 value값이 일치하면 해당 클래스나 메소드가 실행. Contrller 객체 안의 메소드와 클래스에 적용 가능 Class 단위에 사용하면 하위 메소드에 모두 적용 메소드에 적용되면 해당 메소드에서 지정한 방식으로 URI를 처리 |
| @RequestParam | URL에 전달되는 파라미터를 메소드의 인자와 매칭시켜, 파라미터를 받아서 처리할 수 있음 JSON 형식의 Body를 MessageConverter를 통해 JAVA객체로 변환 |
| @RequestBody | Body에 전달되는 데이터를 메소드의 인자와 매칭시켜 데이터를 받아서 처리할 수 있음 클라이언트가 보내는 HTTP요청 본문 (JSON, XML)을 JAVA Object로 변환 |
| @ModelAttribute | 클라이언트가 전송하는 HTTP parameter, Body 내용을 Setter 함수를 통해 1:!로 객체에 데이터를 연결 RequestBody와 다르게 HTTPBody 내용은 multipart/form-data 형태를 요구 @RequestBody가 json을 받는 것과 달리 @ModelAttribute는 json처리 불가 |
| @ResponseBody | 메소드에서 리턴되는 값이 View로 출력되지 않고 HTTPResponseBody에 직접 쓰여짐. return 시에 json, xml과 같은 데이터를 return함 |
| @Autowired | 스프링프레임워크가 Bean객체를 주입받기 위해 사용 Class를 보고 Type에 맞게 Bean주입 (Type 확인 후 맞는 것이 없으면 Name을 확인) |
| @GetMapping | RequestMapping(Method=RequestMathod.GET) 의 역할 |
| @PostMapping | RequestMapping(Method=RequestMathod.POST) 의 역할 |
| @SpringBootTest | Spring Boot Test에 필요한 의존성을 제공 |
| @Test | JUnit에서 테스트 할 대상을 표시 |
Singer,Song 패키지
Singer class
// field private String name; private Song song; // constructor public Singer() { } public Singer(String name, Song song) { super(); this.name = name; this.song = song; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Song getSong() { return song; } public void setSong(Song song) { this.song = song; }
song class
// field private String title; private String genre; // constructor public Song() { } public Song(String title, String genre) { super(); this.title = title; this.genre = genre; } public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public String getGenre() { return genre; } public void setGenre(String genre) { this.genre = genre; }
SpringBeanConfig
-
@Configuration
Bean을 만드는 JAVA 파일
Spring Bean Configuration File와 같은 역할 -
@Bean
Bean을 만드는 메소드
메소드이름이 Bean의 이름(id)이고 반환타입이 Bean의 타입(Class)이다.
@Configuration public class SpringBeanConfig{ 〈bean id="song1" class="song"〉 〈property name="title" value="제목1" /〉 〈property name="genre" value="장르1" /〉 〈/bean〉 @Bean public Song song1() { Song song = new Song(); song.setTitle("제목1"); song.setGenre("장르1"); return song; } }
@Bean에 name값을 지정하면 id로 사용된다. (메소드 이름은 아무거나 적어도 됨)
〈bean id="song2" class="song"〉 〈property name="title" value="제목2" /〉 〈property name="genre" value="장르2" /〉 〈/bean〉 @Bean(name="song2") public Song qwerqwer() { Song song = new Song(); song.setTitle("제목2"); song.setGenre("장르2"); return song; }
〈bean id="song3" class="song"> 〈constructor-arg name="title" value="제목3" /> 〈constructor-arg name="genre" value="장르3" /> 〈/bean> @Bean public Song song3() { return new Song("제목3", "장르3"); }
SpringMain
AbstactApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringBeanConfig.class); Singer s1 = ctx.getBean("singer1",Singer.class); System.out.println(s1.getName()); System.out.println(s1.getSong().getTitle()); System.out.println(s1.getSong().getGenre()); Singer s2 = ctx.getBean("singer2", Singer.class); System.out.println(s2.getName()); System.out.println(s2.getSong().getTitle()); System.out.println(s2.getSong().getGenre()); Singer s3 = ctx.getBean("singer3", Singer.class); System.out.println(s3.getName()); System.out.println(s3.getSong().getTitle()); System.out.println(s3.getSong().getGenre()); ctx.close();
Student 패키지
student class
