부트스트랩을 이용해 화면을 만들겠습니다.
레이아웃 방식으로 화면을 구성하기위해 layout 디렉토리를 templates 하위에 생성하고 footer와 header를 만들겠습니다.
footer.mustache
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.3.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
</body>
</html>header.mustache
<!DOCTYPE HTML>
<html>
<head>
<title>스프링부트 웹서비스</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.3.1/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>페이지 로딩속도를 높이기위해 css는 header에 js는 footer에 두었습니다.
HTML은 위에서부터 코드가 실행되기 때문에 head가 실행되고 body가 그 다음에 실행됩니다.
즉, js의 용량이 크면 클수록 body의 실행 부분이 늦어지기때문에 js는 화면이 다 그려진 후에 호출하는 것이 좋습니다.
또한 부트스트랩을 사용하기위해선 제이쿼리가 필수이므로 부트스트랩보다 제이쿼리를 먼저 호출해야합니다.
footer와 haeder에 필요한 라이브러리와 모든 화면에 중복될 HTML 태그들이 포함되어있으므로 index는 다음과 같이 나타낼수 있습니다.
index.mustache
{{>layout/header}}
<title>스프링부트 웹서비스</title>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
</head>
<body>
<h1>스프링 부트로 시작하는 웹 서비스</h1>
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6">
<a href="/posts/save" role="button" class="btn btn-primary">글 등록</a>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{{>layout/footer}}이렇게 작성함으로서 html페이지마다 어떤 컨텐츠가 들어가야하는 지 명확히 알 수 있게 되었습니다.
<a> 태그를 이용해 글 등록 페이지로 이동하기위해서 /posts/save를 주소로 하는 컨트롤러를 생성하겠습니다.
IndexController.java
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/")
public String index(){
return "index";
}
@GetMapping("/posts/save")
public String postSave(){
return "posts-save";
}
}/posts/save로 매핑이된 postSave()는 post-save를 리턴합니다.
즉 Veiw Resolver로 templates 디렉토리 하위에서 아래에 생성한 post-save.mustache로 이동하게 될 것입니다.
post-save.mustache
{{>layout/header}}
<h1>게시글 등록</h1>
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="title">제목</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="title" placeholder="제목을 입력하세요">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="author"> 작성자 </label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="author" placeholder="작성자를 입력하세요">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="content"> 내용 </label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="content" placeholder="내용을 입력하세요"></textarea>
</div>
</form>
<a href="/" role="button" class="btn btn-secondary">취소</a>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" id="btn-save">등록</button>
</div>
</div>
{{>layout/footer}}프로젝트를 실행하고 localhost:8080 에 접속해서 글 등록 버튼을 누르면 아래와 같은 화면이 나오는 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.
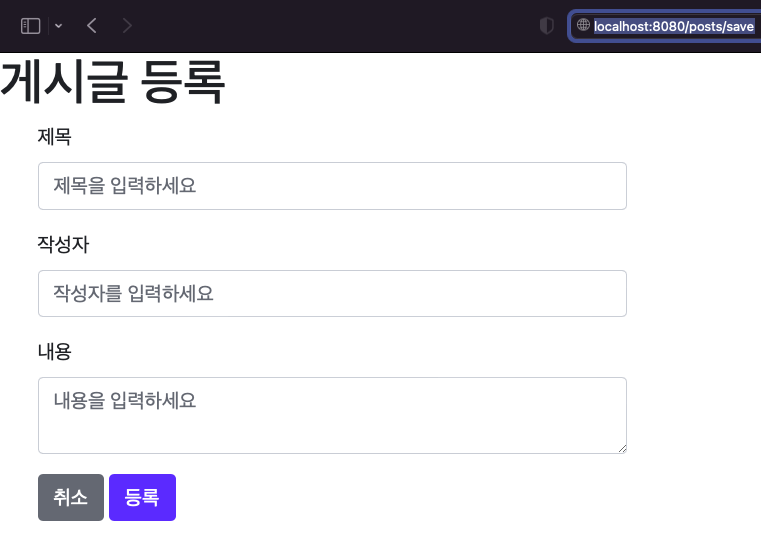
등록하기
게시글 등록 기능을 만들어보겠습니다.
