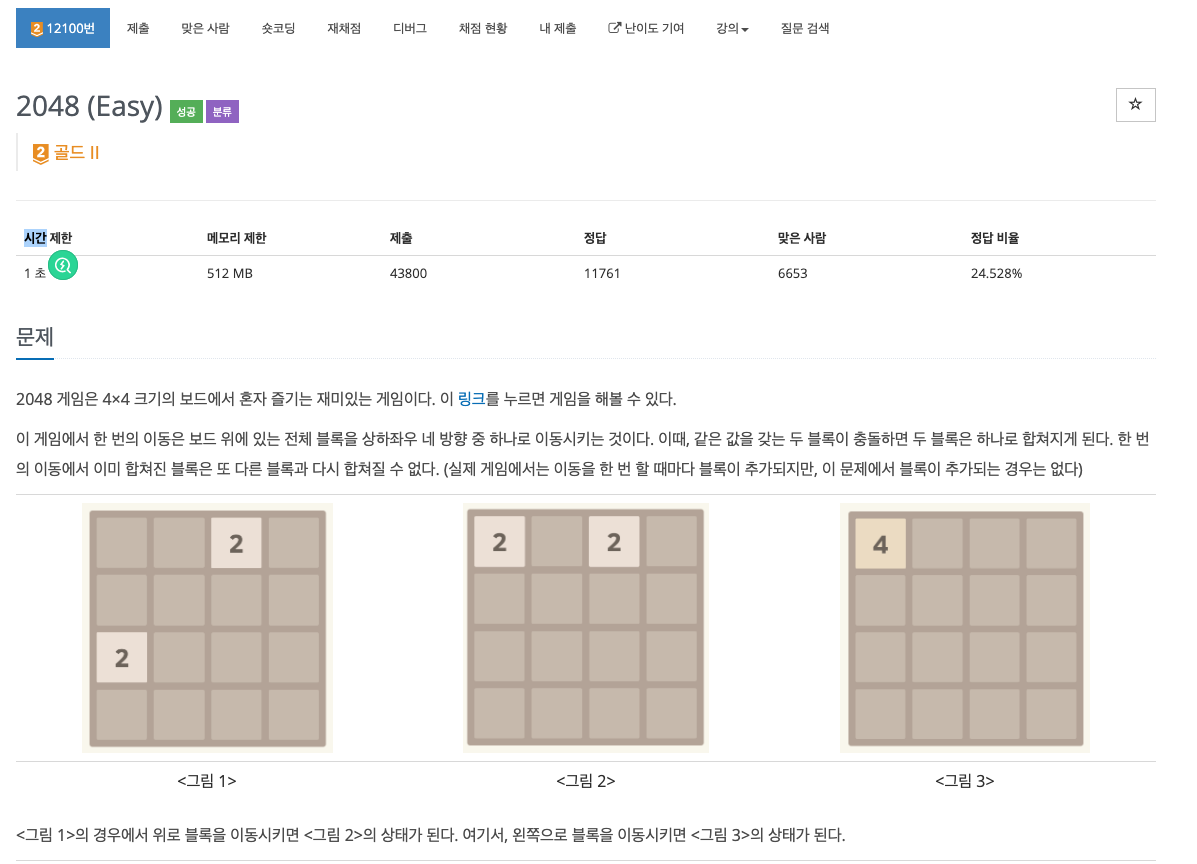
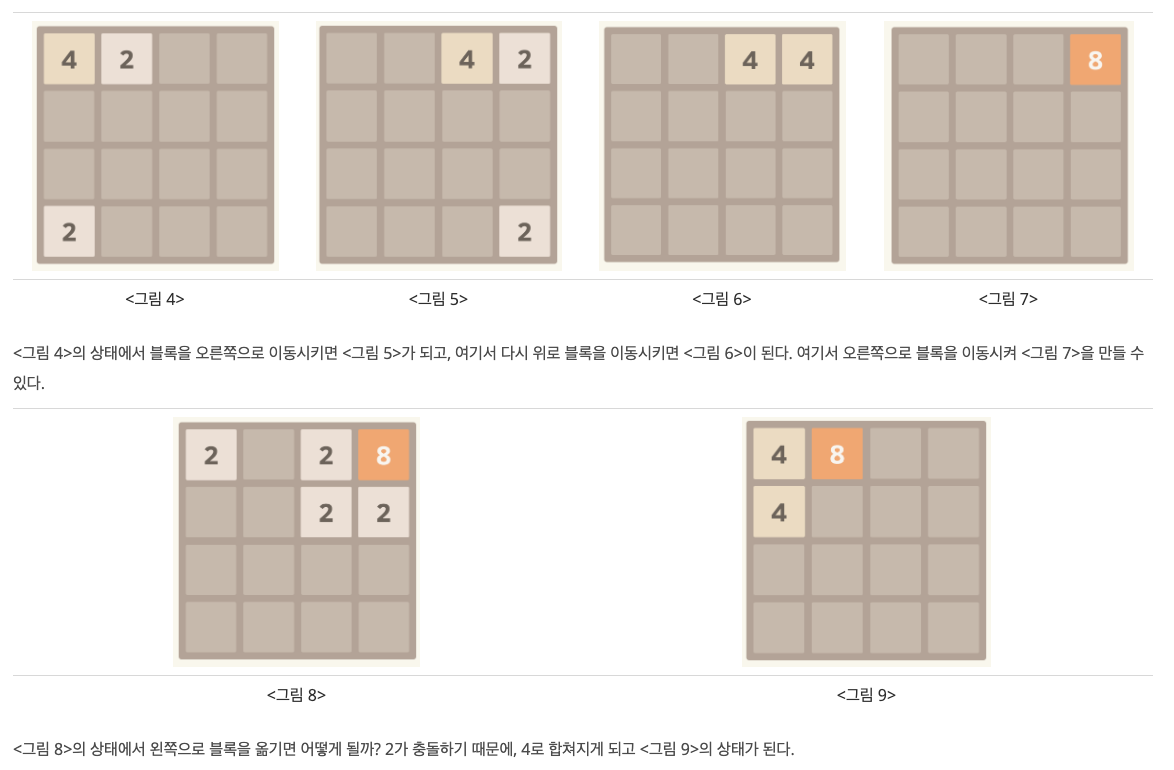
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int dx[4] = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int dy[4] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int N;
int origin[25][25];
int ans;
void DFS(int board[25][25], int depth, int dir)
{
if(depth > 5)
{
int M=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
M = max(M, board[i][j]);
ans = max(M, ans);
return;
}
bool vis[N][N];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
fill(vis[i], vis[i]+N, false);
int stY=0;
int stX=0;
int cal=1;
if(dir == 1 or dir == 3)
{
stY = N-1;
stX = N-1;
cal = -1;
}
for(int i=stY;(i>=0 and i<=N-1);i+=cal)
{
for(int j=stX;(j>=0 and j<=N-1);j+=cal)
{
if(board[i][j] == 0) continue;
int ny = i + dy[dir];
int nx = j + dx[dir];
bool rangeOut = false;
if(nx<0 or ny<0 or nx>=N or ny>=N) continue;
int preY = i;
int preX = j;
while(true)
{
if(nx<0 or ny<0 or nx>=N or ny>=N){
rangeOut = true;
break;
}
if(board[ny][nx] != 0) break;
board[ny][nx] = board[preY][preX];
board[preY][preX] = 0;
preY = ny;
