AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
extends org.springframework.web.filter.GenericFilterBean
implements org.springframework.context.ApplicationEventPublisherAware, org.springframework.context.MessageSourceAwareAbstract processor of browser-based HTTP-based authentication requests.
브라우저 기반의 Http 기반 인증에 대한 추상 프로세서이다.
GenericFilterBean의 상속을 받고 있고, subclass로는 OAuth2LoginAuthenticationFilter, Saml2WebSsoAuthenticationFilter, UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter가 있다.
딱봐도 알겠지만 굉장히 말그대로 Http-Browser-Base의 인증을 하려면 핵심 클래스 이므로 알아둘 필요가 상당히 있다.
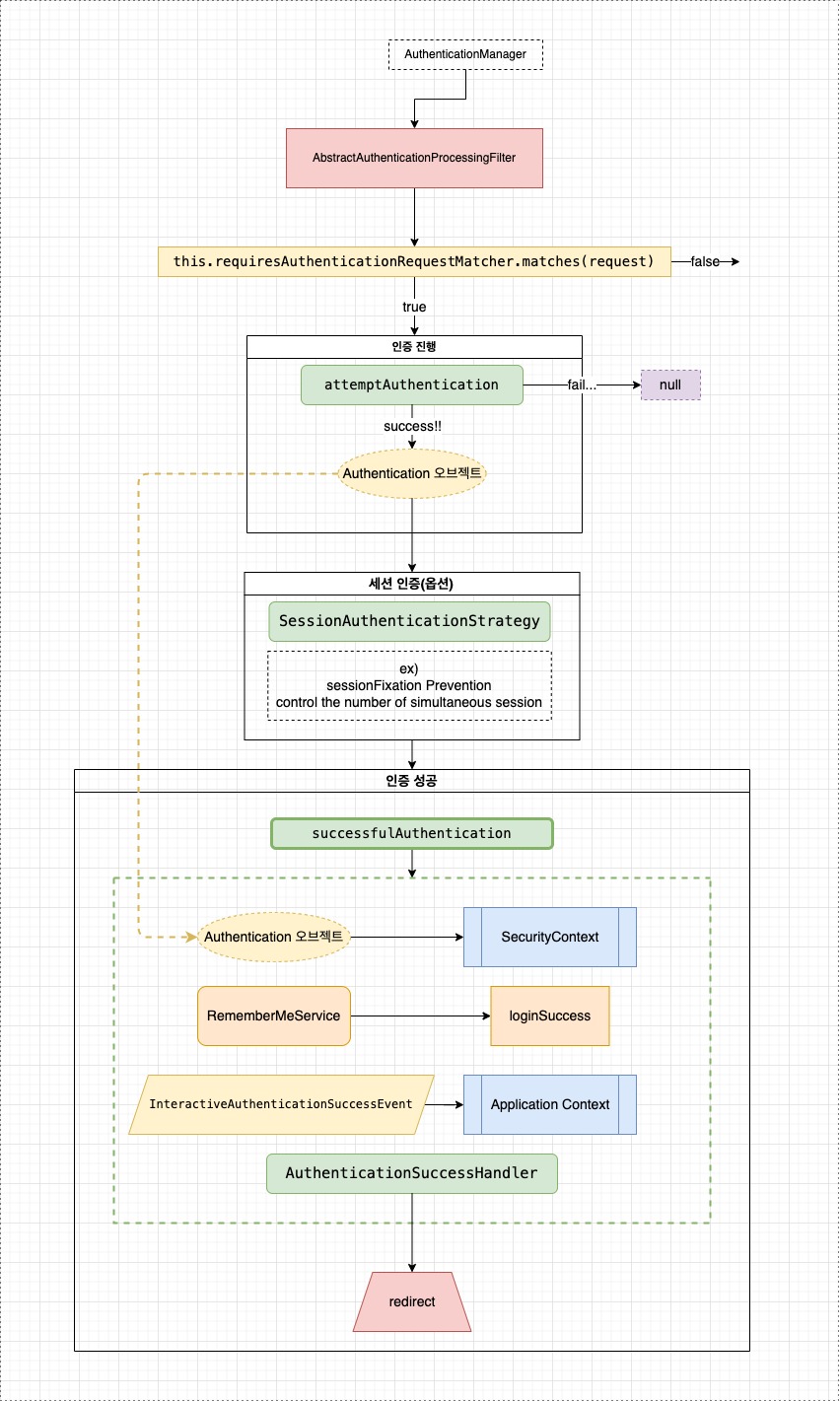
동작 다이어그램
퍼가실땐 출처 필수
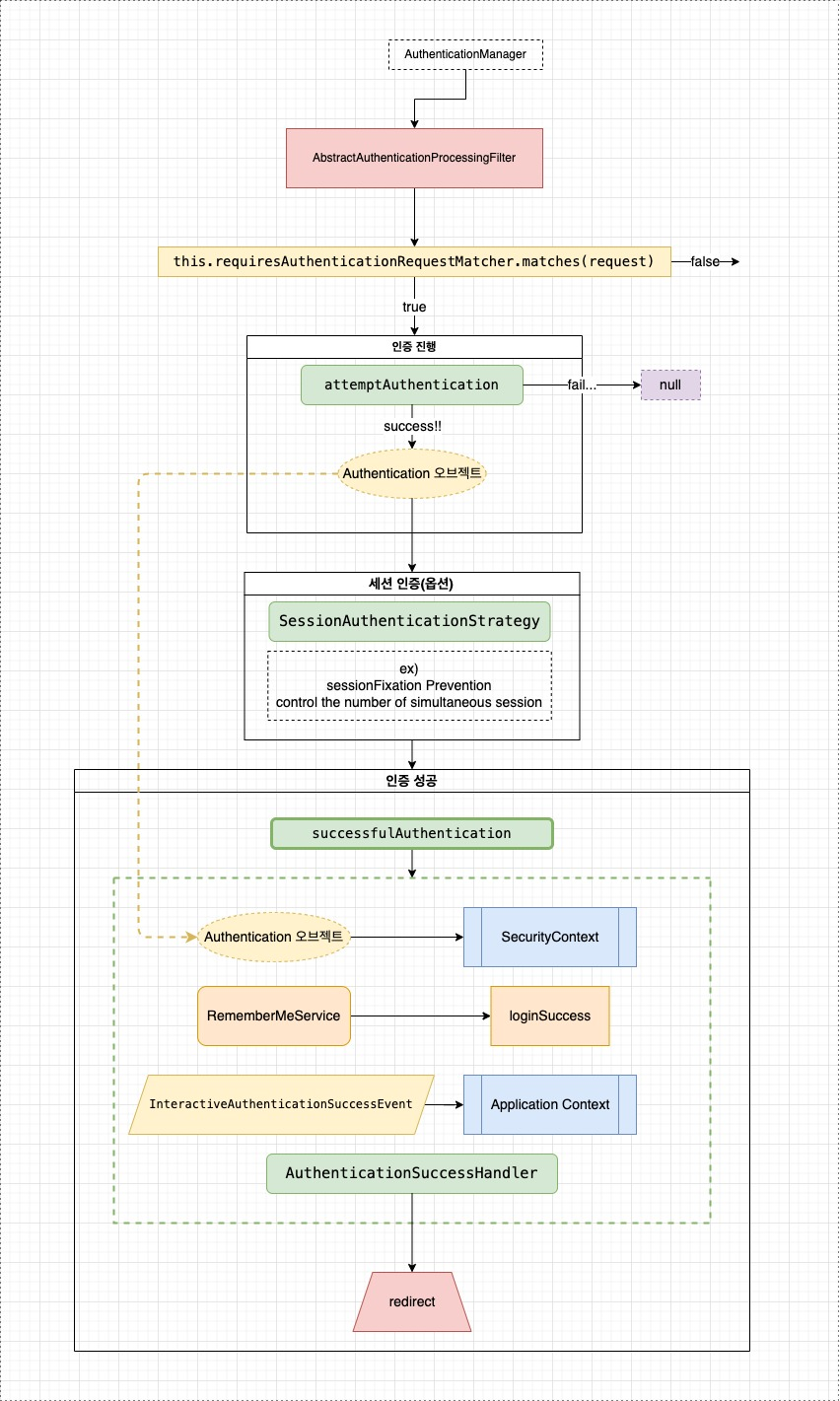
unsuccessfulAuthentication 부분은 생략하고 다이어 그램을 그렸다. 아래 코드 부분을 살펴보자.
이는 간략하게 설명하면, 인증이 실패하면 실행된다. InternalAuthenticationServiceException 이나 AuthenticationException이 발생하면 실행된다.
