S4 : Efficiently Modeling Long Sequences with Structured State Spaces - 1 Introduction
Do We Need Attention?
"Efficiently Modeling Long Sequences with Structured State Spaces"의 Introduction 부분 읽으면서 정리했던 내용
[ Contents ]
LRDSSMLSSLproblemS4- toward - general purpose sequence model
요약하자면, LRD 문제해결을 위해 state space representation 개념을 도입, 이전 연구인 LSSL모델에서 보였던 bottleneck 현상의 해결을 위해 몇 가지 방법의 적용을 통해 S4 model 제안, 해당 모델의 generalized sequence model로의 발전 가능성까지 소개
Introduction
Long-Range Dependencies (LRDs)
-
시퀀스 모델링의 중심 문제 중 하나는 장기간 의존성(LRDs)을 효율적으로 처리하는 것. → 먼 거리의 데이터의 dependency를 유지하는것
LRD: spatial or time-series data의 분석에서 주로 발생하는 현상으로, time interval / spatial distance의 증가에 따라 두 지점(point)간의통계적 의존성(statistical dependence)이 감소하는 속도와 관련이 있음
(통계적 의존성이 감소 → 두 데이터 포인트가 관련이 없어짐)
-
Real-world에서의 시계열 데이터는 수 만개의 time-step에 걸쳐 추론을 요구하는데, 수 천개의 time-step을 다루는 소수의 모델만이 있음.
-
Long-Range Arena(LRA)의 벤치마크 결과는 LRD에서 현재의 시퀀스 모델들이 결과가 좋지 못하며, Path-X와 같은 작업에서는 무작위 추측보다도 못한 결과를 보임.
LRA: benchmark, Long-Range Arena, specifically focused on evaluating model quality under “long-context scenarios”
-
LRD를 해결하기 위해 기존 모델(continuous-time models (CTMs), RNNs, CNNs, and Transformers등)에많 은 특수한 변형들이 시도되었음.
예 :
- vanishing gradients를 해결하기 위한 orthogonal RNN, Lipschitz RNNs
- context size의 증가를 위한 dilated convolutions
- sequence 길이의 quadratic dependence를 줄이기 위한 다양한 Transformer들 -
LRD를 대상으로 한 이런 시도들에도, LRA나 raw audio classification에서 결과가 좋지 못함.
State Space Model (SSM)
- 최근에 LRD 문제에 대한 접근으로
SSM의 도입이 제시됨 : SSM(상태공간모형) - Markov chain을 기반으로 하는 시계열 모형의 일종
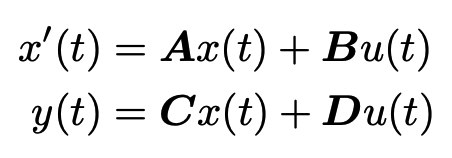
- SSM은 control theory, computational neuroscience 등 다양한 과학분야에서 사용되던 모델이지만 딥러닝에서는 잘 사용되지 않았었다.
- 특히 Gu 등 [18]은 deep SSM이 실제로 단순한 작업에서도 고전하기 때문에, continuous-time memorization(CTM) 문제를 해결하기 위해,
최근에 유도된 특별한state matrices A가 적용되었을 때 예외적으로 우수한 성능을 발휘할 수 있음을 보여주었습니다. - 이들이 제시한 그들의 선형 상태 공간 레이어(
Linear State Space Layer,LSSL)는 CTM, RNN 및 CNN 모델의 강점을 개념적으로 통합하며,
deep SSM이 원칙적으로 LRD를 해결할 수 있음을 입증하는 개념적 증명을 제공합니다.
LSSL Problem
- 근데, LSSL는 연산, 메모리 문제 때문에 실제로 사용하기에 어려움이 있음
- dimension and sequence length , computing the latent state requires :
- operations
- and space - compared to a lower bound for both.
-
Thus for reasonably sized models (e.g. N = 256 in Gu et al. [18])의 경우 LSSL은 비슷한 크기의 CNN, RNN보다 더 많은 메모리를 사용
-
LSSL를 위한 이론적인 efficient algorithms이 제안되었지만 우리는 이들이 numerically하게 불안정한 것을 보였다.
-
특히 “special A matrix”는 선형대수학적으로 아주 “non-normal”해서 일반적인 알고리즘의 적용을 어렵게 한다.
