Exception이란?
Error 와 다르게 Exception은 코드 수정으로 해결이 가능한 동작 중 문제를 나타냄
예외 처리 사용 구문
try{...} : 예외 발생되는 범위를 블록으로 지정
catch{...} try 블록 뒤에 사용 .
try 블록에서 발생된 예외 객체 잡아 처리하는 블록
예외 객체가 생성되면 매치되는 catch()를 호출한다 이해
finally {...} : 필요 시 사용하는 블록
예외발생 여부와 관계없이 무조건적으로 실행할 코드 적는 블록
throw : 예외 객체를 catch로 전달하는 구문
throws : 해당 메서드에서 발생되는 예외클래스를 선언(예외처리가 아닌 예외 전가)
throws 가 선언된 메서드를 사용하는 클래스에서 예외처리 필요
기본적 예외 사용 예시
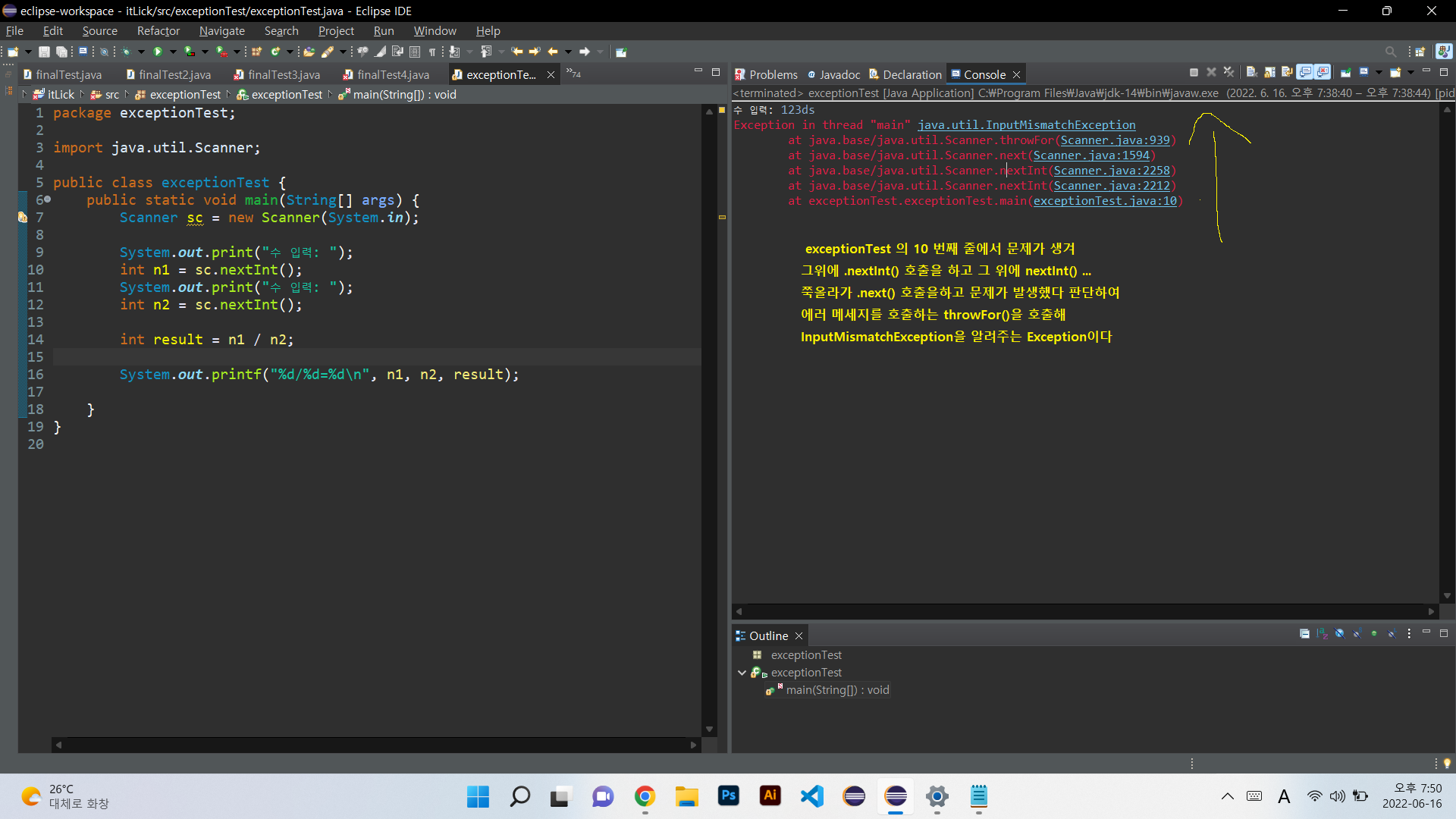
Scanner sc를 통해 수입력을 받는데 문자를 사용하게 되면 저렇게 exception이 발생하게 된다
이러 한문제들을 try catch를 통해 예외문을 만들수 가있다
Exception의 사용 코드1
package exceptionTest;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class exceptionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("수 입력: ");
int n1 = 0 , n2 = 0, result = 0;
//예외가 발생할 수 있는 부분은 try로 묶는다
try {
//int n1 = sc.nextInt(); // 블록 안에 선언된 변수는 외부에서 사용 불가이므로
// 외부에서 선언
n1 = sc.nextInt();
// 여기서 문자열이 입력되면 생성되는 InputMismatchException() 이 throw 가되는데
// catch가 없어서 프로그램이 자동 종료 된 것
}catch(InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("입력 형식 예외!");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.print("수 입력: ");
try {
n2 = sc.nextInt();
}catch(InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("입력 형식 예외");
