SpringBoot Basic Weekly Mission 2
🔖 소감
데이터 베이스
-
JDBC
백엔드의 시작이자, 꽃이라고 생각하는 영역이다.
맨날 말로만 들어봤는데 실제로 사용해보니 어떤 특성이 있는지 파악할 수 있었다.
과제에서는 NamedParameteredJdbcTemplate을 사용해서 구현했다.
앞으로도 datasource를 직접 만드는 방식보다는 template을 이용해서 만들 것 같다. -
내장 DB
테스트 용으로 사용했다.
wix 라는 내장 DB도 써보고, 도커 열어서 테스트 용 스키마도 만들어보고 했다.
최종적으로 h2 라는 스프링에서 자주 쓰는 내장 DB를 사용하는 것으로 결론 냈다.
mysql 문법에 맞게 작성하고 싶으면 wix 쓰는게 좋긴 한데,
매 테스트 클래스마다 embedded 설정을 하기가 귀찮았다.
가독성도 안 좋은 것 같고..
처음엔 내장 DB가 왜 필요한지도 몰랐다가, 나중에는 이것저것 내가 필요한 설정을 yaml에 추가해서 쓰게됐다.
그 과정까지 얼마나 멘토님과 팀원을 괴롭히고, 구글을 괴롭혔는지 모른다.
올바른 설계
-
클래스로 만들기
진짜 이번 과제하면서 정말 많이 느끼고, 성장한 부분이다.
특히 팀원과 스터디 중인 <내 코드가 그렇게 이상한가요?> 라는 책과 함께 진행한터라, 엄청 배웠다.너무 좋아
간략하게 적어보자면,- 최대한 작은 개념 단위로 클래스를 만들어라
- 확장을 고려해서 클래스를 만들어라
- 클래스로만 이뤄진 프로그램을 만들어라 (원시값 포장 적극 채용)
- 의존 관계를 잘 정립하도록 설계해라
-
유효성 검사 (가드)
클래스로 나누면서 유효성 검사가 가능해진다.
덕분에 응집도는 증가하고, 결합도는 낮아지게 된다.
허구한날 정처기랑 면접준비로 주구장창 외우던 응집, 결합도를 내 손으로 만져보는 과제였다.
진짜 마음에 들었다.
그리고 생성자에 가드를 둠으로써 프로그램 내부 로직에는 부적절한 인스턴스가 아예 발생하지 않는다는 것을 보장해주므로, 아주 편안하고 안정적으로 코딩이 가능했다.
효자템 -
레포지토리 패턴
영속성 레이어를 추상화하라는 거였다.
지금은 jdbc를 사용했고, 지난 과제에서는 파일을 사용했던 것처럼 앞으로 영속성 구현은 계속 늘어날 수 있다.
그래서 추상화를 통해 전체 프로그램의 유연성을 보장하라는 거였다.
난 또 괜히 쫄아서 인터페이스 안 쓰고 덤비다가 큰 코 다칠 뻔. -
정적 팩토리 패턴
이번 과제는 static 메소드와의 전쟁이라고 해도 과언이 아니었다.
결국엔 클래스를 나누고, 의존성을 정리하면서 자연스럽게 해결되는 문제였다.
바꿔 말하면 static 같이 응집도를 낮추고, 결합도를 늘리는 코드를 계속 제거하면서 프로그램을 좀더 클린하게 만들 수 있었다.
이유야 많이 찾아봤지만, static 자체를 지양하는 편이 훗날의 내가 편하다는게 내 결론이다.
보안
- jasypt
피드백으로 이런게 있다고 해서 찾아본건데, 보안이 중요하긴 하더라.
관련 글에서 어떤 팀이 AWS 요금이 3천만원 청구됐다는 썰을 들었는데, 암호키를 public으로 github에 올린게 원인이 된 모양이다.
나도 크건 작건 암튼 비밀번호는 무조건 감춰야 된다는 생각이 들었다.
저번 과제에서 gitignore 사용법에 대해서 배웠으니, 이걸 활용해서 앞으로도 민감정보를 따로 관리하며 커밋에서 제외하는 방식으로 진행해보려고 한다.
테스트
이놈의 테스트는 아마 올해가 끝나기 전까지 나를 괴롭힐거다.
이것 때문에 몇 시간을 날렸고, 몇 시간을 고민했는지 모른다.
그리고 다시 한 번 느낀게, 테스트를 먼저 작성해야 한다.
괜시리 로직 먼저 작성했다가 테스트가 불편하거나 안 되서 몇 번을 수정했는지 모른다.
진짜 테스트 먼저 작성해야 한다.
아 그리고, 어느정도 테스트 컨벤션이 정리되고 나니까 효자긴 효자더라.