동작 해설 / api 해설
🔴 Authentication Process (인증 과정)
-
이 필터는
authenticationManager를 필요로 한다. (나의 글 참고해도 좋음 링크)
authenticationManager은 구현 클래스들에 의해 만들어진Authentication request tokens를 처리하는데 필요하다. -
만약 요청이
private RequestMatcher requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher에 맞으면, 이 필터는 요청을 가로채서 그 요청의 인증 수행을 시도할 것이다. -
attemptAuthentication메서드에 의해 Authentication이 실행된다. 이는 구현 클래스에 의해 반드시 구현되어야 한다.
중간 해설 : RequestMatcher
org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RequestMatcher 인터페이스는 HttpServletRequest가 인증이 필요한지 결정하는데 사용한다.
AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter의 내부 RequestMatcher에 관련된 부분
//내부 멤버 변수
private RequestMatcher requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher;
//...
//생성자 중 하나에도 notnull로 들어가있고 이를 통해 주입해줌
protected AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter(RequestMatcher requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher) {
Assert.notNull(requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher, "requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher cannot be null");
this.requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher = requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher;
}
//...
//또 다른 생성자
protected AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter(RequestMatcher requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher,
AuthenticationManager authenticationManager) {
setRequiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher(requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher);
setAuthenticationManager(authenticationManager);
}
//...
//RequestMatcher을 이용하여 Authentication이 필요한지 확인하는 모습
protected boolean requiresAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
if (this.requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher.matches(request)) {
return true;
}
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger
.trace(LogMessage.format("Did not match request to %s", this.requiresAuthenticationRequestMatcher));
}
return false;
}
RequestMatcher이 초면인것 같은가? 그러면 다음 코드를 살펴보자.
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class FormLoginSecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeHttpRequests().requestMatchers("/**").hasRole("USER").and().formLogin();
return http.build();
}우리가 매우 익숙한 코드이다.
이 HttpSecurity에는 Nested Classes로 HttpSecurity.RequestMatcherConfigurer라는 클래스가 존재한다.
public class HttpSecurity.RequestMatcherConfigurer
extends AbstractRequestMatcherRegistry<HttpSecurity.RequestMatcherConfigurer>이 클래스와 부모 클래스인 AbstractRequestMatcher에 우리가 아주 익숙한 메서드 들이 담겨있다.
(and(), requestMatchers, anyRequest 등등이다)
그리고 HttpSecurity.RequestMatcherConfigurer의 필드로
protected List<RequestMatcher> matchers가 존재한다.
즉 우리는 알게 모르게 RequestMatcher로 필터의 적용범위를 설정하고 있었고,
이는 Http-Base , Browser-Base의 인증을 담당하는 추상클래스 AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter의 인증 필요 여부를 결정 하고 있었던 것이다.
_Spring api 문서에 다음을 검색해보라 :
HttpSecurity , HttpSecurity.RequestMatcherConfigurer, AbstractRequestMatcher, RequestMatcher
🟠 Authentication Success (인증 성공)
SercurityContext에 배치
인증이 성공적으로 완료되면 결과로써 나온Authentication오브젝트는 현재 쓰레드의SecurityContext에 배치된다.
(SecurityContext는 이전filter들에 의해 생성됨이 보장된다)
//AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContext context = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(authResult);
this.securityContextHolderStrategy.setContext(context);
this.securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response);AuthenticationSuccessHandler를 통해 적절한 redirect
설정된AuthenticationSuccessHandler가 성공적인 로그인 이후 적절한 주소로 redirect 시킨다. (기존에 시도했던 주소로 보내는것도 가능)
기본적으로는SavedRequestAwareAuthenticationSuccessHandler이 구현되어있으며,ExceptionTranslationFilter가 설정한DefaultSavedRequest을 사용해서 redirect 시킨다.
이를 구현한 다른 클래스를 주입하여 원하는 동작을 취할 수 있다.
🟡 Event Publication (이벤트 발행)
- 만약 인증이 성공적이라면,
application context를 통해InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent가 발행된다. - 만약 인증이 성공적이지 않다면 아무런 이벤트도 발행되지 않는다.
왜냐면 이는 일반적으로 AuthenticationManager관련 application event 를 통해 기록 되기 때문이다.
🟢 Session Authentication (세션 인증)
이 클래스는 옵션으로 SessionAuthenticationStrategy를 가지고 있다.
