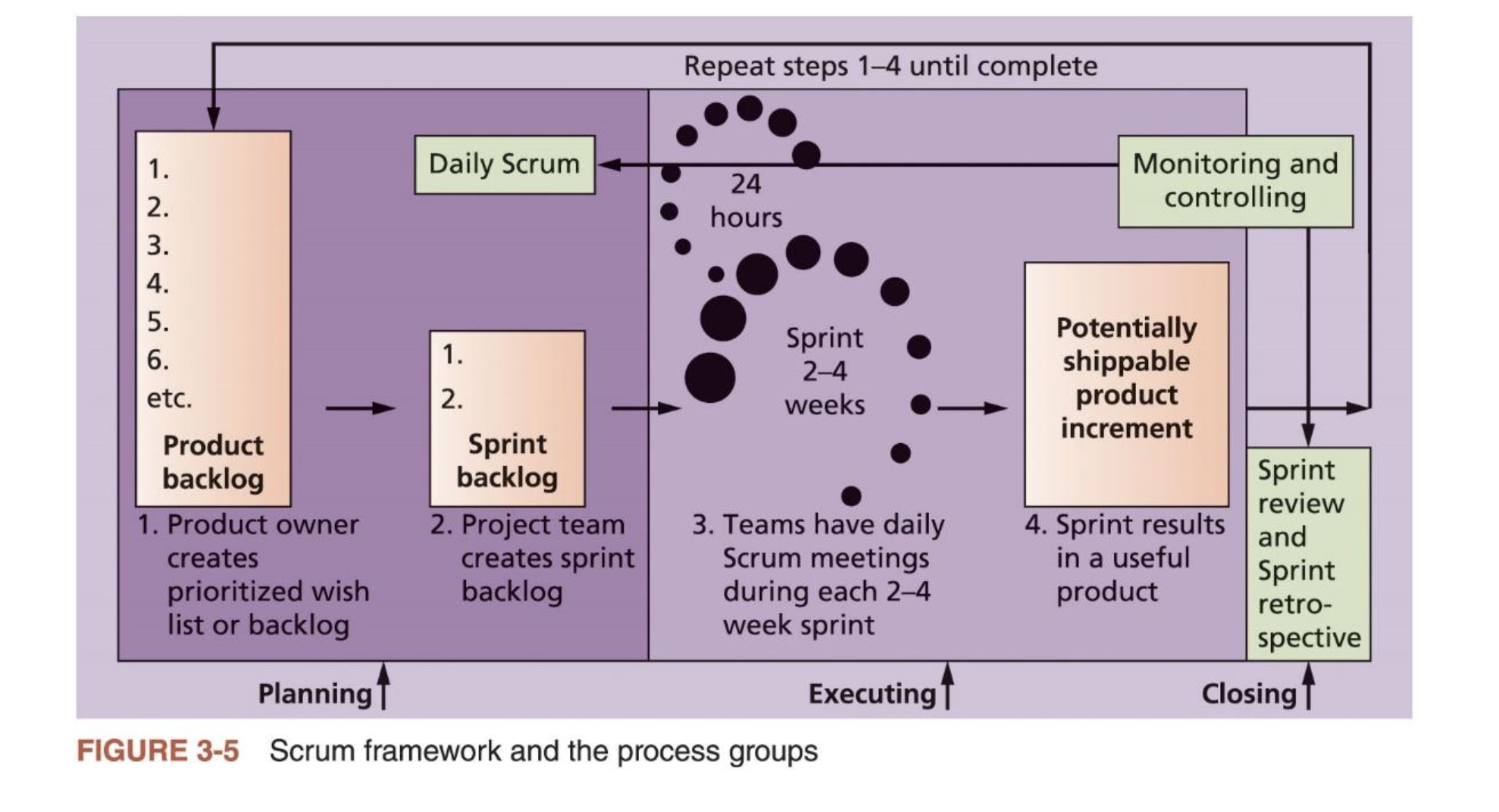
ITPM - 03. Project Management Process Groups
5 Project management process groups
- Initiaing, Planning, Executing, Monitoring/Controlling, Closing
~ A process is a series of actions directed toward a particular result
- Spending more time on planning should pay off in execution
Project Pre-Initiation and Project Initiation
- Include recognizing and starting a new project
- need projects for the right reasons
프로젝트를 인식하고 시작하는 과정 / 왜 이 프로젝트를 해야하는지 근거 필요
Pre-initiatin Tasks
- Determining the scope, time, cost constraints
- Identify the project sponsor
- Selecting the project manager
- Developing a business case
- Meeting with the project manager to review the process and expectations for managing the project
- Determining if the project should be divided
Business Case
- Business cases provide the concrete reasons why we should start a new project
Initiating
There are two main activities
- Project Integration Management - Develop project charter
- Project Stakeholder Management - Identify Stackholders
- Determine roles
- Decide how many sprints / how many releases of sw to deliver
Kick-off meeting
Stackeholders can
1) meet each other,
2) review the goals of the project and,
3) discuss future plans
Stackeholder Managment Strategy
for gaining support or reducing obstacles from each stakeholder.