로직이 바뀌거나 기능이 추가되었는데도 이미 만들어둔 단위 테스트 한 번 쫙 돌리면 영향이나 버그를 몇 초 안에 확인 가능하니, 효자긴 함.
📌 과제 설명
흐름도
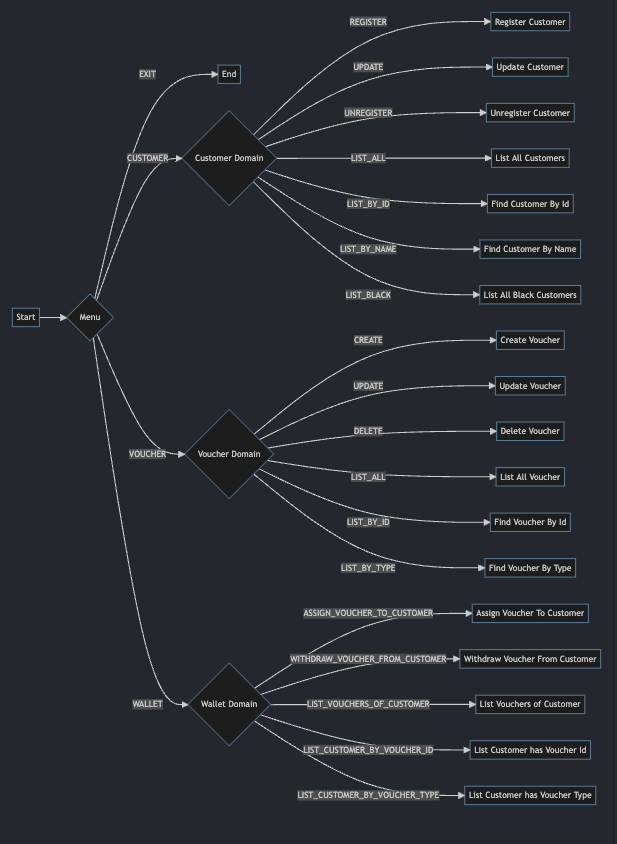
클래스 다이어그램
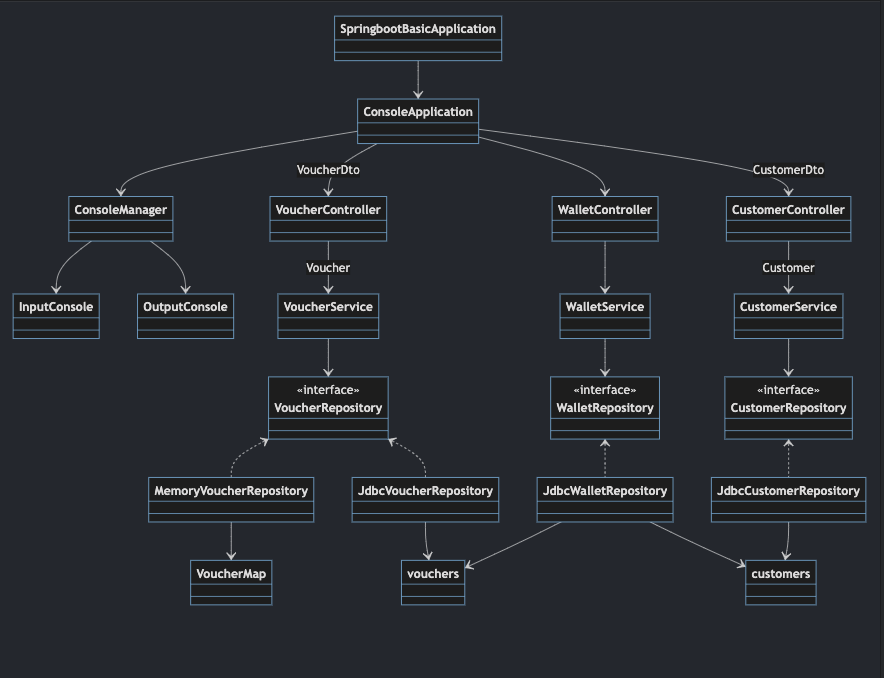
✅ PR 포인트 & 궁금한 점
- Wallet 기능
- 따로 Wallet 테이블을 만들지 않고, vouchers 테이블에 customer_id를 외래키로 받아 사용했습니다.
- 이 과정에서 customer_id를 Optional로 처리했는데, 안정적으로 사용했는지 확인 부탁드립니다.
- try - catch
- 예외가 발생한 부분에서 catch를 하는 것 vs. 서비스 로직에서 catch를 하는 것
- 둘 중에 어떤 방식이 더 나은지 궁금합니다.
