💎 방향그래프 응용(사이클 판별)
💍 그래프의 표현 방법
행렬(2차원 배열) 이용하기
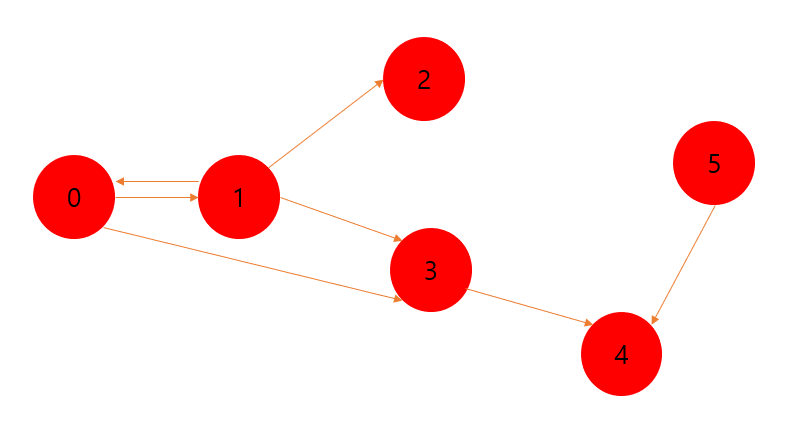
vector<vector<int32> > adjacent = vector<vector<int32> >(
{
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{ 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
});- 메모리 소모가 심하지만, 빠른 접근이 가능하다.
- 정점은 적고, 간선이 많은 경우 이점이 있다.
- 접근 속도를 높이기 위해, 행렬을 사용 할 수도 있다.
💍 DFS
const int32 VERTEX_COUNT = 6;
vector<bool> visited = vector<bool>(VERTEX_COUNT, false); // 각 정점 방문 여부 기록
void Dfs(int32 here)
{
//방문OK
visited[here] = true;
//모든 인접 정점을 순회
for(int32 i=0 ; i < adjacent[here].size(); i++)
{
int32 here = adjacent[here][i];
// 아직 방문한 적이 없다면 방문
if(visited[there] == false)
Dfs(there);
}
}
//위의 코드 만으로는 모든 정점을 방문하지는 못한다. 왜냐? 5번 정점과 같이
//나 자신으로부터 뻗아가는 간선만 있고 5번 정점으로 들어오는 간선이 없기 때문이다.
//모든 정점 방문 함수
void DfsAll()
{
for(int32 here = 0 ; here < adjacent.size() ; here++)
{
if(visited[here] == false)
Dfs(here);
}
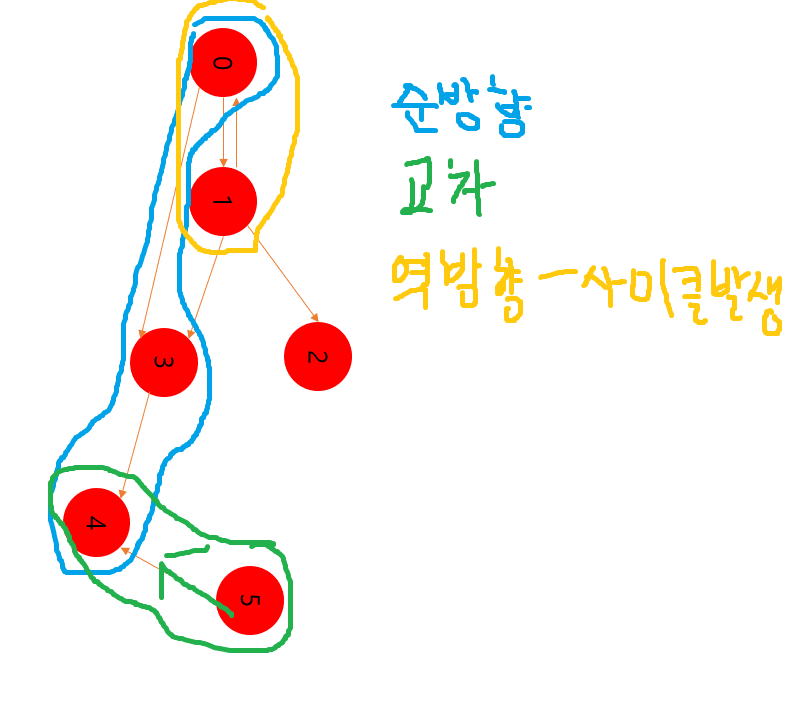
}💍 순방향간선, 교차간선, 역방향 간선
-
순방향 간선이란 0번을 시작이라고 봤을 때,
0 👉 3 👉 4
0 👉 1 👉 3 👉 4
0 👉 1 👉 2
위와 같은 경우들이 있다. -
교차 간선은 위의 0번이 순회를 돌아 방문을 했다고 했을 때,
5번 정점이 DFS를 돌게되어서
5 👉 4 를 돌게 된다. 이렇게 돌게 되면 4번이 0번 순회할때와 5번 순회 할 때 두번 교차하게 되는데 이를 교차간선이라 한다. -
마지막으로 역방향 간선이다.
역방향 간선의 경우는 위의 순방향 순회를 설명하면서 0번 순회를 돌 때 적지 않은 한가지 경우이다.
0 👉 1 👉 0 이 경우이다. 이 경우 사이클이 발생한다. -
방문한 순서를 추적 할 것이다. 방문한 길을 체크하면서 어떤 점이 이미 방문이 됐고, 심지어 먼저 방문이 된 정점이라 한다면 이상한 상황이라고 인지를 한다.
