CPU(The Central Processing Unit)
- ALU, Register, Control Unit(or Execution Unit)으로 구성
- 위의 3가지 구성요소를 core라고 함. 이외에도 CPU는 cache memory, internal bus 등을 포함하고 있음.
Microprocessor
- 과거 CPU는 여러 개의 chip으로 만들어졌으나 현재는 대부분 one-chip으로 구현됨. 때문에 microprocessor와 혼용되어 사용됨.
- Processor 중 device의 중심이 되는 것을 CPU라 하고 보조적 역할의 processor는 co-processor라고 부름. (그래픽 카드가 일종의 co-processor)
Micro Controller Unit(MCU)
- CPU의 기능을 하는 핵심 장치과 그 주변 장치들을 포함하고 있는 통합형 칩셋. 보통 고성능의 연산이 필요하지 않으면서 제어 기능이 필요한 분야에서 사용.
Arithmetic and Logic Unit(ALU)
- instruction에 따라 데이터에 대해 산술 연산(arithmetic operation)과 논리 연산(logic operation)을 수행하는 소자
Control Unit
- storage에서 main memory로부터 data를 load하는 명령어, main memory에서 storage로 data를 save하는 명령어, 특정 address로부터 instruction을 load하는 명령어 등에 따라 명령을 내리는 장치
- Program counter가 가르키는 address에서 수행할 명령어를 fetch하고 fetch된 instruction을 decode하여 execute.
- instruction에 따라 memory와 ALU, I/O device에 제어 신호를 보내고 해당 장치들로부터 신호를 받아 다음 처리를 제어
- Random logic으로 구현할 수 있지만,
microcode(microinstruction을 지원하는 memory(=writable ROM)로 구현된 방식)로 구현되는 경우가 많음.
Microcode로 구현된 traffic control은 다음과 같은 memory로 만들어짐.
- instruction의 opcode, mode, counter 등을 조합을 address로 삼고 해당 address에 해당하는 적절한 signal을 출력하는 memory
- control에 사용되는 여러 signal들 각각을 하나의 state라 보고 해당 state에 address를 할당한 일종의 state-machine
Register
- 주로 CPU 내에서 data를 저장하고 있는 memory로 가장 빠른 memory
condition code register: overflow, underflowprogram counter(pc): 다음 수행할 instruction이 저장된 memory 위치accumulator: ALU의 operation의 result가 저장되는 registeraddress extension register: 주소확장 register. MSB를 포함하는 상위주소 부분을 지정하는데 사용index register: relative addressing에서 사용되는 register. 현재 address에 더해질 값을 가지고 있음indirect address register: memory에서 읽어들인(fetched) indirect address를 저장하고 있는 registerinstruction register: memory로부터 fetch된 instruction을 저장하고 있는 register
ALU, Shifter, Control Unit
ALU
- 연산이 실제 수행되는 장치로 selector와 combinatorial logic circuit(gate)로 구성.
- shift operation은 shift register로, data flow control은 control unit에서 이루어짐.
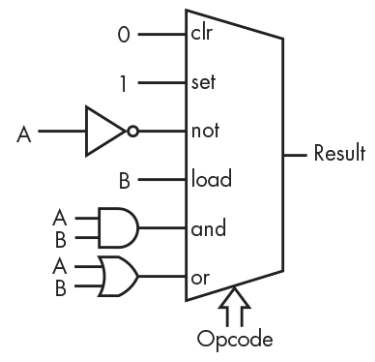
- Control unit에서 오는 control signal(opcode)에 따라 data를 가져와서 연산 수행
- Accumulator와 condition code register 등에 연산결과와 status가 저장됨.