- 테스트용 DB
- 과제를 하면서 wix, h2, mysql 를 한 번씩 모두 사용해봤습니다.
- 각자 장단점이 있는것 같은데, 주로 어떤 걸 사용하는지 궁금합니다.
- Mocking 테스트
- controller에서는 로직에서 얻어지는 데이터를 넘겨주고 받는 역할을 수행하도록 구현했습니다.
- 해당 부분까지 빈을 주입받아 테스트하면 first 속성에 위반하는 것 같아, mock 테스트를 수행했습니다.
👩💻 요구 사항과 구현 내용
- 테스트
- Customer
- Voucher
- Wallet
✅ 피드백 반영사항
📮 1차 피드백
유효성 검사-
Null 방어
if (name == null || name.isBlank()) { throw new InvalidDataException(ErrorMessage.INVALID_PROPERTY.getMessageText()); } -
유효 조건을 메소드로 분리
public static CommandMenu getCommandMenu(String menuString) { return Arrays.stream(CommandMenu.values()) .filter(commandMenu -> isMatched(menuString, commandMenu)) .findAny() .orElseThrow(() -> new InvalidDataException(ErrorMessage.INVALID_MENU.getMessageText())); } private static boolean isMatched(String menuString, CommandMenu commandMenu) { boolean isMatchedName = Objects.equals(menuString, commandMenu.name()); boolean isMatchedOrdinal = Objects.equals(menuString, String.valueOf(commandMenu.ordinal())); return isMatchedName || isMatchedOrdinal; }
- 장점
- 객체 생성 관리 이점 → 팩토리 메소드를 통해 쉽게 객체 생성 가능
- 대신 생성자는 private 이어야 함
- 간단한 메소드 이름
- 구현부분에 대한 정보은닉
- 단점
- 상속 통한 기능확장 불가
- static 키워드 자체의 응집도 이슈
- 범용 클래스인 경우 private 생성자 사용하기
- 영속성 변경에 안정성 부여
- 쉽게 말해서 repository를 인터페이스로 구현해서 사용
- 지양할 곳 (내 의견임)
- 테스트코드
- 프론트엔드가 볼 수 있는 컨트롤러
- 핵심 비즈니스 로직
- 여러 군데에서 활용하는 범용 클래스
-
jasypt 모듈
-
build 종속성
implementation 'com.github.ulisesbocchio:jasypt-spring-boot-starter:3.0.4' -
설정 클래스
@Configuration @EnableEncryptableProperties public class JasyptConfiguration { @Value("${jasypt.encryptor.algorithm}") private String algorithm; @Value("${jasypt.encryptor.pool-size}") private int poolSize; @Value("${jasypt.encryptor.string-output-type}") private String stringOutputType; @Value("${jasypt.encryptor.key-obtention-iterations}") private int keyObtentionIterations; @Bean public StringEncryptor jasyptStringEncryptor() { PooledPBEStringEncryptor encryptor = new PooledPBEStringEncryptor(); SimpleStringPBEConfig configuration = new SimpleStringPBEConfig(); configuration.setAlgorithm(algorithm); configuration.setPoolSize(poolSize); configuration.setStringOutputType(stringOutputType); configuration.setKeyObtentionIterations(keyObtentionIterations); configuration.setPassword(getJasyptEncryptorPassword()); encryptor.setConfig(configuration); return encryptor; } private String getJasyptEncryptorPassword() { try { ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("src/main/resources/jasypt-encryptor-password.txt"); return String.join("", Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(resource.getPath()))); } catch (IOException e) { throw new InvalidDataException(ErrorMessage.INVALID_FILE_ACCESS.getMessageText(), e.getCause()); } } } -
테스트 클래스
class JasyptConfigurationTest { @Test void jasypt() { String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:/"; String username = ""; String password = "!"; String encryptUrl = jasyptEncrypt(url); String encryptUsername = jasyptEncrypt(username); String encryptPassword = jasyptEncrypt(password); System.out.println("encrypt url : " + encryptUrl); System.out.println("encrypt username: " + encryptUsername); System.out.println("encrypt password: " + encryptPassword); assertThat(url).isEqualTo(jasyptDecrypt(encryptUrl)); } private String jasyptEncrypt(String input) { String key = "!"; StandardPBEStringEncryptor encryptor = new StandardPBEStringEncryptor(); encryptor.setAlgorithm("PBEWithMD5AndDES"); encryptor.setPassword(key); return encryptor.encrypt(input); } private String jasyptDecrypt(String input) { String key = "!"; StandardPBEStringEncryptor encryptor = new StandardPBEStringEncryptor(); encryptor.setAlgorithm("PBEWithMD5AndDES"); encryptor.setPassword(key); return encryptor.decrypt(input); } } -
