INTRO
오늘은 자바의 스트림에 대해 학습한 내용입니다.
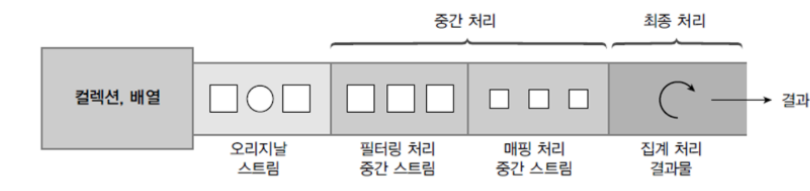
1. 스트림 (Stream)
자바8 추가된 컬렉션(배열 포함)의 저장 요소를 하나씩 참조해서 람다식으로 처리할 수 있도록 해 주는 반복자.
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.stream.Stream;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> lists = Arrays.asList("aaa", "bbb", "ccc");
// Iterator
Iterator<String> it = lists.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
String item = it.next();
System.out.println(item);
}
// Stream
Stream<String> st = lists.stream();
st.forEach(item -> System.out.println(item));
st = lists.stream();
st.forEach(System.out::println);
}
} 2. 스트림의 장점
병렬처리, 함수의 연속 사용에 유용하다.
// 순차 처리
Stream<Student> stream = students.stream();
stream.forEach(Example::print);
System.out.println();
// 병렬 처리
Stream<Student> parallelStream = students.parallelStream();
parallelStream.forEach(Example::print);
// 함수의 연속 사용
List<Student> students = Arrays.asList(
new Student("홍길동", 90), new Student("고길동", 80),
new Student("일길동", 90), new Student("이길동", 80),
new Student("삼길동", 90), new Student("사길동", 80));
double average = students.stream()
.mapToInt(Student::getScore) // 학생의 점수를 맵핑
.average()
.getAsDouble();
System.out.println(average);
3. 종류
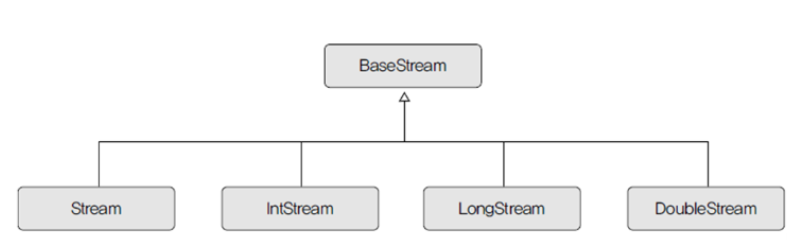
- 메서드
대표적인 예시로 filter(), distinct(), flatMapXXX() 등이 있다.
flatMap은 아래와 같은 상황을 말한다.
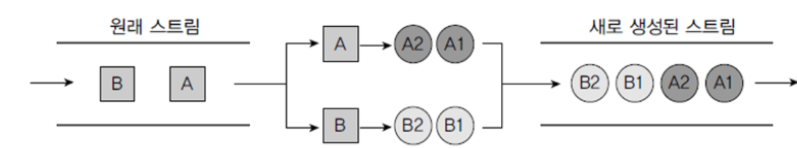
코드로 보는 예시
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
List<String> stations = Arrays.asList("부평시장", "홍대입구", "강남", "신도림", "역삼", "삼성", "신림", "부평구청", "신도림");
stations.stream()
.distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
stations.stream()
.filter(s -> s.startsWith("신"))
.forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println();
stations.stream()
.filter(s -> s.startsWith("신"))
.distinct()
.forEach(System.out::println);
List<String> list1 = Arrays.asList("java8 lambda", "stream mapping api");
list1.stream()
.flatMap(d -> Arrays.stream(d.split(" ")))
.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