resources 하위에 static/js/app 디렉토리를 만들고 index.js 파일을 생성하겠습니다.
index.js
var main = {
init: function () {
var _this = this;
$('#btn-save').on('click', function () {
_this.save();
});
},
save: function () {
var data = {
title: $('#title').val(),
author: $('#author').val(),
content: $('#content').val()
};
$.ajax({
type: 'POST',
url: '/api/v1/posts',
dataType: 'json',
contentType: 'application/json; charset=utf-8',
data: JSON.stringify(data)
}).done(function () {
alert('글이 등록되었습니다.');
window.location.href = '/';
}).fail(function (error) {
alert(JSON.stringify(error));
});
},
}
main.init();var = main = {}이라는 코드를 선언한 이유는 중복된 함수 이름이 생겨날 수 있기 때문입니다.
만약 다른 js에서도 init과 save라는 function이 있으면 브라우저의 스코프는 공용 공간으로 쓰이기 때문에 동일한 이름의 함수가 있다면 나중에 로딩된 함수가 먼저 로딩된 함수를 덮어쓰게됩니다.
그래서 index.js만의 스코프를 만들기 위해 객체를 새로 만들어 해당 객체에서 필요한 모든 function을 선언해 놓는 것입니다.
그리고 js는 footer에 넣기로 했었으니 아래와 같이 추가해주면 됩니다.
<script src="https://code.jquery.com/jquery-3.3.1.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://stackpath.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/4.3.1/js/bootstrap.min.js"></script>
<!--index.js 추가-->
<script src="/js/app/index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>이제 글 등록을 해보겠습니다.
등록버튼을 누르면 글이 등록되었다는 alret이 노출됩니다.
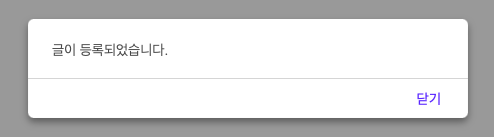
데이터베이스에도 실제로 데이터가 등록되었는지 확인해보겠습니다.
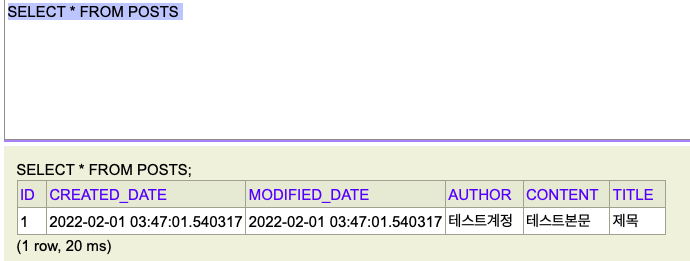
전체 조회 만들기
전체조회를 위해 index.mustache의 ui를 아래와 같이 수정했습니다.
{{>layout/header}}
<h1>스프링부트로 시작하는 웹 서비스 Ver.2</h1>
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-6">
<a href="/posts/save" role="button" class="btn btn-primary">글 등록</a>
</div>
</div>
<br>
<!-- 목록 출력 영역 -->
<table class="table table-horizontal table-bordered">
<thead class="thead-strong">
<tr>
<th>게시글번호</th>
<th>제목</th>
<th>작성자</th>
<th>최종수정일</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody id="tbody">
{{#posts}} // posts 리스트 순회
<tr>
<td>{{id}}</td> // 리스트에서 뽑아낸 id라는 변수명의 값을 출력
<td>{{title}}</td>
<td>{{author}}</td>
<td>{{modifiedDate}}</td>
</tr>
{{/posts}}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
{{>layout/footer}}머스테치의 문법을 볼 수 있습니다.
- {{#posts}}
- posts라는 List를 순회합니다.
- java의 for문과 동일합니다.- {{ 변수명 }}
- List에서 뽑아낸 객체의 필드를 사용합니다 .
전체 리스트 조회를 위해선 PostRepository 인터페이스에 쿼리를 새로 추가해야합니다.