private List〈Integer> scores; private Set〈String> award; private Map〈String, String> contact; public List〈Integer> getScores() { return scores; } public void setScores(List〈Integer> scores) { this.scores = scores; } public Set〈String> getAward() { return award; } public void setAward(Set〈String> award) { this.award = award; } public Map〈String, String> getContact() { return contact; } public void setContact(Map〈String, String> contact) { this.contact = contact; }
SpringBeanConfig
@Configuration public class SpringBeanConfig{ // List List〈Integer> scores = new ArrayList〈Integer>(); for(int cnt = 0; cnt<5; cnt++){ scores.add((int)(Math.random() * 101 + 0)); // 0부터 101개의 난수가 발생 (0~100) } // Set Set〈String> awards = new HashSet〈String>(); awards.add("개근상"); awards.add("장려상"); awards.add("우수상"); //Map〈String, String> contact = new HashMap〈String, String>(); contact.put("address","서울"); contact.put("tel", "02-1111-1111"); // Bean 생성 및 반환 Student student = new Student(); student.setScores(scores); student.setAward(awards); student.setContact(contact); return student; }
SpringMain
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringBeanConfig.class); Student student = ctx.getBean("stud", Student.class); System.out.println(student.getScores()); System.out.println(student.getAward()); System.out.println(student.getContact());
Book, Publisher 패키지
Book class
// field private String title; private String author; private Publisher publisher; // getter setter public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } public String getAuthor() { return author; } public void setAuthor(String author) { this.author = author; } public Publisher getPublisher() { return publisher; } public void setPublisher(Publisher publisher) { this.publisher = publisher; }
Publisher class
// field private String name; private String tel; // getter setter public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getTel() { return tel; } public void setTel(String tel) { this.tel = tel; }
SpringBeanConfig
@Configuration public class SpringBeanConfig{ @Bean public Publisher publisher1() { Publisher publisher = new Publisher(); publisher.setName("한국출판사"); publisher.setTel("02-1111-1111"); return publisher; } @Bean public Book book1(){ Book book = new Book(); book.setTitle("소나기"); book.setAuthor("황순원"); book. setPublisher(publisher1()); return book; } }
SpringMain
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("java03/appCtx.xml"); Book book1 = ctx.getBean("book1", Book.class); System.out.println(book1.getTitle()); System.out.println(book1.getAuthor()); System.out.println(book1.getPublisher().getName()); System.out.println(book1.getPublisher().getTel()Book book2 = ctx.getBean("book2", Book.class); System.out.println(book2.getTitle()); System.out.println(book2.getAuthor()); System.out.println(book2.getPublisher().getName()); System.out.println(book2.getPublisher().getTel()); ctx.close();
appCtx.xml
〈bean id="publisher2" class="con.gdu.app01.java03.Publisher"> 〈property name="name" value="국제출판사" /> 〈property name="tel" value="02-2222-2222" /> 〈/bean> 〈bean id="book2" class="con.gdu.app01.java03.Book"> 〈property name="title" value="어린왕자" /> 〈property name="author" value="생텍쥐베리" /> 〈property name="publisher" value="publisher2" /> 〈/bean>
- SpringBeanConfig.java에 등록된 Bean을 appCtx.xml로 가져오기
- Namespaces 탭에서 context 옵션을 체크한다.
- appCtx.xml에 〈context:annotation=config /> 태그를 추가한다.
- SpringBeanConfig.java를 〈bean> 태그로 등록한다.