그리고 DFS가 다 끝나서 종결된 시점에서의 점인지 또는 현재 DFS가 진행중인 점인지를 확인한다.
💎 소스
헤더
class DeadLockProfiler
{
public:
void PushLock(const char* name);
void PopLock(const char* name);
void CheckCycle();
private:
void Dfs(int32 index);
private:
// 클래스의 이름과 락번호를 저장하는 사전
unordered_map<const char*, int32> _nameToId;
unordered_map<int32 const char*> _idToName;
//락이 실행되는 것을 스택으로 추적해준다.
stack<int32> _lockStack;
//어떤 락이 몇번 몇번째 락을 잡았는지 역사를 담는다. 간선에 정보를 담는다
map<int32, set<int32>> _lockHistory;
//멀티 쓰레드 환경에서 돌아가게끔 Mutex를 만들어준다.
Mutex _lock;
private:
//사이클 체크를 할 때마다 초기화되는 것들
//사이클을 찾기 위해서는 발견된 순서를 알아야 한다.
//노드가 발견된 순서를 기록하는 배열
vector<int32> _discoveredOrder;
//노드가 발견된 순서를 추적하기 위해 카운팅
int32 _discoveredCount = 0 ;
//Dfs(i)가 종료 됐는지 여부 확인
vector<bool> _finished;
//내가 발견된 순서에 대한 부모님
vector<int32> _parent;
}cpp
void DeadLockProfiler::PushLock(const char* name)
{
//멀티쓰레드 환경에서 돌아가기 위해서 락가드를 잡는다.
LockGuard guard(_lock);
//아이디를 찾거나 발급한다.
int32 lockId = 0;
//아규먼트로 받은 name을 nameToId 에서 찾아서 없는경우에 nameToId에 값을 추가해준다.
auto findlt = _nameToId.find(name);
if(findlt == _nameToId.end())
{
lockId = static_cast<int32>(_nameToId.size());
_nameToId[name] = lockId;
_idToName[lockId] = name;
}
//전에 발급받은 적이 있는 Id라면 단순히 name에 해당하는 LockId 값을 가져온다.
else
{
lockId = findlt->second;
}
//그리고 기존에 잡고 있던 락이 있는 경우 사이클이 발생 할 수도 있기 때문에
//체크해주어야 한다. 기존에 정점에서 간선이 하나 더 생기는 경우
if(_lockStack.empty() == false)
{
//기존에 발견되지 않은 케이스라면 데드락 여부를 확인 해야한다.
//lockStack이 비어있지 않았다면 현재 호출하는 lock은 전에 호출한 lock에서 재귀호출된
//경우 이므로 lockStack top에 있는 값에 history에 현재 호출한 lock을 추가해주어야 한다.
const int32 prevId = _lockStack.top();
if(lockId != prevId)
{
//만약에 history에 현재 lock이 없다면
set<int32>& history = _lockHistory[prevId];
if (history.find(lockId) == history.end())
{
history.insert(lockId);
CheckCycle();
}
}
}
//현재 push하는 락을 lockStack에 추가한다.
_lockStack.push(lockId);
}
void DeadLockProfiler::PopLock(const char* name)
{
LockGuard guard(_lock);
if(_lockStack.empty())
CRASH("MULTIPLE_UNLOCK");
int32 lockId = _nameToId(name);
if(_lockStack.top() != lockId)
CRASH("INVALID_UNLOCK");
_lockStack.pop();
}
void DeadLockProfiler::CheckCycle()
{
//그래프의 정점의 개수에 대한 초기값들을 세팅해준다.
const int32 lockCount = static_cast<int32>(_nameToId.size());
_discoveredOrder = vector<int32>(lockCount, -1);
_discoveredCount = 0;
_finished = vector<bool>(lockCount, false);
_parent = vector<int32>(lockCount, -1);
for(int32 lockId = 0 ;lockId < lockCount ; lockId++)
Dfs(lockId);
//연산이 끝났으면 정리한다.
_discoverdOrder.clear();
_finished.clear();
_parent.clear();
}
void DeadLockProfiler::Dfs(int32 here)
{
//이미 방문 했다면 Order에 대한 값을 넣을 필요가 X
if(_discoveredOrder[here] != -1)
return;
//방문을 하지 않았을 때에 대하여 방문순서 값을 넣어준다.
_discoveredOrder[here] = discoveredCount++;
//모든 인접한 정점을 순회한다.
//lockHistory가 비어있다면 이는 간선이 생성되지 않은 정점이므로 넘어간다.
auto findlt = _lockHistory.find(here);
if (findlt == _lockHistory.end())
{
_finished[here] = true;
return;
}
set<int32>& nextSet = findlt->second;
for(int32 there : nextSet)
{
//아직 방문한 적이 없다면 방문한다.
//이미 방문을 했다면 이미 Dfs가 돌았을 것이기 때문이다.
if(_discoveredOrder[there] == -1)
{
_parent[there] = here;
Dfs(there);
continue;
}
//here가 there보다 먼저 발견됐다면, there는 here의 후손이다. (순방향 간선)
if(_discoveredOrder[here] < _discoveredOrder[there])
continue;
//순방향이 아니고, Dfs(there)가 아직 종료하지 않았다면,
//there는 here의 선조이다. (역방향 간선)
if(_finished[there] == false)
{
printf("%s -> %s\n", _idToName[here], _idToName[there]);
int32 now = here;
while(true)
{
printf("%s -> %s\n", _idToName[_parent[now]], _idToName[now]);
if(now == there)
break;
}
CRASH("DEADLOCK_DETECTED");
}
}
_finished[here] = true;
}