1260 DFS와 BFS
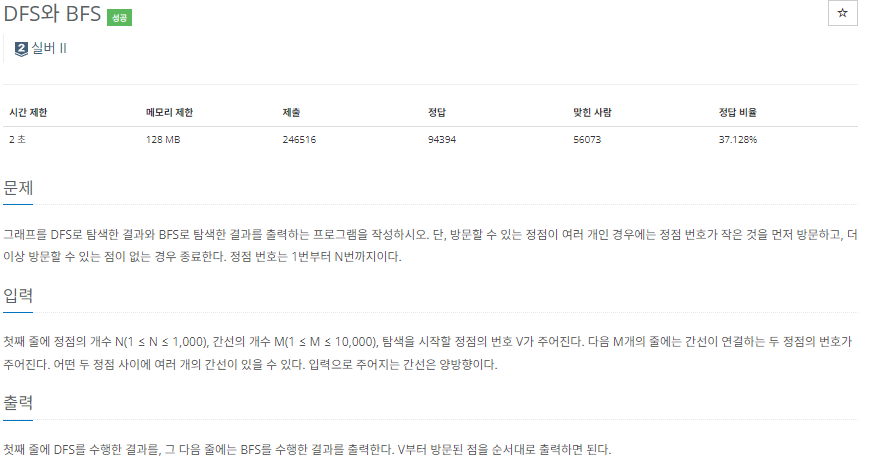
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<bool>> adj;
vector<bool> visit;
vector<int> dfso, bfso;
int N, M, V;
void dfs(int here) {
visit[here] = 1;
dfso.emplace_back(here);
for (int i = 1; i < N + 1; i++) {
if (adj[here][i] && !visit[i]) dfs(i);
}
}
void bfs(int here) {
queue<int> q;
visit[here] = 1;
q.push(here);
while (!q.empty()) {
int now = q.front();
bfso.emplace_back(now);
q.pop();
for (int i = 1; i < N + 1; i++) {
if (adj[now][i] && !visit[i]) {
q.push(i);
visit[i] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M >> V;
adj = vector<vector<bool>>(N + 1, vector<bool>(N + 1, 0));
int a, b;
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
cin >> a >> b;
adj[a][b] = 1;
adj[b][a] = 1;
}
visit = vector<bool>(N + 1, 0);
dfs(V);
visit.clear();
visit = vector<bool>(N + 1, 0);
bfs(V);
for (int i : dfso) {
cout << i << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
for (int i : bfso) {
cout << i << " ";
}
}인접 리스트로 푸는게 메모리랑 시간 덜 쓸듯🤨
2178 미로 탐색
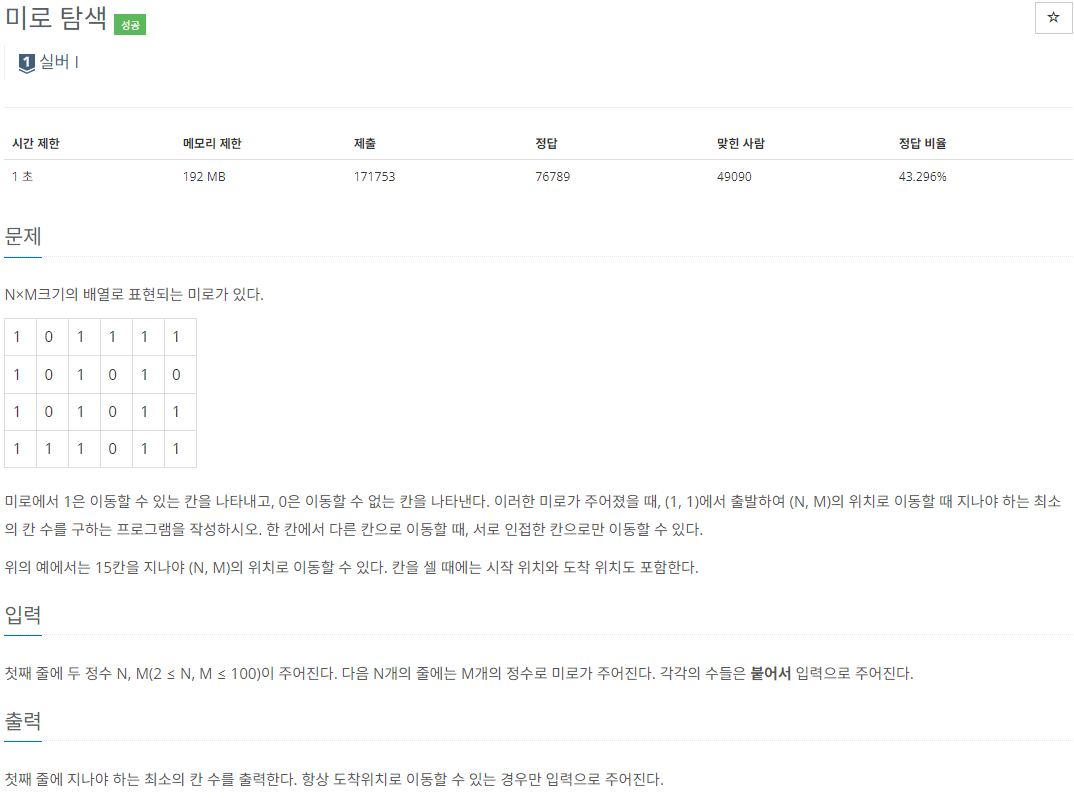
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int N, M;
vector<vector<int>> grid, visit, dis;
int dy[4] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int dx[4] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
void bfs(int x, int y) {
visit[x][y] = 1;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push(pair<int, int>(x, y));
dis[x][y] = 1;
while (!q.empty()) {
int nowx = q.front().first;
int nowy = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = nowx + dx[i];
int nexty = nowy + dy[i];
if (nextx >= 0 && nextx < N && nexty >= 0 && nexty < M) {
if (grid[nextx][nexty] && !visit[nextx][nexty]) {
q.push(pair<int, int>(nextx, nexty));