SessionAuthenticationStrategy은attemptAuthentication()이 성공한 직후 즉시 실행된다.- 각자 다른 구현은 주입될 수 있다.
session-fixation attack prevention이나 한 계정의 동시 세션 제어 와 같은 구현이 포함될 수도 있다.(예시)
코드 뜯어보기 - 핵심
doFilter
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
doFilter((HttpServletRequest) request, (HttpServletResponse) response, chain);
}
private void doFilter(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain)
throws IOException, ServletException {
if (!requiresAuthentication(request, response)) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
return;
}
try {
Authentication authenticationResult = attemptAuthentication(request, response);
if (authenticationResult == null) {
// return immediately as subclass has indicated that it hasn't completed
return;
}
this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authenticationResult, request, response);
// Authentication success
if (this.continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authenticationResult);
}
catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException failed) {
this.logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user.", failed);
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, failed);
}
catch (AuthenticationException ex) {
// Authentication failed
unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, ex);
}
}doFilter를 오버라이드해서 HttpServletRequest와 HttpServletResponse를 받는 메서드로 연결해준다.
보면 이 과정이 핵심 골자임을 알 수 있다.
🔺requiresAuthentication
requiresAuthentiaction은 미리 지정해둔 RequestMatcher를 통해 이 HttpServletRequest가 매칭 되는지 알려준다.
만약 매칭되지 않으면 chain.doFilter로 필터 체인을 타게 한다.
🔺attemptAuthentication
attemptAuthentication메서드를 이용해 인증을 진행한다.
이는 자손 클래스에서 구현해주어야 한다.
인증이 진행되었다면, Authentication객체를, 아니라면 null을 반환해야한다.
대표적인 자손 클래스인 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter에서는 username과 password를 받아서 this.authenticationManager.authenticaete()를 사용하여 인증후 객체를 반환한다.
이는 내가 이전에 포스팅 한 내용과 이어진다. 링크
주요 뼈대를 나열하자면
1. 각종 체크(post 같은거도 체크할 수 있음)
2. 어떻게든 정보를 얻어냄 (username, password)
3. 그거로 인증을 거침(this.authenticationManager.authenticate())
4. Authentication 오브젝트나,null 을 반환해준다.
null 반환시 여기선 return을 통해 종료를 시키고 있다.
예시로 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter의 오버라이드 메서드를 가져왔다.
@Override
public Authentication attemptAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws AuthenticationException {
if (this.postOnly && !request.getMethod().equals("POST")) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException("Authentication method not supported: " + request.getMethod());
}
String username = obtainUsername(request);
username = (username != null) ? username.trim() : "";
String password = obtainPassword(request);
password = (password != null) ? password : "";
UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken authRequest = UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.unauthenticated(username,
password);
// Allow subclasses to set the "details" property
setDetails(request, authRequest);
return this.getAuthenticationManager().authenticate(authRequest);
}🔺this.sessionStrategy.onAuthentication();
인증 성공시 세션 인증 실행
successfulAuthentication
필요시 오버라이드
하는일 :
SecurityContext에 Authentication오브젝트 저장,
rememberMeServices.loginSuccess()
InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent 발행
this.successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess 를 통해 리다이렉트
protected void successfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain chain,
Authentication authResult) throws IOException, ServletException {
SecurityContext context = this.securityContextHolderStrategy.createEmptyContext();
context.setAuthentication(authResult);
this.securityContextHolderStrategy.setContext(context);
this.securityContextRepository.saveContext(context, request, response);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug(LogMessage.format("Set SecurityContextHolder to %s", authResult));
}
this.rememberMeServices.loginSuccess(request, response, authResult);
if (this.eventPublisher != null) {
this.eventPublisher.publishEvent(new InteractiveAuthenticationSuccessEvent(authResult, this.getClass()));
}
this.successHandler.onAuthenticationSuccess(request, response, authResult);
}🔺unsuccessfulAuthentication
protected void unsuccessfulAuthentication(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
AuthenticationException failed) throws IOException, ServletException {
this.securityContextHolderStrategy.clearContext();
this.logger.trace("Failed to process authentication request", failed);
this.logger.trace("Cleared SecurityContextHolder");
this.logger.trace("Handling authentication failure");
this.rememberMeServices.loginFail(request, response);
this.failureHandler.onAuthenticationFailure(request, response, failed);
}