-
결과적으로 : LSSL은 SSM이 strong performance를 보여주었지만, 현실적이지 않음
(S4) Structured State Space sequence model
→ 이 paper에서 제시한 모델
- 이전 연구의 computational bottleneck(LSSL Problem)의 해결을 위해 SSM에 기반한
S4 model을 제시- S4는 structured state matrices A를
reparameterize: decomposing them as the “sum of a low-rank and normal term” - *추가적으로 standard SSM을 coeifficient space(parameter의 공간)수준에서 확장시키는 대신,
SSM의 frequency space 수준에서truncated generating function을 계산해서
multipole-like evaluation로 단순화시킴
- S4는 structured state matrices A를
- 위의 두 가지 아이디어를 조합해서 우리는 다음을 통해 :
궁극적으로, 잘 연구되어있고 안정적인 “1) low-rank term은
Woodbury identity로 수정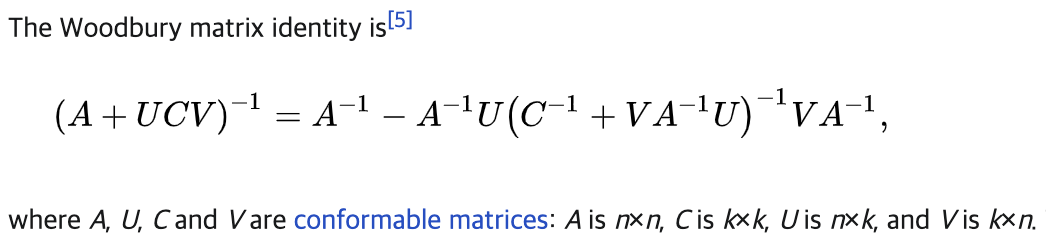
2) normal term은 안정적으로 diagonalized(대각화)
Cauchy kernel”로 축소될 수 있었음
- 결과 :
-
computation,
-
memory usage
→ sequence model에 적합해짐
-
- LSSL과 비교해서 30배 빨라지고 메모리 사용량은 400배 줄였으며 경험적으로 LSSL보다 나아짐
- 실험적으로, S4는 significantly advances the state-of-the-art for LRD
- On the LRA benchmark for efficient sequence models :
- S4는 모든 베이스라인과 비슷한 속도로 작동하면서 평균적으로 20점 이상의 성능을 능가
- S4 는 어려운 LRA Path-X task(length-16384)을 해결하는 첫 번째 모델 ,
- 이전 모든 연구 대비 achieving 88% accuracy, ~ compared to 50% random guessing
- On speech classification with length-16000 sequences,
- S4는 specialized Speech CNN의 test error를 절반으로 줄였지만,
이와 비교해서 모든 RNN, Transformer baseline은 학습에 실패
- S4는 specialized Speech CNN의 test error를 절반으로 줄였지만,
- On the LRA benchmark for efficient sequence models :
Towards a general-purpose sequence model
- LRD 문제를 넘어서, 머신러닝의 broad goal은
wide range of problem을 다루는 single model의 개발. → generalization - 오늘날의 모델들은 전형적으로 particular domain에서 특정 문제를 다루거나, narrow range of capabilities에 specialized 되어있음
- This specialization is typically expressed via
domain-specific preprocessing,inductive biases, andarchitectures.
- This specialization is typically expressed via
- Sequence models provide a general framework for solving many of these problems with “reduced specialization”
-
Deep SSM은 이런 general sequence modeling solution에 개념적으로 강점이 있음 :- LRD에대한 접근 + ability to move between ontinuous-time, convolution and recurrent model representation
- Large-scale generative modeling.
On CIFAR-10 density estimation,
S4 is competitive with the best autoregressive models (2.85 bits per dim).
On WikiText-103 language modeling,
S4 substantially closes the gap to Transformers (within 0.8 perplexity),
”settingSoTA for attention-free models". - Fast autoregressive generation
On CIFAR-10 and WikiText-103 에서
RNN처럼, latent state를 사용해서
autoregressive model의 standard보다 60배 빠른 pixel/token generation을 수행 - Sampling resolution change
Like specialized CTMs,
S4는 time-series sampling frequency의 변화에 retraining 없이 적응할 수 있음
(e.g. at0.5×frequency on speech classification.) - Learning with weaker inductive biases
architectural changes없이,
S4는
- speech classification에서 “Speech CNNs”을 능가,
- time-series forecasting problems에서 “specialized Informer model”을 능가
- sequential CIFAR에서90% accuracy이상으로 “2-D ResNet” 과 일치하는 결과
- LRD에대한 접근 + ability to move between ontinuous-time, convolution and recurrent model representation
이후 background에서 S4 이전의 연구 내용들(HiPPO, LSSL)과 state space 의 continuous to discrete time 등, method section에서는 S4 architecture의 세부적인 내용들을 다룬다
Background
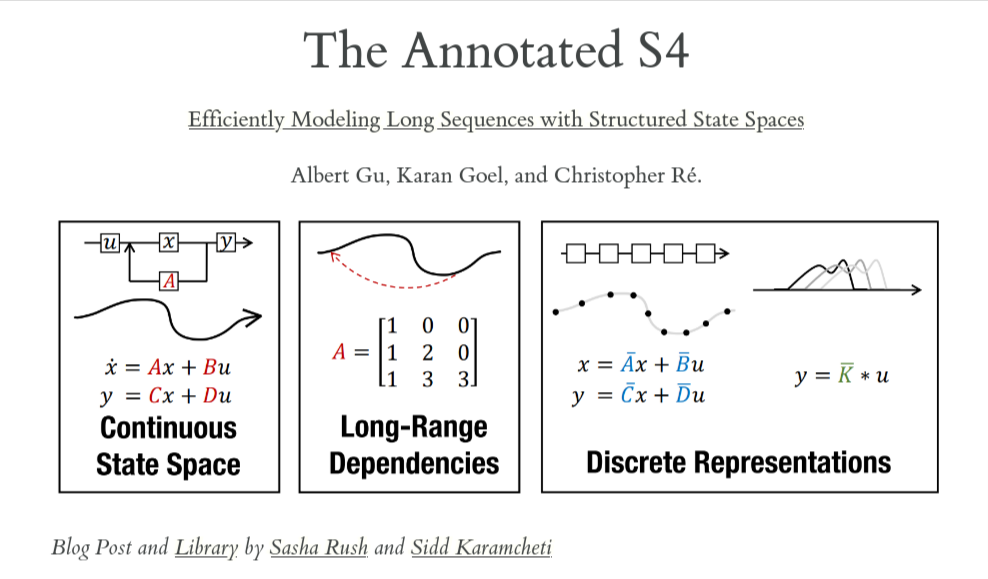
State Space Models: A Continuous-time Latent State Model
Addressing Long-Range Dependencies with HiPPO
Discrete-time SSM: The Recurrent Representation
Training SSMs: The Convolutional Representation
Method : Stuctured State Space (S4)
Motivation: Diagonalization
The S4 Parameterization: Normal Plus Low-Rank
S4 Algorithms and Computational Complexity
Architecture Details of the Deep S4 Layer
