1. Divide and Conquer란?
Divide and Conquer (분할 정복)는 문제 해결 전략 중 하나로, 다음의 세 가지 단계로 구성됩니다:
- Divide (분할) : 문제를 동일한 유형의 더 작은 하위 문제들로 나눈다.
- Conquer (정복) : 하위 문제들을 재귀적으로 해결한다.
- Combine (결합) : 하위 문제들의 해를 적절하게 결합하여 원래 문제의 해를 구한다.
2. 재귀(Recursive) 방식
- 재귀적인 방법은 Divide and Conquer와 밀접한 관련이 있음.
- 큰 문제를 더 작은 문제로 나눠서 해결하고, 그 해답을 이용해 큰 문제를 푸는 방식.
- 비재귀적(non-recursive) 방법이 더 빠를 수도 있음. 예: 동적 계획법(Dynamic Programming)
3. 예제: Merge Sort
- Merge Sort는 Divide and Conquer를 대표하는 알고리즘입니다.
- 단계별 정리:
1) 숫자 리스트를 계속 절반씩 분할 (Divide)
2) 각 부분을 정렬하며 병합 (Conquer + Combine)
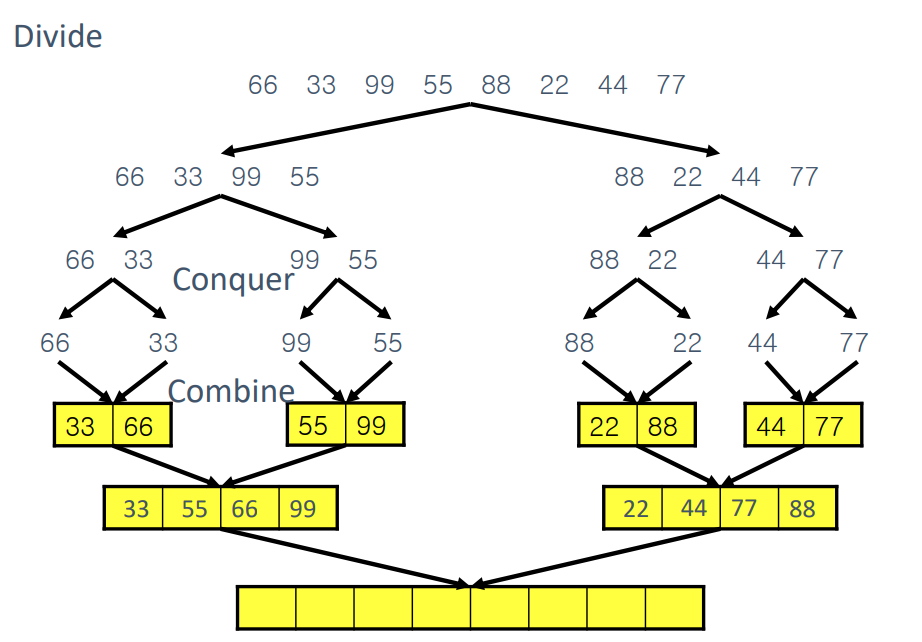
예시 문제 1) Merge Sort
public class MergeSort {
// 메인 정렬 함수
public static void mergeSort(int[] arr, int left, int right) {
if (left < right) {
// 배열을 둘로 나누기
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
// 왼쪽 절반 정렬
mergeSort(arr, left, mid);
// 오른쪽 절반 정렬
mergeSort(arr, mid + 1, right);
// 병합
merge(arr, left, mid, right);
}
}
// 병합 함수: 정렬된 두 배열을 하나로 병합
public static void merge(int[] arr, int left, int mid, int right) {
// 크기 계산
int n1 = mid - left + 1;
int n2 = right - mid;
// 임시 배열 생성
int[] L = new int[n1];
int[] R = new int[n2];
// 데이터 복사
for (int i = 0; i < n1; i++)
L[i] = arr[left + i];
for (int j = 0; j < n2; j++)
R[j] = arr[mid + 1 + j];
// 병합 과정
int i = 0, j = 0, k = left;
while (i < n1 && j < n2) {
if (L[i] <= R[j]) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
} else {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
}
k++;
}
// 남은 요소 복사
while (i < n1) {
arr[k] = L[i];
i++;
k++;
}
while (j < n2) {
arr[k] = R[j];
j++;
k++;
}
}
// 테스트
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 38, 27, 43, 3, 9, 82, 10 };
mergeSort(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);
// 출력
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
}
예시 문제 2)
Problem Description
Given an integer, implement an algorithm using the divide and conquer approach with the following rules:
-
If the number of digits is 1, return the digit.
-
If the number of digits is 2, return the product of the two digits.
-
If the number of digits is even (2n), split into two halves, solve each recursively, and multiply the results.
-
If the number of digits is odd (2n+1), split into two halves around the middle digit, solve each recursively, multiply the results, and add the middle digit.
API
public int processDigits(String num)
input: A single integer with up to 100,000 digits.
output: A single integer results computed using the described process.
constraints:
-
Input integer contains only digits (0-9).
-
No leading zeros except when the number is 0.
Main method for Test
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Itm itm = new Itm();
System.out.println("24: "+(itm.processDigits("1234")==24?24:-1)); // Output: 24
System.out.println("43: "+(itm.processDigits("12345")==43?43:-1)); // Output: 43
}
}Solution
public class Itm {
public int processDigits(String s) {
int num = Integer.parseInt(s);
int len = s.length();
if (len == 1) {
return num;
} else if (len == 2) {
return (num%10) * (num/10);
}
if (num % 2 == 0) {
String left = s.substring(0, len/2);
String right = s.substring(len/2);
return processDigits(left) * processDigits(right);
} else {
String left = s.substring(0, len/2);
int mid = Integer.parseInt(s.substring(len/2, len/2 + 1));
String right = s.substring(len/2 + 1);
return processDigits(left) * processDigits(right) + mid;
}
}
}