visit[nextx][nexty] = 1;
dis[nextx][nexty] = dis[nowx][nowy] + 1;
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> N >> M;
grid = vector<vector<int>>(N, vector<int>(M, 0));
visit = vector<vector<int>>(N, vector<int>(M, 0));
dis = vector<vector<int>>(N, vector<int>(M, 0));
char c;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
cin >> c;
grid[i][j] = c - '0';
}
}
bfs(0, 0);
cout << dis[N - 1][M - 1];
}📍 거리 구하는건 모든 정점의 최단 거리를 구해서 저장한 뒤 답만 출력
7576 토마토
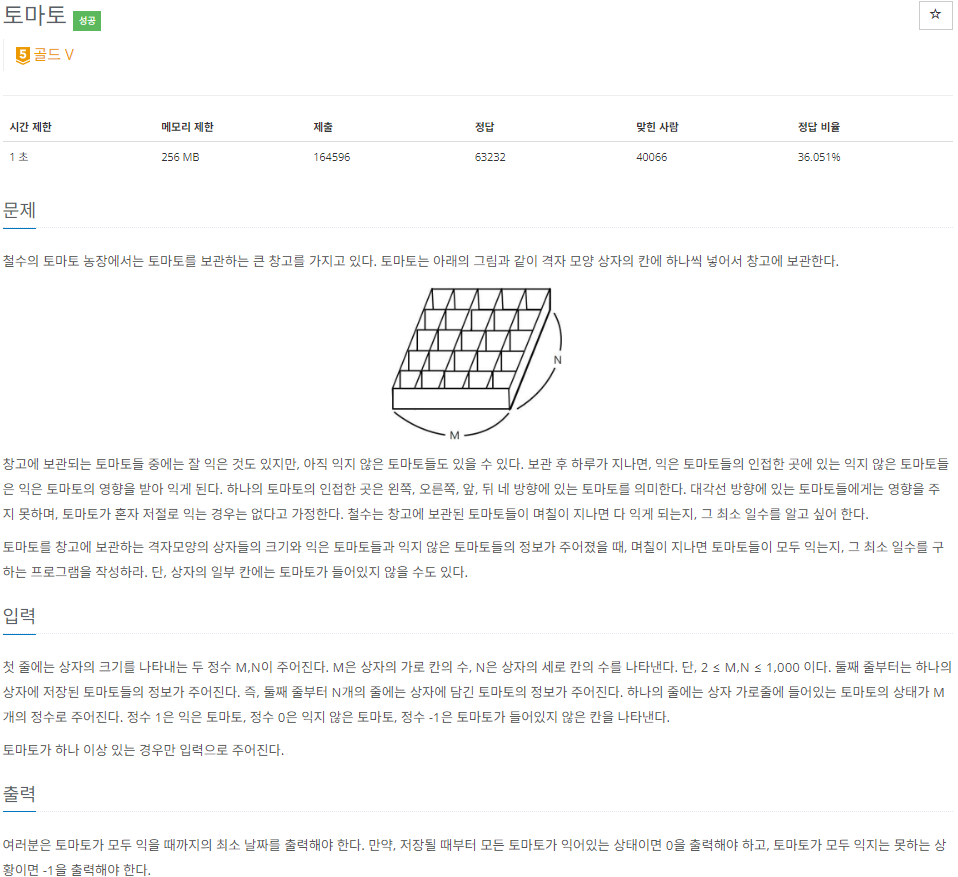
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int N, M;
vector<vector<int>> grid, visit;
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
int dx[4] = { 1, -1, 0, 0 };
int dy[4] = { 0, 0, 1, -1 };
void bfs() {
while (!q.empty()) {
int nowx = q.front().first;
int nowy = q.front().second;
visit[nowx][nowy] = 1;
q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextx = nowx + dx[i];
int nexty = nowy + dy[i];
if (nextx >= 0 && nextx < N && nexty >= 0 && nexty < M) {
if (!visit[nextx][nexty] && grid[nextx][nexty] == 0) {
q.push(pair<int, int>(nextx, nexty));
grid[nextx][nexty] = grid[nowx][nowy] + 1;
visit[nextx][nexty] = 1;
}
}
}
}
}
int main() {
cin >> M >> N;
grid = vector<vector<int>>(N, vector<int>(M, 0));
visit = vector<vector<int>>(N, vector<int>(M, 0));
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
cin >> grid[i][j];
if (grid[i][j] == 1) {
q.push(pair<int, int>(i, j));
}
}
}
bfs();
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == 0) {
max = -1;
break;
}
else max = max < grid[i][j] ? grid[i][j] : max;
}
if (max == -1) break;
}
cout << (max == -1 ? max : max - 1);
}입력 시점에서 1을 입력받았을 때 큐(queue)에 좌표를 push하면 1에서부터 퍼져나갈(?) 수 있다. grid에서 +1씩 해주고.. 마지막에는 grid에서의 최댓값을 출력하면 된다. grid에 0이 남아있는 경우 -1을 출력