e.printStackTrace(); }
try {
result = n1 / n2;
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("0으로 나눌수 없음");
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 문제 원인을 확인할수있음
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.printf("%d/%d=%d\n", n1, n2, result);
}
}
이 방법은 조금 지저분 하므로 멀티 방법을 이용하는게 더좋다
package exceptionTest;
import java.util.InputMismatchException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class exceptionTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n1 = 0 , n2 = 0, result = 0;
// 멀티로 작성 시
// catch(exception e) 를 사용하면 업케스팅으로 인해 나머지 가 적용이 안되기에
// 이것만 주의
try {
System.out.println("수 입력: ");
n1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("수 입력: ");
n2 = sc.nextInt();
result = n1 / n2;
System.out.printf("%d/%d=%d\n", n1, n2, result);
}catch(InputMismatchException e) {
System.out.println("입력 형식 예외!");
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("0으로 나눌수 없음");
System.out.println(e.getMessage()); // 문제 원인을 확인할수있음
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("무조건 실행되는 블록");
System.out.println("자원 해제 용도");
//finally 사용 이유
//1 데이터나 파일에 입출력, 네트워크를 통해 입출력 하는 경우 예외가 발생해
// 읽고 있거나 쓰고있는데 프로그램이 꺼지면 안되므로 예외가 발생해도 stream 잘 끊을 수 있도록 하기위해
// 따라서 연결되있는 빨때를 관리할 수없음
}
System.out.println("프로그램 정상 종료!");
}
}
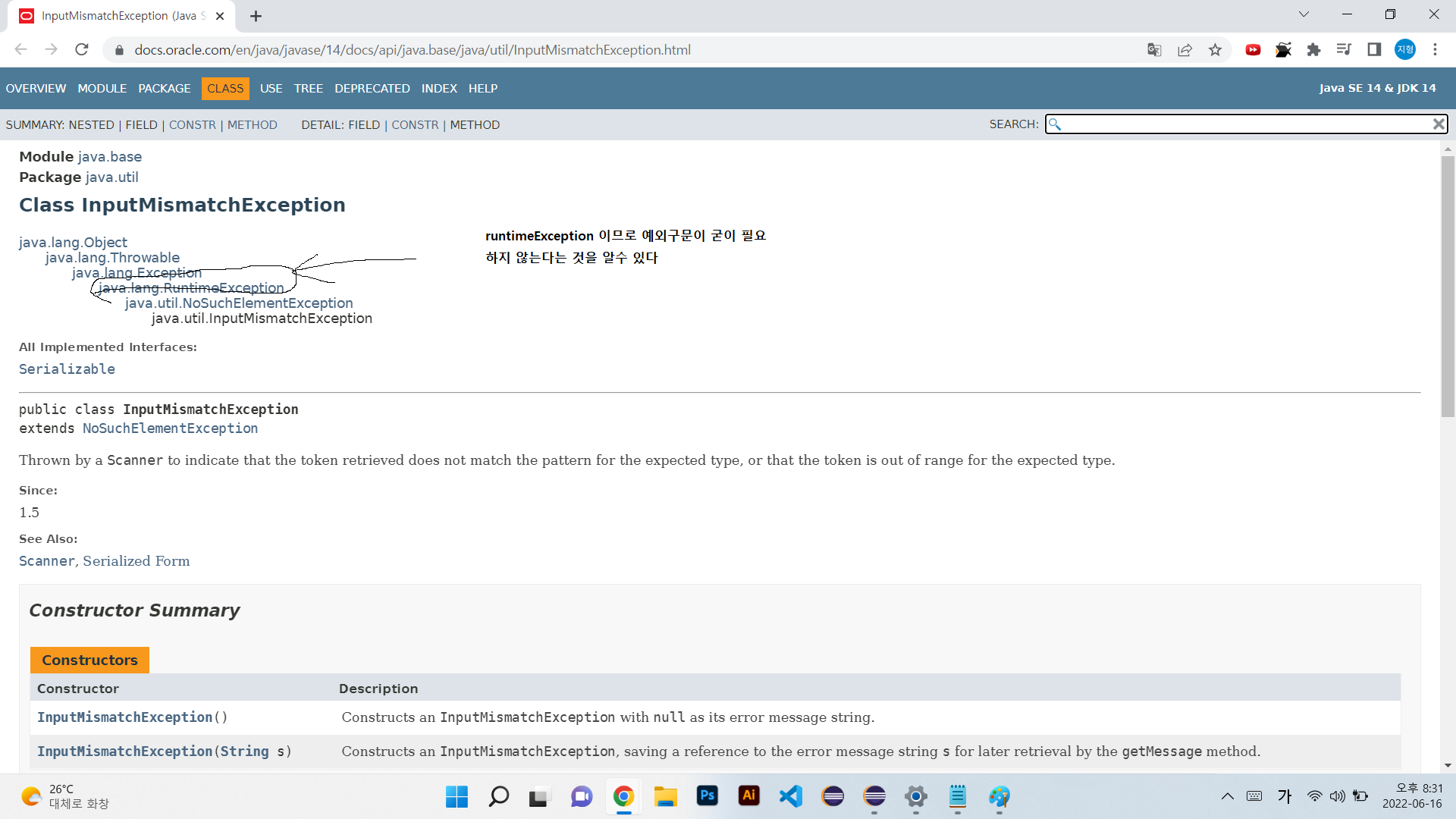
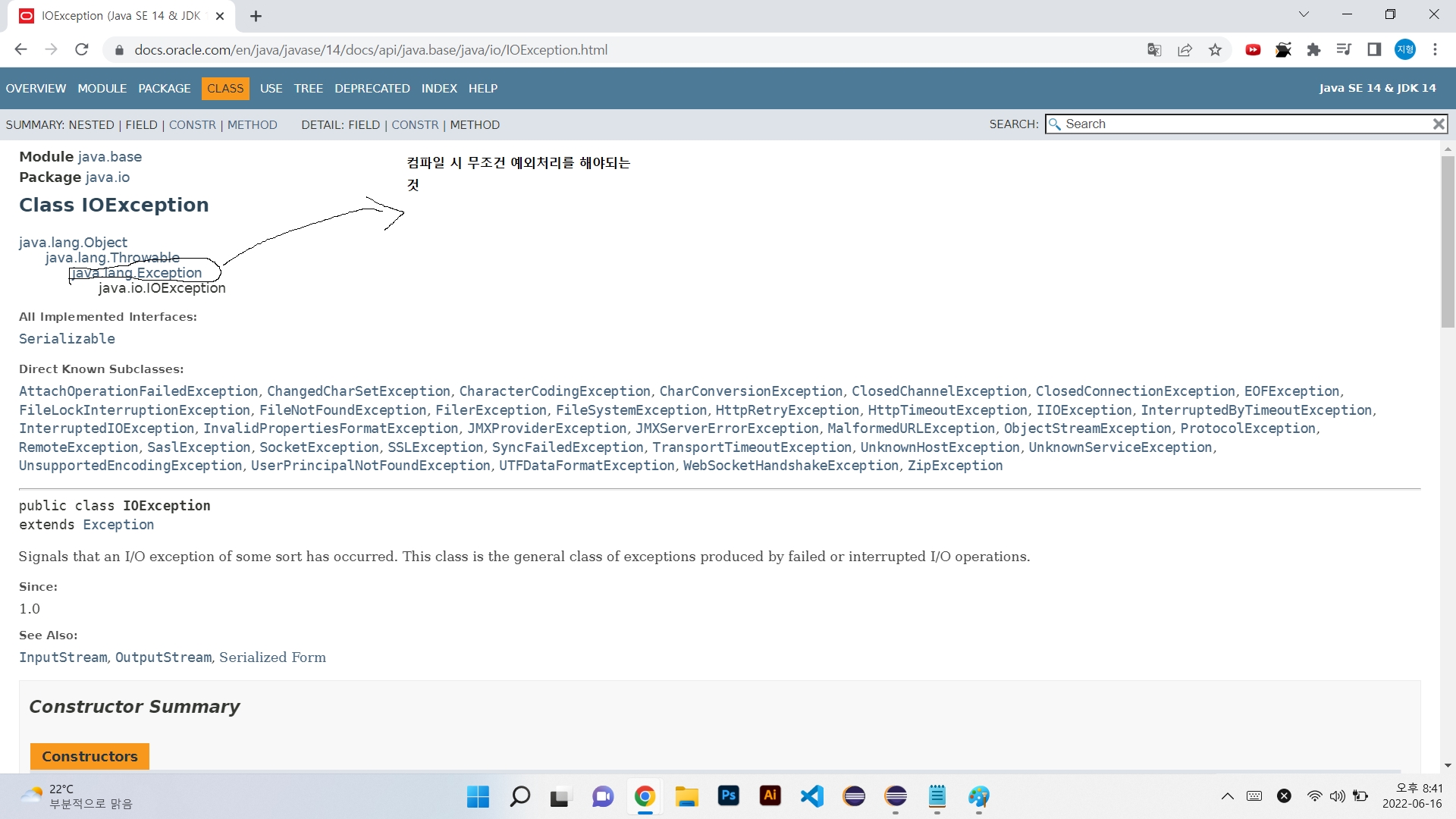
exception(예외) 종류 2가지
exception - 컴파일 시 예외 처리 구문 작성 여부 확인 ㅇ
runtimeException - 예외처리 구문이 반드시 필요하지 않음
throws의 사용
위에서 개념부분에서 보았듯이 사용하는 객체에게 try catch 예외를 전가하는 것을 이야기 한다
throws : 해당 메서드에서 발생되는 예외클래스를 선언(예외처리가 아닌 예외 전가)
throws 가 선언된 메서드를 사용하는 클래스에서 예외처리 필요
package exceptionTest;
import java.io.IOException;
class myInput{
int input() throws IOException {
int result = 0;
result = System.in.read();
return result;
}
}
public class exception3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
myInput mi = new myInput();
try {
mi.input();
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
자기가 설정하는 예외 사용
위의 내용들은 내제 Exception을 이용해 만든 것이지만
만약에 더하는 계산기를 만들고 싶은데 두 수의 합이 0 미만이면 예외처리를 하는 방법을 공부 해 보았다.
- 계산기 class
package exceptionTest;
public class AddCalculator {
public int add(int n1, int n2) {
int result = n1 + n2;
if(result < 0) {
throw new ResultScopeException("result =" + result);
}
return result;
}
}
- result가 0 미만일때 발생 시킬 예외 클래스
package exceptionTest;
public class ResultScopeException extends RuntimeException{
public ResultScopeException(String msg) { //메세지를 발생시키고 싶을 때 만든 String msg 메서드
super(msg);
}
}
- main 클래스
package exceptionTest;
public class main4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AddCalculator addcalc = new AddCalculator();
int ret = 0;
try {
ret = addcalc.add(1, -9);
}catch(ResultScopeException e) {
//e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(ret);
}
}
만약에 예외클래스가 runtime이 아닌 exception일경우
1.계산기 class
package exceptionTest;
public class AddCalculator {
public int add(int n1, int n2) throws ResultScopeException2 // exception 예외라 알려줘야함 {
int result = n1 + n2;
if(result < 0) {
throw new ResultScopeException2("result =" + result);
}
return result;
}
}
2.exception class
package exceptionTest;
public class ResultScopeException2 extends Exception{
public ResultScopeException2(String msg) {
super(msg);
}
}
- main class
package exceptionTest;
public class main4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AddCalculator addcalc = new AddCalculator();
int ret = 0;
try {
ret = addcalc.add(1, -9);
}catch(ResultScopeException2 e) {
//e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println(ret);
}
}