문제
Sometimes it's better to use dynamic size arrays. Java's Arraylist can provide you this feature. Try to solve this problem using Arraylist.
You are given lines. In each line there are zero or more integers. You need to answer a few queries where you need to tell the number located in position of line.
Take your input from System.in.
Input Format
The first line has an integer . In each of the next lines there will be an integer denoting number of integers on that line and then there will be space-separated integers. In the next line there will be an integer denoting number of queries. Each query will consist of two integers and .
Constraints
Each number will fit in signed integer.
Total number of integers in lines will not cross .
Output Format
In each line, output the number located in position of line. If there is no such position, just print "ERROR!"
Sample Input
5
5 41 77 74 22 44
1 12
4 37 34 36 52
0
3 20 22 33
5
1 3
3 4
3 1
4 3
5 5Sample Output
74
52
37
ERROR!
ERROR!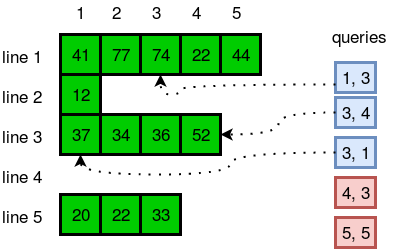
첫번째 시도 : Compile Error
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* Enter your code here. Read input from STDIN. Print output to STDOUT. Your class should be named Solution. */
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
ArrayList<Integer>[] arr = new ArrayList[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
String[] input = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
arr[i] = new ArrayList[Integer.parseInt(input[0])];
for(int j = 1; j < input.length; j++) {
arr[i].add(input[j]);
}
}
int d = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i < d; i++){
String[] input = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
int x = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
try {
String answer = arr[x].get(y);
System.out.println(answer);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ERROR!");
}
}
}
}문제 원인 및 해결 방법
1. ArrayList[] arr = new ArrayList[n]; 선언 문제
- Java에서는 제네릭 배열을 직접 생성할 수 없습니다.
- 해결 방법: ArrayList[] arr = new ArrayList[n];로 선언한 뒤, 각 인덱스에 new ArrayList()를 할당해야 합니다.
- sc.nextLine()을 통한 입력 처리 문제
- sc.nextInt()를 사용한 후 sc.nextLine()을 호출하지 않으면 nextInt() 뒤에 남은 개행 문자(\n)가 다음 nextLine()에서 읽혀서 의도한 입력이 제대로 처리되지 않습니다.
- 해결 방법:n = sc.nextInt(); 다음에 sc.nextLine();을 추가해 개행 문자를 처리해야 합니다.
- arr[i] = new ArrayList[Integer.parseInt(input[0])]; 문제
- 위 코드는 잘못된 배열 선언이며, new ArrayList[Integer.parseInt(input[0])]는 ArrayList 객체를 생성하는 것이 아니라 배열을 생성하려는 코드로 잘못되었습니다.
- 해결 방법: 단순히 arr[i] = new ArrayList<>();로 선언하면 됩니다.
- arr[i].add(input[j]); 문제
- input[j]는 String인데, arr[i]는 ArrayList입니다. 따라서 Integer.parseInt(input[j])로 변환해야 합니다.
- 해결 방법: arr[i].add(Integer.parseInt(input[j]));로 수정합니다.
- arr[x].get(y)을 가져올 때 예외 처리 문제
- arr[x]가 존재하는지, 그리고 arr[x].get(y)이 존재하는지 확인 없이 접근하면 ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException이 발생할 수 있습니다.
- 해결 방법: x와 y가 arr의 범위를 벗어나지 않는지 체크한 후 값을 가져오도록 수정합니다.
두번째 시도 : Success
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Solution {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* Enter your code here. Read input from STDIN. Print output to STDOUT. Your class should be named Solution. */
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
ArrayList<Integer>[] arr = new ArrayList[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
String[] input = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
arr[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int j = 1; j < input.length; j++) {
arr[i].add(Integer.parseInt(input[j]));
}
}
int d = Integer.parseInt(sc.nextLine());
for(int i=0; i < d; i++){
String[] input = sc.nextLine().split(" ");
int x = Integer.parseInt(input[0]);
int y = Integer.parseInt(input[1]);
try {
int answer = arr[x-1].get(y-1);
System.out.println(answer);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("ERROR!");
}
}
}
}알아야할 개념
- ArrayList 선언 방법 : ArrayList<>[] arr = new ArrayList[];
- 2중 ArrayList : arr[i] = new ArrayList<>();
- ArrayList 요소 추가 방법 : .add(n)
- ArrayList 요소 조회 방법 : .get(idx)
- ArrayList 의 제네릭으로 타입을 명시를 안하면 추후에 추가하거나 조회시 타입 에러 발생할 수 있다.