PostRepository.java
public interface PostsRepository extends JpaRepository<Posts, Long> {
@Query("SELECT p FROM Posts p ORDER BY p.id DESC")
List<Posts> findAllDesc();
}SpringDataJpa에서 제공하지 않는 메소드는 @Query를 사용해 위처럼 쿼리로 직접 작성합니다.
다만 위 코드는 SpringDataJpa에서 제공하는 기본 메소드만으로도 해결이 가능하나 @Query를 사용하는 것이 가독성이 훨씬 좋습니다.
데이터의 조회는 FK조인, 복잡한 조건등으로 Entity클래스만으로 처리하기 어렵기 때문에 조회용 프레임워크를 사용하기도 합니다. (Querydsl, jooq, MyBatis)
PostService.java
...
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public List<PostsListResponseDto> findAllDesc() {
return postsRepository.findAllDesc().stream()
.map(PostsListResponseDto::new)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}@Transactional(readOnly = true) 에 옵션을 주면 트랜잭션 범위는 유지하되, 조회 기능만 남겨두어 조회 속도가 개선됩니다.
.map(PostsListResponseDto::new)는.map(posts - >new PostsListResponseDto(posts))와 같은 코드입니다.
postsRepository로 넘어온 Posts의 stream을 map을 통해 PostsListResponseDto 변환 -> List로 반환하는 메소드입니다.
PostListResponseDto.java
@Getter
public class PostsListResponseDto {
private Long id;
private String title;
private String author;
private LocalDateTime modifiedDate;
public PostsListResponseDto(Posts entity) {
this.id = entity.getId();
this.title = entity.getTitle();
this.author = entity.getAuthor();
this.modifiedDate = entity.getModifiedDate();
}
}IndexController.java
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Controller
public class IndexController {
private final PostsService postsService;
@GetMapping("/")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("posts", postsService.findAllDesc());
return "index";
}
...Model
- 서버 템플릿 엔진에서 사용할 수 있는 객체를 저장할 수 있습니다.
모두 완성이 되었다면 프로젝트를 실행해보겠습니다.
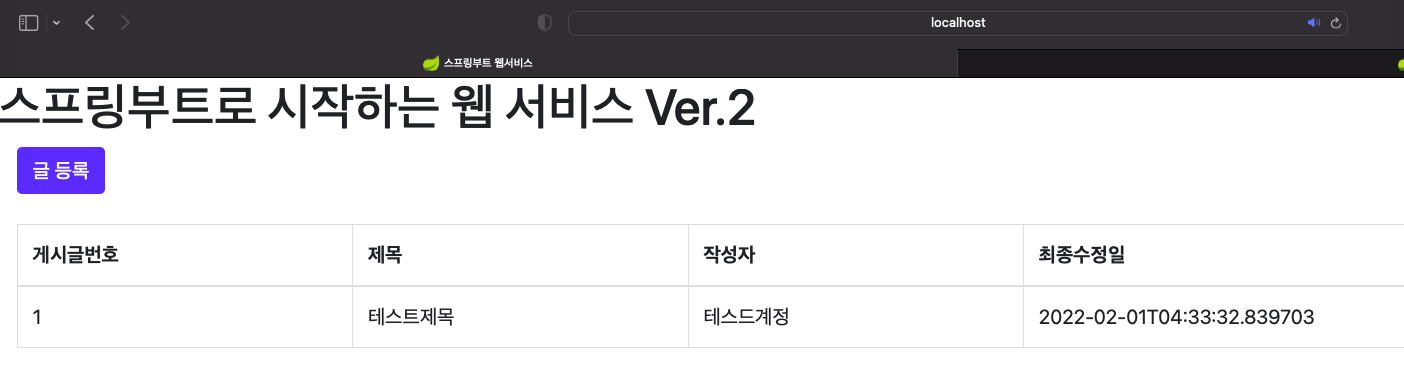
위와 같이 목록이 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
수정 / 삭제
게시글 수정 삭제 머스테치를 만들겠습니다.
posts-update.mustache
{{>layout/header}}
<h1>게시글 수정</h1>
<div class="col-md-12">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="title">글 번호</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="id" value="{{post.id}}" readonly>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="title">제목</label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="title" value="{{post.title}}">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="author"> 작성자 </label>
<input type="text" class="form-control" id="author" value="{{post.author}}" readonly>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="content"> 내용 </label>
<textarea class="form-control" id="content">{{post.content}}</textarea>
</div>
</form>
<a href="/" role="button" class="btn btn-secondary">취소</a>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-primary" id="btn-update">수정 완료</button>
<button type="button" class="btn btn-danger" id="btn-delete">삭제</button>
</div>
</div>
{{>layout/footer}}
객체의 필드를 접근할땐 . 로 구분합니다.