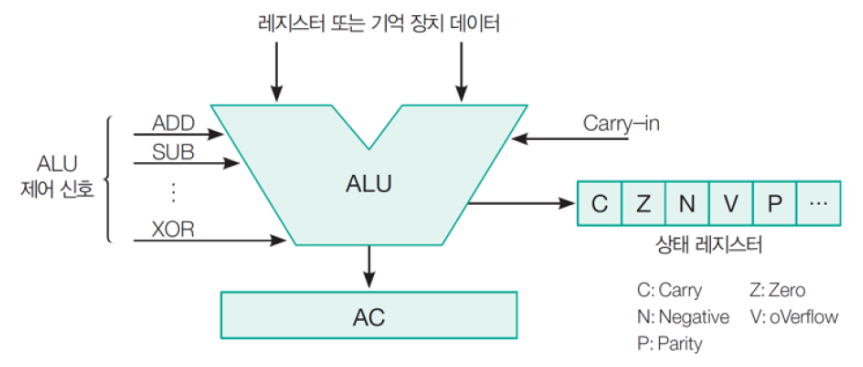
- 위의 그림에서 status register가 바로 condition code register
- ALU 제어 신호는 달리 말하면, opcode(operation code)로 연산의 종류를 의미
- 상단의 register에서 들어오는 data를 operand라고 함.
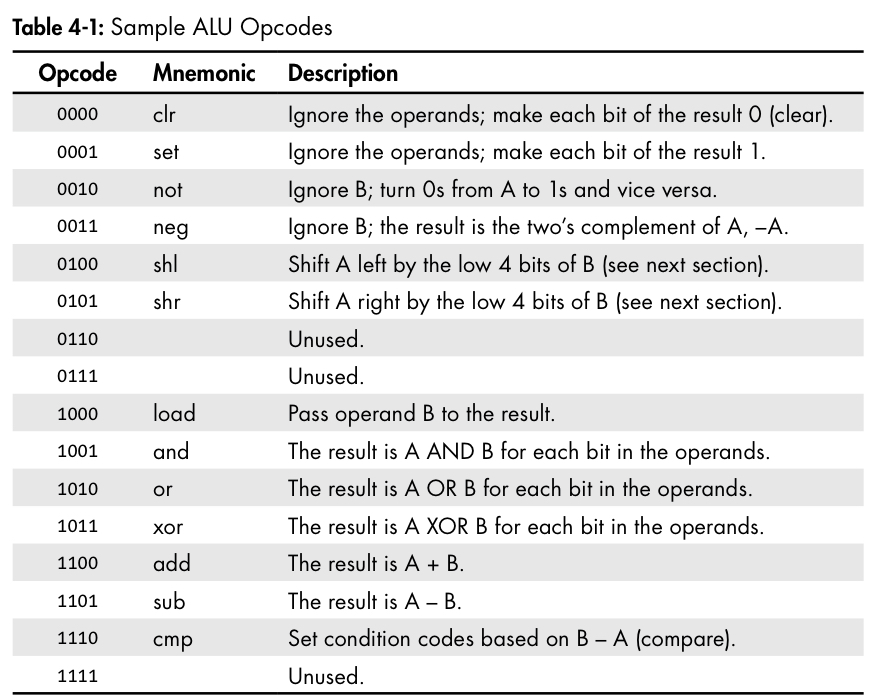
- 위의 표는 ALU가 수행하는 opcode를 나타낸 것 (example)
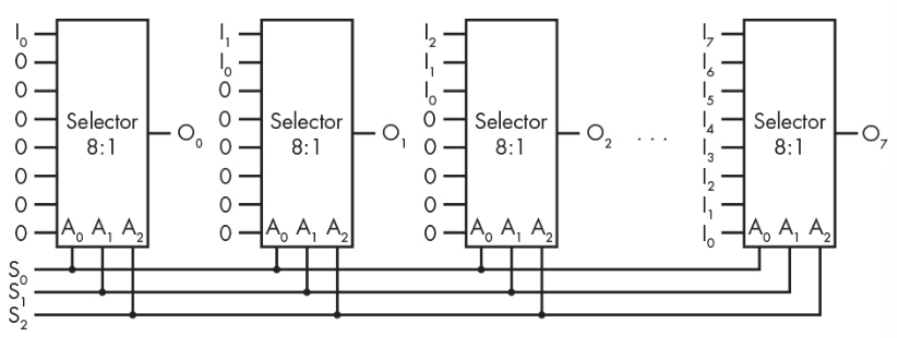
Shift Registers
shift연산 담당- shifter를 만드는데 들어가는 기본 구성요소는 EDA(Electronic Design Automation)에서 component로 제공됨.
