해당 내용은 아주대학교 '김상훈' 교수님의
'운영체제' 수업을 바탕으로 작성되었습니다.
[목차]
- von Neumann architecture
- CPU
- Computer System Organization
- Storage structure
1. von Neumann architecture
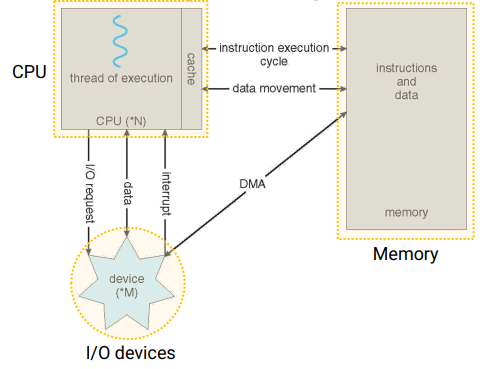
- 현재 대부분의 computer system architecture는 'von Neumann architecture'이다.
- 폰 노이만 구조는 CPU, Memory, program으로 구성된 구조이다.
- 과거 컴퓨터 구조와 크게 달라진 점은 program을 storage에 저장하고 이를 실행시키려면 memory로 가져와 cpu가 처리하는 구조이다.
2. CPU
- Processor 라고도 부름
- 대부분의 processor들은 general - purpose processor임
- GPU(Graphic Processing Unit), TPU(Tensor Processing Unit)과 같은 special - purpose processor( = hardware accelerators)도 존재함
Computer System
3. Computer System Organization
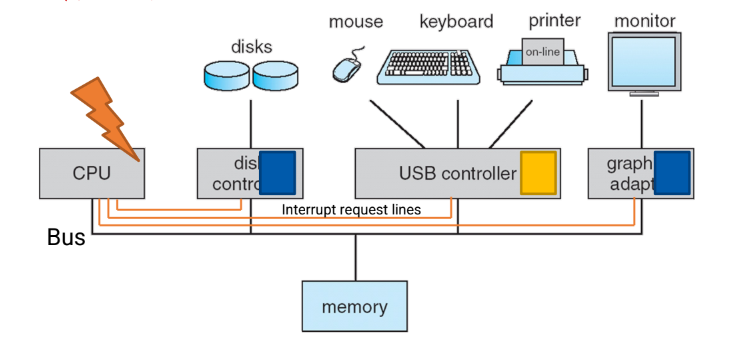
Device Controller
- 각 DC(device controller)들은 common bus에 연결되어 있다
- 각 DC는 local buffer를 가지고 있다
- CPU는 DC의 buffer의 data에 direct로 접근하지 못한다
- bus를 통해 command를 보내고 interrupt를 보낸다
Interrupt
- DC가 CPU에게 event 발생을 알리는 방법
- CPU는 interrupt를 감지하면 해당하는 function을 실행하도록 구현되어 있다.
- 어떤 interrupt에 대해서 어떤 함수를 실행시켜야 하는지는 IDT(interrupt descriptor table) 또는 interrupt vector를 참고해서 실행시킨다.
- IDT에는 해당하는 function, service routines의 주소가 담겨있다.
- 즉, interrupt number/ID를 받으면 IDT를 look up 해 해당하는 interrupt handler의 주소를 알려준다.
I/O structure
- Device driver : OS가 DC와 communication하는 것을 도와주는 것. device와 buffer 사이 data transfer 해줌
4. Storage structure
main memory
- CPU가 direct로 접근할 수 있는 유일한 Storage media
- CPU는 direct로 disk에서 data를 읽을 수 없다
- Random Access : 주소를 읽어오는 시간이 동일하다
- byte addressable : byte 단위로 주소에 접근 가능하다
Secondary storage
- HDDs, SSD와 같은 main memory를 제외한 나머지 storage
- block addressable : block단위로 storage에 접근 가능
self quiz 링크
https://overjoyed-goldfish-618.notion.site/f81e3c203cff4bfcb5841da8e9bfbc02?pvs=4
