문제
You are given the pointer to the head node of a linked list and an integer to add to the list. Create a new node with the given integer. Insert this node at the tail of the linked list and return the head node of the linked list formed after inserting this new node. The given head pointer may be null, meaning that the initial list is empty.
Function Description
Complete the insertNodeAtTail function with the following parameters:
- SinglyLinkedList pointer head : a reference to the head of a list
- int data : the data value for the node to insert
Returns
SinglyLinkedList pointer : reference to the head of the modified linked list
Input Format
The first line contains an integer n, the number of elements in the linked list.
The next n lines contain an integer each, the value that needs to be inserted at tail.
Constraints
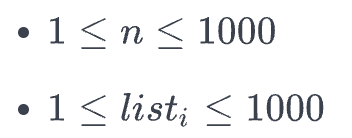
Sample Input
STDIN Function
----- --------
5 size of linked list n = 5
141 linked list data values 141..474
302
164
530
474Sample Output
141
302
164
530
474Explanation
First the linked list is NULL. After inserting 141, the list is 141 -> NULL.
After inserting 302, the list is 141 -> 302 -> NULL.
After inserting 164, the list is 141 -> 302 -> 164 -> NULL.
After inserting 530, the list is 141 -> 302 -> 164 -> 530 -> NULL. After inserting 474, the list is 141 -> 302 -> 164 -> 530 -> 474 -> NULL, which is the final list.
첫번째 시도 : Success
static SinglyLinkedListNode insertNodeAtTail(SinglyLinkedListNode head, int data) {
if(head == null) {
SinglyLinkedListNode newNode = new SinglyLinkedListNode(data);
return newNode;
}
SinglyLinkedListNode beforeHead = head;
SinglyLinkedListNode newNode = new SinglyLinkedListNode(data);
while (head.next != null) {
head = head.next;
}
head.next = newNode;
return beforeHead;
}로직
- 가장 처음 노드인 경우에는 새로 생성해주기
- 이후에 들어오는 노드인 경우에는 기존 head를 따로 저장해두고, tail로 가서 next를 새로 생성한 노드로 지정해주기