- selector에 해당하는 chip들을 배선으로 연결하여 만드는 것이 아닌 EDA에서 component로 제공되는 block들을 조합하여 하나의 chip으로 설계하여 만드는 방식.
- 위와 같은 방식은 마치 programming이 여러 function과 class들을 조합하는 것과 비슷함.
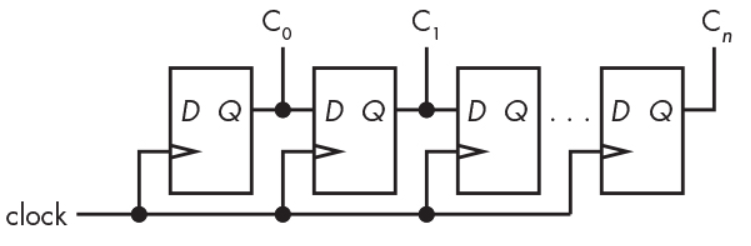
Sequential Shift Register
- flip-flop들로 구성한 shift register
- 1bit를 shift하는데 1clk가 필요함. 매우 느림
Barrel Shifter
- selector(MUX) 기반의 shift register
Instruction Sets
Instruction
- computer가 수행해야 할 명령을 나타내는 bit pattern.
- CPU에서 control unit이 이를 해석하여 이에 해당하는 제어신호를 보내게 됨.
- 일반적으로
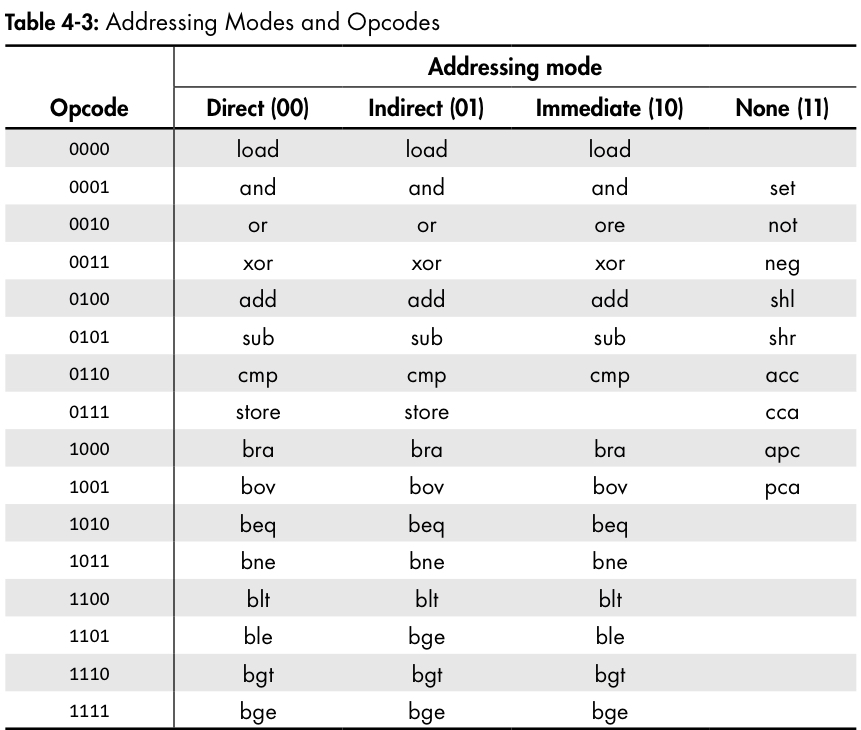
mode,operation code(opcode),address로 구성됨. (Single-address instruction layout)mode: addressing mode를 가르킴. 간단히 말하면 3가지의 다른 addressing mode가 존재함.opcode: 수행할 명령어를 나타내는 codeaddress: 현재 수행할 instruction과 관련된 data들이 놓인 memory location 혹은 data 그 자체 또는 memory location이 놓여있는 memory location
- Single-address instruction layout은 ALU에서의 결과가 accumulator에 저장되고 해당 accumulator를 operand로 사용하는 형태.
