프로세스와 스레드
프로세스
- 일반적으로 CPU에 의해 메모리에 올려져 실행중인 프로그램을 의미
- 자신만의 메모리 공간을 포함한 독립적인 실행 환경을 가지고 있음
- 자바 JVM은 주로 하나의 프로세스로 실행되며, 동시에 여러 작업을 수행하기 위해 멀티 스레드를 지원함
스레드
- 프로세스 안에서 실질적으로 작업을 실행하는 단위
- 자바에서는 JVM에 의해 관리됨
스레드 생성
생성자
1. Thread() // 새로운 스레드 객체 할당
2. Thread(String name) // 스레드 이름이 name인 새로운 스레드 객체 할당
3. Thread(Runnable target) // Runnable target이 구현된 스레드 객체 할당
4. Thread(Runnable target, String name) // Runnable target이 구현되고, 스레드 이름이 name인 새로운 스레드 객체 할당Thread 클래스 상속
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
MyThread myThreadWithName = new MyThread("myThreadname");
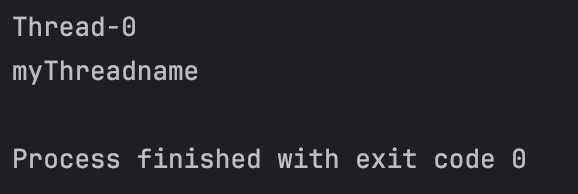
myThread.run();
myThreadWithName.run();
}
}
class MyThread extends Thread {
MyThread(){}
MyThread(String name){
super(name);
}
public void run() {
System.out.println(this.getName());
}
}실행 결과
Runnable 인터페이스 구현
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new MyThread_Runnable();
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
Thread threadWithName = new Thread(runnable, "myThreadName");
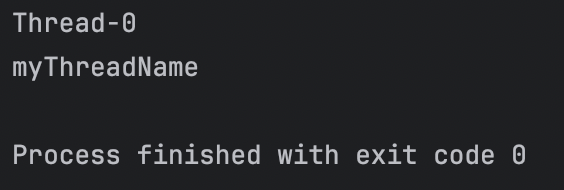
thread.start();
threadWithName.start();
}
}
class MyThread_Runnable implements Runnable{
public void run(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}실행 결과
Runnable 인터페이스

함수형 인터페이스로, 1개의 메소드만을 가지므로 람다로 사용할 수 있다.
스레드를 구현하기 위한 템플릿.
스레드 메소드
메소드
sleep(사용 예제
MyThread.java
public class MyThread implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
int cnt = 0;
while (!Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
Main.threadSleep(Thread.currentThread(), 500);
cnt++;
if (cnt == 20) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().toString() + "-인터럽트됨]");
}
}
}
}run() 메서드를 실행하면 cnt 값을 증가시키다가 cnt == 20일 때, 인터럽트한다.
Main.java
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new MyThread();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runnable, "thread1");
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runnable, "thread2");
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
static void threadSleep(Thread thread, long time) {
try {
Thread.sleep(time);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(thread.toString() + "-인터럽트됨]");
thread.interrupt();
}
}
}main 메서드는 스레드 2개를 생성 후 start()를 호출한다.
threadSleep 메서드는 주어진 time동안 스레드를 일시중지한다.