〈context:anntation-config /> 〈bean class="com.gdu.app01.java03.SpringBeanConfig" />
Gun,Soldier 패키지
Gun class
// field private String model; private int bullet; // constructor public Gun(String model, int bullet) { super(); this.model = model; this.bullet = bullet; } // info() public void info() { System.out.println("모델명 : " + model); System.out.println("총알수 : " + bullet); }
soldier class
// field private String name; private Gun gun; // constructor public Soldier(String name, Gun gun) { super(); this.name = name; this.gun = gun; } // info() public void info() { System.out.println("이름 : " + name); gun.info(); }
SpringBeanConfig
`@ImportResource(value="java04/appCtx.xml")``
- java04/appCtx.xml에 등록된 Bean을 가져오라는 뜻
@ImportResource(value="java04/appCtx.xml") @Configuration public class SpringBeanConfig { }
SpringMain
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringBeanConfig.class); Soldier soldier = ctx.getBean("soldier", Soldier.class); soldier.info(); ctx.close();
appCtx.xml
〈bean id="gun" class="com.gdu.app01.java04.Gun"> 〈constructor-arg value="AWM" /> 〈constructor-arg value="25"></constructor-arg> 〈bean> 〈bean id="soldier" class="com.gdu.app01.java04.Soldier"> 〈constructor-arg value="허하사" /> 〈constructor-arg ref="gun" /> 〈bean>
Student,Calculator 패키지
Student class
// field private String name; private String school; private Calculator calculator; // method(getter, setter) public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getSchool() { return school; } public void setSchool(String school) { this.school = school; } public Calculator getCalculator() { return calculator; } public void setCalculator(Calculator calculator) { this.calculator = calculator; }
Calculator class
// method public void add(int a, int b) { System.out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + (a + b)); } public void sub(int a, int b) { System.out.println(a + "-" + b + "=" + (a - b)); } public void mul(int a, int b) { System.out.println(a + "*" + b + "=" + (a * b)); } public void div(int a, int b) { System.out.println(a + "/" + b + "=" + (a / b)); }
SpringMain
- 기존 방식
Calculator calculator = new Calculator();- 개발자가 Bean을 만들었다
- 새로운 프레임워크
- 프레임워크가 만든 Bean을 가져다 쓴다.
- XML에 저장된 Bean을 가져오는 클래스
GenericXmlApplicationContext
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("xml01/appCtx.xml"); // 만든 xml의 경로를 전달 제네릭엑스엠엘대신 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 써도 돌아감 Calculator calculator = ctx.getBean("calc", Calculator.class); calculator.add(5, 2); calculator.sub(5, 2); calculator.mul(5, 2); calculator.div(5, 2); Student student = ctx.getBean("haksang", Student.class); // 캐스팅 하기 싫어서 이 방식 사용, Student student = (Student)ctx.getBea("haksang") 와 같다 System.out.println(student.getName()); System.out.println(student.getSchool()); student.getCalculator().add(7, 3); student.getCalculator().sub(7, 3); student.getCalculator().mul(7, 3); student.getCalculator().div(7, 3); ctx.close(); // 생략가능
appCtx.xml
- SpringBeanConfigurationFile
Bean을 만드는 xml, 여기서 만든 Bean은 Container에 보관된다
디폴드생성자 + setter (property 태그)
〈bean id="calc" class="com.gdu.app01.xml01.Calculator" >〈/bean> <!-- 클래스 이름 + ctrl + space , id는 bean의 이름--> 〈bean id="haksang" class="com.gdu.app01.xml01.Student"> 〈property name="name"> <!-- 필드와 1:1 매칭하는 놈 --> 〈value>홍길동〈/value> <!-- value 쓰는 애들 : 기본타입 byte, short, float, chat, string ... --> 〈/property> 〈property name="school"> 〈value>가산대학교〈/value> 〈/property> 〈property name="calculator"> 〈ref bean="calc"/> <!-- value 말고 다른 애들 전부 ref씀 : 참조타입 --> 〈/property> 〈/bean>

Car,Engine 패키지
Car
// feild private String model; private String maker; private Engine engine; public String getModel() { return model; } public void setModel(String model) { this.model = model; } public String getMaker() { return maker; } public void setMaker(String maker) { this.maker = maker; } public Engine getEngine() { return engine; } public void setEngine(Engine engine) { this.engine = engine; }
Engine
// feild private String fuel; // 연료 (디젤, 가솔린) private double efficency; // 연비 (12.5) private int cc; // 배기량 (1998) // method(getter/setter) public String getFuel() { return fuel; } public void setFuel(String fuel) { this.fuel = fuel; } public double getEfficency() { return efficency; } public void setEfficency(double efficency) { this.efficency = efficency; } public int getCc() { return cc; } public void setCc(int cc) { this.cc = cc; }
appCtx.xml