yaml 파일
jasypt: encryptor: algorithm: PBEWithMD5AndDES bean: jasyptStringEncryptor pool-size: 2 string-output-type: base64 key-obtention-iterations: 100 spring: datasource: url: ENC(암호화된 url 스트링) username: ENC(암호화된 유저이름) password: ENC(암호화된 패스워드) driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
- 컨벤션
- given - when - then
- FIRST 속성
- @JdbcTest
- Jdbc 관련된 빈 만 컴포넌트 스캔 → DataSourse 같은거 주입해줌
- 대신 내가 만든 컴포넌트는 주입 안 해줌 → Import 로 따로 해줘야 함
- all(*) 키워드 지양
- 원하는 컬럼을 직접 지정해서 얻어오셈
- count 함수는 필요한 경우만, 아니면 where 조건이 있는 경우만
📮 2차 피드백
확장을 고려한 구조 선택- 등록과 수정에 같은 dto 사용 -> 추후 더 필요할 것으로 보임
- CreateRequest, UpdateRequest 등
- Customer 상태를 boolean으로 판단
- 추후 상태가 늘어날 것을 대비해 enum으로 관리하면 좋음
- 기본 자료형을 그대로 사용하려고 하지 말고, 프로그램을 클래스의 모음으로 구성하면 유지보수 용이
- String name; -> Name name;
- 필드가 많은 설정 클래스에서는 @Value 보다는 @ConfigurationProperties
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties("jasypt.encryptor")
@EnableEncryptableProperties
public class JasyptConfiguration {
private String algorithm;
private int poolSize;
private String stringOutputType;
private int keyObtentionIterations;
@Bean("jasyptStringEncryptor")
public StringEncryptor jasyptStringEncryptor() {
PooledPBEStringEncryptor encryptor = new PooledPBEStringEncryptor();
SimpleStringPBEConfig configuration = new SimpleStringPBEConfig();
configuration.setAlgorithm(algorithm);
configuration.setPoolSize(poolSize);
configuration.setStringOutputType(stringOutputType);
configuration.setKeyObtentionIterations(keyObtentionIterations);
configuration.setPassword(getJasyptEncryptorPassword());
encryptor.setConfig(configuration);
return encryptor;
}
private String getJasyptEncryptorPassword() {
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("src/main/resources/jasypt-encryptor-password.txt");
return String.join("", Files.readAllLines(Paths.get(resource.getPath())));
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new InvalidDataException(ErrorMessage.INVALID_FILE_ACCESS.getMessageText(), e.getCause());
}
}
public String getAlgorithm() {
return algorithm;
}
public int getPoolSize() {
return poolSize;
}
public String getStringOutputType() {
return stringOutputType;
}
public int getKeyObtentionIterations() {
return keyObtentionIterations;
}
public void setAlgorithm(String algorithm) {
this.algorithm = algorithm;
}
public void setPoolSize(int poolSize) {
this.poolSize = poolSize;
}
public void setStringOutputType(String stringOutputType) {
this.stringOutputType = stringOutputType;
}
public void setKeyObtentionIterations(int keyObtentionIterations) {
this.keyObtentionIterations = keyObtentionIterations;
}
}- 메소드 호출 테스트는 verify
- verify() 메소드로 특정 메소드가 호출되었는지를 증명(테스트)
- void 메소드 테스트에 찰떡! 우와!
- 테스트 코드에 추가 로직 금지!
- 조건문 같은 암튼 로직은 다 안 됨.
- 필요하다면 테스트 메소드를 쪼개자
- Optional은 직렬화 안 됨.
- 필드로 쓰면 안 됨.
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:test;MODE=MySQL
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
username: test
password: test1234!
h2:
console.enabled: true
sql:
init:
mode: always
schema-locations: classpath:schema/schema.sql📮 3차 피드백
ERD 수정- 기존 ERD
- vouchers(voucher_id, voucher_type, discount_value, created_at, customer_id)
- customers(customer_id, name, black)
- 이렇게 둘 만 있고, vouchers 에 fk(customer_id) 로 지갑 기능을 구현
- 변경 ERD
- vouchers(voucher_id, voucher_type, discount_value, created_at)
- customers(customer_id, name, black)
- wallets(wallet_id, voucher_id, customer_id)
- 이렇게 새로 지갑 테이블을 만들어서 확장 대비
- 테스트 코드에서만 사용하는 함수는 어떻게 처리할까?
- 로직 코드에 넣어두지 말고, 테스트 클래스 내에서 해당 기능 클래스를 새로 생성
- 빈을 주입받는 방식으로 실행
