배열 정렬
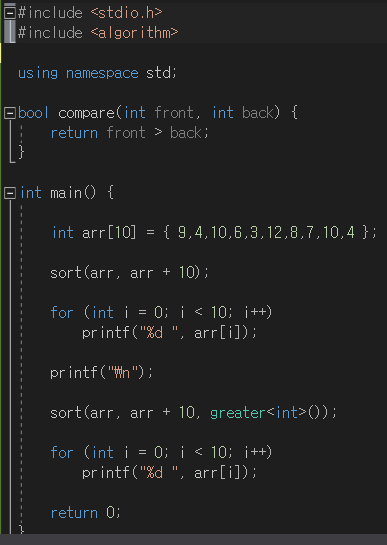
- #include < algorithm >
- sort(배열 변수 이름, 배열 변수 이름 + 배열길이)
- compare 함수를 명시적으로 정의하여 원하는 기준으로 정렬 가능
- int 타입인 경우 위와 같이 int 타입 인자를 2개 받으면 된다
- greater = 내림차순 정렬
- true로 조건 성립하면 우선순위가 높다고 생각하면 된다!!
1차원 vector 정렬
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool compare(int first, int second) {
return first > second;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
vector<int> v;
v.push_back(4);
v.push_back(3);
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(1);
v.push_back(9);
v.push_back(2);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), compare);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
return 0;
}

- 배열 정렬과 매우 유사
- 단, sort 사용 시 begin, end 를 사용한다!!
2차원 벡터 정렬
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<vector<int>> v;
v.push_back({2, 4, 10});
v.push_back({3, 4, 6});
v.push_back({2, 4, 6, 8});
v.push_back({3});
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < v[i].size(); j++) {
cout << v[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
return 0;
}
2 4 6 8
2 4 10
3
3 4 6
pair 타입 우선순위 정의하기
- 따로 정의한 compare 함수 없이 기본 sort를 사용하면 pair 타입은 first를 기준으로 정렬된다
bool cmp1(pair<string, int> a, pair<string, int> b){
return a.second > b.second;
}
bool cmp2(const pair<int, int>& a, const pair<int, int>& b){
if(a.first == b.first)
return a.second < b.second;
return a.first > b.first;
}
- const, & 를 사용하도 동일한 결과가 나타난다
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool compare(pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b) {
if (a.first == b.first)
return a.second > b.second;
return a.first > b.first;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
vector<pair<int,int>> v;
v.push_back({ 4, 5 });
v.push_back({ 1, 4 });
v.push_back({ 5, 2 });
v.push_back({ 2, 1 });
v.push_back({ 4, 3 });
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
cout << v[i].first << " " << v[i].second << "\n";
}
cout << "\n";
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), compare);
for (int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
cout << v[i].first << " " << v[i].second << "\n";
}
cout << "\n";
return 0;

우선순위큐

- 위와 같이하면 최소값이 루트로 간다!!, less = 루트에 최대값!!!
- Sort 함수의 compare 방식과 반대 / 헷갈리지 않게 sort 방식을 일단 외우자
- 또한 greater 사용 시 우선순위 큐에서는 ( ) 사용하지 않는다!!!!
- 비교함수 구조체를 활용하는 방법도 있다
- 우선순위큐의 경우에는 비교함수를 구조체로 선언하고 bool operator( ) 함수를 구현해야 한다!


- 이 역시 sort와 반대!
- 위 예제에서는 pair 이 아닌 사용자가 정의한 구조체 타입을 활용

구조체 벡터 정렬
- 구조체 타입 벡터에서 sort로 정렬하는 경우에도 일반 bool compare 함수를 구현해주면 된다
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Data {
int x;
int y;
};
bool compare(Data first, Data second) {
if (first.x > second.x) return true;
else if (first.x < second.x) return false;
else {
if (first.y > second.y) return true;
else return false;
}
}
int main(void) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
vector<Data> dataV;
dataV.push_back({ 1, 2 });
dataV.push_back({ 1, 1 });
dataV.push_back({ 3, 4 });
dataV.push_back({ 3, 6 });
dataV.push_back({ 3, 5 });
sort(dataV.begin(), dataV.end(), compare);
for (int i = 0; i < dataV.size(); i++) {
cout << dataV[i].x << " " << dataV[i].y << "\n";
}
return 0;
}

참고링크
https://luv-n-interest.tistory.com/965