즉 Post 클래스의 id필드 접근은 post.id로 사용하면 됩니다.
id와 author는 수정할 수 없도록 readonly속성을 사용합니다.
그리고 업데이트 버튼에 기능을 추가하기위해 index.js에 다음과 같은 코드를 추가하겠습니다.
var main = {
init: function () {
var _this = this;
...
$('#btn-update').on('click', function () {
_this.update();
});
$('#btn-delete').on('click', function () {
_this.delete();
});
},
...
update : function () {
var data = {
title: $('#title').val(),
content: $('#content').val()
};
var id = $('#id').val();
$.ajax({
type: 'PUT',
url: '/api/v1/posts/'+id,
dataType: 'json',
contentType:'application/json; charset=utf-8',
data: JSON.stringify(data)
}).done(function() {
alert('글이 수정되었습니다.');
window.location.href = '/';
}).fail(function (error) {
alert(JSON.stringify(error));
});
},
delete : function () {
var id = $('#id').val();
$.ajax({
type: 'DELETE',
url: '/api/v1/posts/'+id,
dataType: 'json',
contentType:'application/json; charset=utf-8'
}).done(function() {
alert('글이 삭제되었습니다.');
window.location.href = '/';
}).fail(function (error) {
alert(JSON.stringify(error));
});
}
}
...update, delete라는 함수를 생성했습니다.
HPPT Method 는 controller에 매핑한 선언그대로 따라야한디ㅏ.
REST에서 CRUD는 다음과 같이 매핑됨니다.
create - POST
read - GET
update - PUT
delete - DELETE
URL Path를 지정하기위해 '/api/v1/posts/'+id 와 같이 Path에 id를 추가합니다.
index.mustache
목록페이지에서 수정페이지로 이동 할 수 있게 다음과 같이 수정합니다.
<td>{{id}}</td>
<td><a href="/posts/update/{{id}}">{{title}}</a></td>
<td>{{author}}</td>
<td>{{modifiedDate}}</td> IndexController.java
수정 버튼을 눌렀을 때 화면과 연결할 메소드를 다음과 같이 추가합니다.
@GetMapping ("posts/update/{id}")
public String postsUpdate(@PathVariable Long id, Model model) {
PostsResponseDto dto = postsService.findById(id);
model.addAttribute("post", dto);
return "posts-update";
} 게시글 삭제는 본문을 수정하는 페이지에서 작동해야하므로 수정하는 페이지에 추가해야합니다.
다음과 같이 서비스와 컨트롤러에 메소드를 추가합니다.
PostsApiController.java
@DeleteMapping ("/api/v1/posts/{id}")
public Long delete(@PathVariable Long id){
postsService.delete(id);
return id;
}PostsService.java
@Transactional
public void delete(Long id ){
Posts posts = postsRepository.findById(id).orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 게시글이 없습니다. = " + id));
// 존재하는 Posts인지 확인 후 삭제
postsRepository.delete(posts);
}postsRepository.delete(posts);는 이미 JpaRepository에서 지원하고 있는 메소드입니다.
이는 엔티티를 파라메터로 삭제할 수도 있고 deleteById를 이용하면 id로 삭제할 수도 있습니다.
소스코드가 완성되면 테스트를 진행하겠습니다.