- 한번에 하나의 memory location에 접근하면 되며 적은 크기의 instruction으로 수행가능하다는 장점
Addressing Mode
- absolute addressing과 relative addressing이 있음.
- 여기서 설명하는 건 absolute addressing
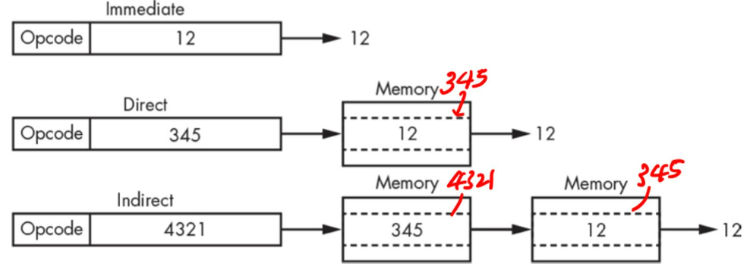
1. immediate mode addressing
- instruction에 address가 아닌 실제 값이 들어가 있는 경우
- 작은 크기(bit)의 상수값을 이용하는 경우 사용되며 가장 속도가 빠른 방식
2. direct addressing
- instruction에 포함된 address가 reference하는 곳(memory location)에 instruction이 사용할 value가 있음
3. indirect addressing
- instruction에 포함된 address가 가르키는 곳에 또 address가 들어 있음.
- instruction에 포함된 address가 reference하고 있는 memory location에 가서 값을 가져오는 것이 아니라 해당 memory location의 값이 또 address로서 다시 address가 reference하고 있는 memory location으로 가서 값을 가져옴.
- instruction의 크기를 늘리지 않고도 보다 큰 용량의 memory로 확장할 수 있지만 2번에 걸쳐 memory에 접근하므로 가장 느림.
Condition Code Instructions
- Condition code register를 직접 다루는 instruction
1. cca instruction
- Condition code register => accumulator
- Condition code register의 저장된 값을 accumulator로 copy.
2. aac instruction
- Accumulator => Condition code register
Branching
- 일반적으로 하나의 instruction이 수행되고 나면, PC register가 가르키고 있는 instruction을 수행하게 되고 해당 다음 instruction을 수행하기 전 PC는 하나가 증가하게 됨.
- 위와 같은 경우 memory에 저장된 instruction들을 순서대로 수행하게 됨.
- 프로그램이 항상 순서대로만 수행되는 게 아닌 특정 조건에 따라 다른 순서로 수행해야 하는 경우도 있기 때문에 이를 위한 branching 명령어가 존재.
- branching 명령어는 PC register 값을 직접 변경하여 instruction들의 수행순서를 바꿈.
PC(Program Counter)
- Control Unit은 PC register에 저장된 주소가 reference하는 memory location에 있는 instruction을 fetch(instruction을 instruction register에 저장)하고 instruction register에 저장된 instruction을 decode하여 실행시킴
- PC register는 instruction의 size만큼 증가하는 counter로 다음에 수행할 instruction이 저장된 memory의 address가 저장됨.