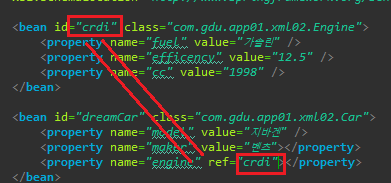
〈bean id="crdi" class="com.gdu.app01.xml02.Engine"> 〈property name="fuel" value="가솔린" /> 〈property name="efficency" value="12.5" /> 〈property name="cc" value="1998" /> 〈/bean> 〈bean id="dreamCar" class="com.gdu.app01.xml02.Car"> 〈property name="model" value="지바겐" /> 〈property name="maker" value="벤츠">〈/property> 〈property name="engine" ref="crdi">〈/property> <!-- 참조타입은 태그, 레퍼런스이다 --> 〈/bean>
Address,Person 패키지
Address
private String jibun; private String road; private String zipCode; public String getJibun() { return jibun; } public void setJibun(String jibun) { this.jibun = jibun; } public String getRoad() { return road; } public void setRoad(String road) { this.road = road; } public String getZipCode() { return zipCode; } public void setZipCode(String zipCode) { this.zipCode = zipCode; }
Person
private String name; private int age; private Address address; public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public Address getAddress() { return address; } public void setAddress(Address addrss) { this.address = addrss; }
SpringMain
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("xml03/appCtx.xml"); Person person = ctx.getBean("person", Person.class); System.out.println(person.getName()); System.out.println(person.getAge()); Address address = person.getAddress(); System.out.println(address.getJibun()); System.out.println(address.getRoad()); System.out.println(address.getZipCode()); ctx.close();
appCtx.xml
Namespaces 탭에서 "p"옵션을 체크하면 〈property> 태그를 〈bean> 태그의 p: 속성으로 바꿔서 사용할 수 있다
〈bean id="address" class="com.gdu.app01.xml03.Address" p:jibun="가산동" p:road="디지털로" p:zipCode="12345"/> 〈bean id="person" class="com.gdu.app01.xml03.Person" p:name="홍길동" p:age="25" p:address-ref="address" />
Dao 패키지
Dao
public void list() { System.out.println("목록 가져오기"); } public void detail() { System.out.println("상세보기"); }
SpringMain
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("xml04/appCtx.xml"); Dao dao1 = ctx.getBean("dao", Dao.class); Dao dao2 = ctx.getBean("dao", Dao.class); Dao dao3 = ctx.getBean("dao", Dao.class); System.out.println(dao1 == dao2); System.out.println(dao2 == dao3); System.out.println(dao1 == dao3); ctx.close();
appCtx.xml
- 〈bean> 태그의 scope 속성
scope="singleton"- bean을 하나만 만들어 둔다
- 생략하면 singletone이 사용된다.
scope="prototype" - bean을 요청할때마다 만들어준다.
- 자주 사용되지는 않는다.
〈bean id="dao" class="com.gdu.app01.xml04.Dao" scope="prototype"/>
MyConnection 패키지
MyConnection
private String driverClassName; private String url; private String user; private String password; public String getDriverClassName() { return driverClassName; } public void setDriverClassName(String driverClassName) { this.driverClassName = driverClassName; } public String getUrl() { return url; } public void setUrl(String url) { this.url = url; } public String getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(String user) { this.user = user; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } // connection 반환메소드 public Connection getConnection() { Connection con = null; try { con = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password); System.out.println("Connection 생성 완료"); } catch(Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return con; }
SpringMain
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("xml05/appCtx.xml"); MyConnection myCon = ctx.getBean("conn", MyConnection.class); Connection con = myCon.getConnection(); if(con != null) { con.close(); System.out.println("Connection 해제 완료"); } ctx.close();
appCtx
〈bean id="conn" class="com.gdu.app01.xml05.MyConnection"> 〈property name="driverClassName" value="orcle.jdbc.OracleDriver" /> 〈property name="url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:xe"/> 〈property name="user" value="SCOTT"/> 〈property name="password" value="TIGER" /> 〈/bean>
Person 패키지
Person
// field private List〈String> hobbies; private Set〈String> contacts; private Map〈String, String> friends; // method getter/setter public List〈String> getHobbies() { return hobbies; } public void setHobbies(List〈String> hobbies) { this.hobbies = hobbies; } public Set〈String> getContacts() { return contacts; } public void setContacts(Set〈String> contacts) { this.contacts = contacts; } public Map〈String, String> getFriends() { return friends; } public void setFriends(Map〈String, String> friends) { this.friends = friends; } // info() 메소드 public void info() { // List for (int i = 0; i 〈hobbies.size(); i++) { System.out.println(( i + 1) + "번째 취미 : " + hobbies.get(i)); } // Set (인덱스 없음) for(String contact : contacts) { System.out.println(contact); } // Map (Key + Value ==> Entry) for(Map.Entry〈String, String> entry : friends.entrySet()) { System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ":" + entry.getValue()); } }