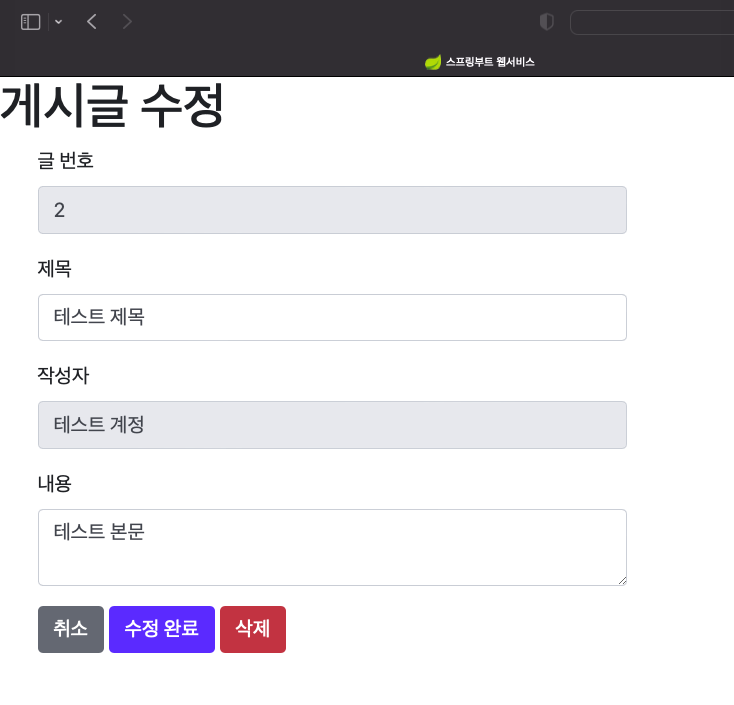
readonly 속성이 적용된 것을 볼 수있습니다.
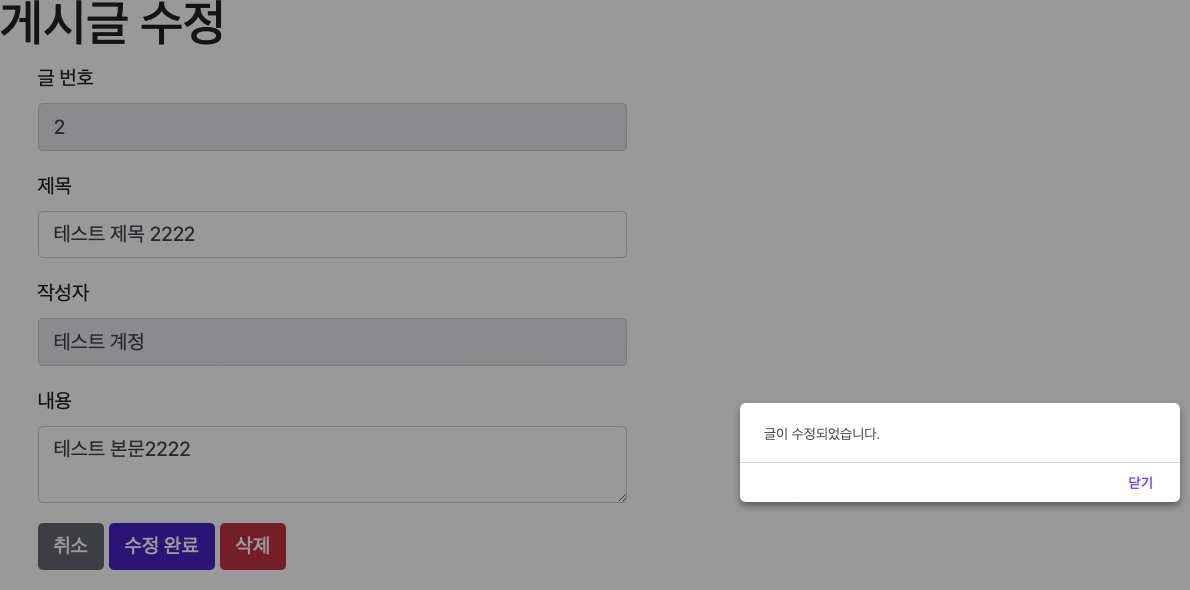
글을 수정하고 삭제하면 다음과 같이 목록에서 글이 삭제된 것을 확인 할 수 있습니다.

전체 소스는 깃허브에서 볼 수 있습니다.