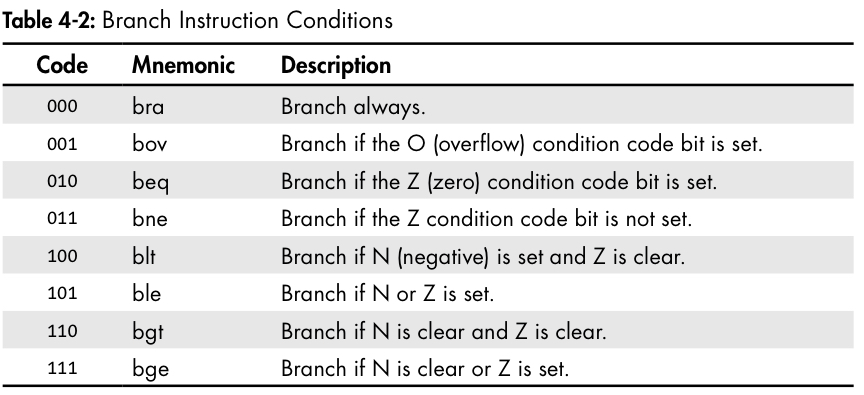
- Condition code register의 해당하는 bit에 대한 조건을 만족하면 branching.
- 조건에 의해 branching 하지 않고, PC register의 값을 명시적으로 그냥 바꾸는 등의 동작을 수행하는 instruction도 존재함.
pca: 현재 PC register 값을 accumulator로 copyapc: 현재 accumulator 값을 PC register로 copy
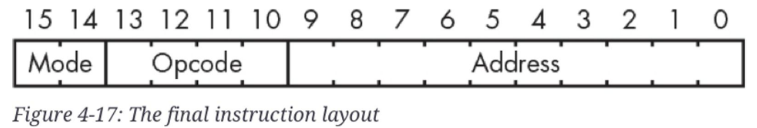
Final Instruction Set
- 16bit 기준 single address instruction layout은 다음과 같음.
Fetch and Execute
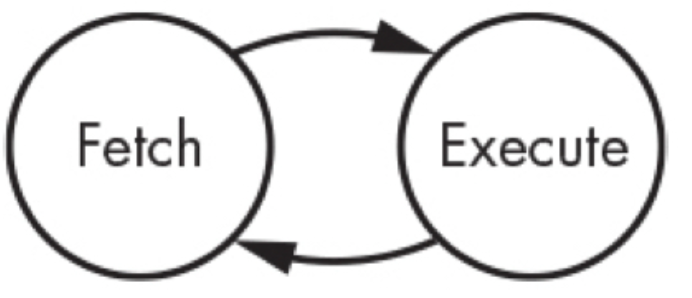
- instruction의 수행은 위와 같이 구성됨.
Fetch
- memory에서 instruction을 instruction register로 가져오는 것
- stored program computer에서는 memory에 처리해야 하는 instruction list가 저장되어 있었음.

- PC에 저장된 address가 address bus를 통해 memory에 주어지고 address bus를 통해 전달된 address에 해당하는 memory location에 저장된 값이 data bus를 통해 instruction register로 저장
Execute
- fetch된 instruction이 해당 instruction의 내용에 따라, memory에서 값을 읽어오는 등의 여러 작업이 이루어지며 이에 따라 해당 instruction이 수행됨. 이 단계를 Execution cycle이라 함.
- 하나의 instruction을 수행하기 위한 fetching-execution cycle은 여러 단계가 필요하기 때문에 현재 단계가 무엇이지 나타내는 counter가 필요함.
- Control Unit은 해당 counter와 opcode, mode 들에 할당된 bit를 읽어들여 현재 필요한 제어 signal을 필요한 component에 전달함.
- 위와 같이 signal들의 흐름을 제어하는 것을 signal traffic control이라고 함.
Traffic Control
- Random logic 기반의 traffic control은 RISC에서 많이 사용
- Microcode 기반의 traffic control은 CISC에서 많이 사용
References:
1) https://dsaint31.me/mkdocs_site/CE
2) Jonathan E., The Secret Life of Programs, p.98, 106, 107