SpringMain
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("xml06/appCtx.xml"); Person p = ctx.getBean("human", Person.class); p.info(); ctx.close();
appCtx
〈bean id="human" class="com.gdu.app01.xml06.Person"> <!-- List --> 〈property name="hobbies"> 〈list> 〈value>여행〈/value> 〈value>운동〈/value> 〈/list> 〈/property> <!-- Set --> 〈property name="contacts"> 〈set> 〈value>010-1111-1111〈/value> 〈value>010-1111-1111〈/value> 〈value>010-1111-1111〈/value> 〈value>010-1234-5678〈/value> 〈/set> 〈/property> <!-- Map --> 〈property name="friends"> 〈map> 〈entry key="동네친구" value="영심이" /> 〈entry key="학교친구" value="최자두" /> 〈entry key="회사친구" value="나루토" /> 〈entry key="사회친구" value="둘리" /> 〈/map> 〈/property> 〈/bean>
User, Contact 패키지
Contact
// field private String address; private String email; private String tel; // constructor public Contact(String address, String email, String tel) { super(); this.address = address; this.email = email; this.tel = tel; } // method public void info() { System.out.println("주소 : " + address); System.out.println("이메일 : " + email); System.out.println("연락처 : " + tel); }
User
// field private String id; private Contact contact; // constructor public User(String id, Contact contact) { super(); this.id = id; this.contact = contact; } // method public void info() { System.out.println("아이디 : " + id); contact.info(); }
SpringMain
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("xml07/appCtx.xml"); User user= ctx.getBean("user", User.class); user.info(); ctx.close();
appCtx
- 생성자 주입 (Constructor Injection) : 〈constructor-arg> 태그
- 주입은 순서대로 진행해야한다!
〈bean id="contact" class="com.gdu.app01.xml07.Contact"> 〈constructor-arg value="가산동" /> 〈constructor-arg value="user@naver.com" /> 〈constructor-arg value="010-1111-1111" /> 〈/bean> 〈bean id="user" class="com.gdu.app01.xml07.User"> 〈constructor-arg value="user"/> 〈constructor-arg ref="contact"/> 〈/bean>
BMICalculator 패키지
BMICalculator
//field private Calculator calc; private double height; private double weight; private double bmi; private String health; //constructor public BMICalculator(Calculator clac, double height, double weight) { super(); this.calc = clac; this.height = height; this.weight = weight; this.bmi = calc.div(weight, calc.div(calc.mul(height, height), 10000)); health = (bmi < 20) ? "저체중" : (bmi < 25) ? "정상" : (bmi < 30) ? "과체중" : "비만"; } // info()메소드 public void info() { System.out.println("BMI : " + bmi); System.out.println("Health : " + health); }
Calculator
// method public double add(double a, double b) { return a + b; } public double sub(double a, double b) { return a - b; } public double mul(double a, double b) { return a * b; } public double div(double a, double b) { return a / b; }
Member
private String name; private List〈String> course; private double height; private double weight; private BMICalculator bmiCalc; public Member(String name, List〈String> course, double height, double weight, BMICalculator bmiCalc) { super(); this.name = name; this.course = course; this.height = height; this.weight = weight; this.bmiCalc = bmiCalc; } // info()메소드 public void info() { System.out.println("Name : " + name); for(String str : course) { System.out.println("Course: " + str); } System.out.println("Height : " + height); System.out.println("Weight : " + weight); bmiCalc.info(); }
SpringMain
AbstractApplicationContext ctx = new GenericXmlApplicationContext("xml08/appCtx.xml"); Member member = ctx.getBean("member", Member.class); member.info(); ctx.close();
appCtx
〈bean id="calc" class="com.gdu.app01.xml08.Calculator" /> 〈bean id="bmiCalc" class="com.gdu.app01.xml08.BMICalculator"> 〈constructor-arg ref="calc" /> 〈constructor-arg value="180.5" /> 〈constructor-arg value="80.5" /> 〈/bean> 〈bean id="member" class="com.gdu.app01.xml08.Member"> 〈constructor-arg value="홍길동" /> 〈constructor-arg> 〈list> 〈value>헬스〈/value> 〈value>수영〈/value> 〈/list> 〈/constructor-arg> 〈constructor-arg value="180.5" /> 〈constructor-arg value="80.5" /> 〈constructor-arg ref="bmiCalc" /> 〈/bean>
- 세터 주입 setter injection
프로퍼티 태그

잘 보고갑니다 ^^*