Project Planning
The main purpose is to guide execution
- Create product backlog
- Create sprint backlog
- Plan work each day in the daily scrum
- Document stumbling blocks in a list (걸림돌 분석)
~ Scrum implies that team members work as a self-directed group, coached by the ScrumMaster, a team charter should not be necessary. (스크럼에서는 팀원들이 스스로 움직이는 자율적인 그룹으로 일하는 것을 전제로 하기 때문에, ScrumMaster가 코치 역할을 하지만, 따로 팀tea charter는 필요하지 않다.)
~ Descriptions of word -> product and sprint backlogs
~ More detailed word -> technical stories -> technical tasks
Project Execution
- this stage takes the most resources to perform.
- PM must use their leadership skills to handle the many challenges
- Many project sponsors and customers focus on deliverables
- It is important to document change requests and update planning documents
- Complete tasks each day during sprints
- Produce a shippable product at the end of each sprint
Project Monitoring and Controlling
- Involves measuring progress toward project objectives, monitoring deviation from the plan, and taking correction actions
- 진척도 측정 / 계획 이탈 감지 / 수정 조치 실행
- affects all other process groups and occurs during all phases of the project life cycle
- Resolve issues and blockers
- Create and update burndown chart
- Demonstrate the completed product during the sprint review meeting
~ Daily Scrum
~ Sprint Review : Project Owner한테 demonstrates 해야함 -> update the product backlog and start next sprint cycle
~ Removing Obstacles : main job duties of the ScrumMaster
~ Burndown chart : not matter how many hours have been spent; what matters is how many hours of word remain
Project Closing
- Gaining acceptance of the final products and services
- Even if projects are not completed successfully, they should be closed out to learn from the past
- Reflect on how to improve the product and process during the sprint retrospective meeting
Outputs
1) Project files
2) Lessons-learned reports
3) Final reports
4) Smooth transition into the normal operation (운영 인수인계 문서)
- Agile Approach에서 closing
After the sprint review, the ScrumMaster leads a sprint retrospective:
- Team reflects on what happened during the sprint
- similar to a lessons-learned report, but it focurses on a shorter period of time.
~ Sprint retrospective
- What went well during the last sprint that we should continue doing?
- what could we do differentlu to improve the product or process?
Agile Approach
Predictive approach VS Agile approach
Agile Approach가 적합한 경우
1) the business team cannot clearly express the scope early in the product life cycle (고객이 처음부터 요구사항을 명확히 정의하기 어려운 경우)
2) the team wants to provide a potentially shippable product earlier rather than later (빠른 배포가 중요)
🔹 less rigid constraints
🔹 experienced and preferably co-located teams
🔹 smaller risks
🔹 unclear requirements
🔹 more flexible scheduling
Predictive Approach가 적합한 경우
🔹 heavy constraints
🔹 inexperienced and dispersed teams
🔹 large risks
🔹 generally clear up-front requirements
🔹 fairly rigid completion date
Scrum Roles
- Product owner : person responsible for the business value of the project / deciding what work to do
- Scrum Master : person who ensures that the team is productive, facilitates daily scrum, enables close cooperation across all toles and function removes barriers that prevent the team
- Scrum team or development team : 5-9 people , 2-4 weeks
--
Scrum Artifacts (스크럼 산출물)
- Product Backlog : list of features prioritized by business value (비즈니스 가치 기준으로 우선순위)
- Sprint Backlog : Product Backlog 에서 상위 우선순위 항목을 뽑아서 구성
- Burndown chart : 남은 작업량 그래프
Scrum Ceremonies
-
Sprint Planning (스프린트 계획 회의)
: to select a set of work from the product backlog (스프린트 동안 어떤 작어을 할지 정하는 회의) -
Daily Scrum
: Short meeting for the development team to share progress and challenges and plan work for the day
- Issues : 24시간 내 해결하지 않아도 되는 항목
- Blockers : 즉시 해결 필요한 항목
-
Sprint Review
: Meeting in which the team demonstrates to the product owner what it has completed during the sprint (PO에게 스프린트 동안 완료된 결과물 시연) -
Sprint Retrospective (스프린트 회고)
: the team looks for ways to improve the product and the process based on a review of the actual performance of the development team (팀의 일하는 방식 되돌아보기)