preX = nx;
ny += dy[dir];
nx += dx[dir];
}
if(rangeOut){
ny -= dy[dir];
nx -= dx[dir];
}
if((ny != preY or nx != preX) and board[ny][nx] == board[preY][preX] and !vis[ny][nx]){
vis[ny][nx] = true;
board[ny][nx] += board[preY][preX];
board[preY][preX] = 0;
}
}
}
for(int d=0;d<4;d++)
{
int cpy[25][25];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
cpy[i][j] = board[i][j];
DFS(cpy, depth+1, d);
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
cin >> N;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
cin >> origin[i][j];
for(int dir=0;dir<4;dir++){
int cpy[25][25];
for(int i=0;i<N;i++)
for(int j=0;j<N;j++)
cpy[i][j] = origin[i][j];
DFS(cpy, 1, dir);
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
- 로직
원본 배열인 origin에 값을 저장하고 유지한다DFS()를 통해 배열을 넘길 때에는 반드시 복사본을 생성한 후 넘겨줘야 한다 DFS 로직
진행방향이 상 or 좌 인 경우 로직을 앞(idx = 0) 순서부터 실행진행방향이 하 or 우 인 경우 로직을 뒤(idx = N-1) 순서부터 실행진행하려는 보드인 board[ny][nx]값이 0이 아닐 때 까지 값을 땡겨줘야 한다범위를 벗어난 경우를 rangeOut 변수로 체크해 한번 Undo 해줘야 한다좌표가 다른 서로의 board값이 같고 합쳐지지 않았다면 값을 합쳐준다
- 핵심
진행방향에 따라서 로직을 앞, 뒤 순서로 실행시켜 주는 것!배열을 매개변수로 넘길 때 항상 복사본을 생성한 뒤 넘겨주는 것!