1. 객체
객체(instance)는 '클래스'라는 틀을 통해 만들어낸 실체를 말한다.
객체를 생성한다는 것은 해당 클래스의 .class 파일을 메모리에 올린다는 것을 의미한다.
2. 문제01
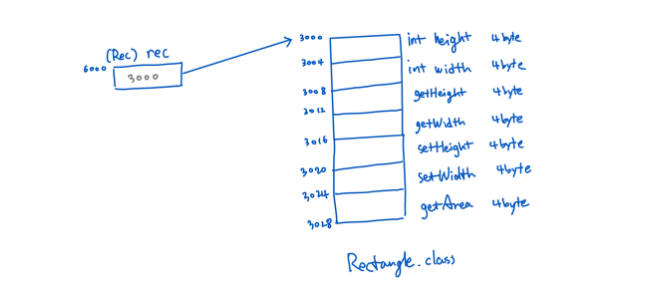
메모리 그림 그리기
Rectangle rec = new Rectangle();
public class Rectangle {
int height;
int width;
public int getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(int height) {
this.height = height;
}
public int getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {
this.width = width;
}
public int getArea() {
return width * height;
}
}
3. 클래스와 객체의 차이
-
클래스 : .class
-
객체: .class를 메모리에 올린것
클래스는 구현 하려는 기능을 모아둔 설계도 라고 볼 수 있다.
객체는 클래스의 기능을 활용하기 위해 메모리를 할당해 실제 사용하는 것을 의미한다.
구현하고자 하는 중복되는 기능이 2개 이상일 때 그것을 하나의 클래스로 정의하고, 그 클래스를 통해 객체를 생성(메모리에 할당)한다.
4. 문제02
1 부터 num 까지 합을 구하는 class 를 작성하기
public class SumMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GetSum getsum = new GetSum(); //1)객체 생성
int num; //2)num 변수 선언
num = 50;
getsum.setNum(num); //3)getsum 객체의 setNum함수 호출, num값 50 저장
getsum.sum(); //4)getsum객체의 sum함수 호출, 1-50까지 합 구함
}
}5. 문제03
StraPrint strPrint = new StarPrint();
public class StarPrint {
public void printTriangle(int num) {
for(int i=1; i<=num; i++) {
for(int j=1; j<=i; j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}6. 생성자
- 생성자 이름은 **클래스의 이름과 동일해야 한다.
- 생성자는 **값을 반환하지 않고(return 안함) return type도 표시하지 않는다.
- 리턴값이 없다는 것은 용도를 제한함을 의미 (연산 등의 용도가 아님)
즉, 생성자의 용도는 값들에 대한 초기화이다.
7. 디폴트 생성자
생성자를 만들지 않았지만 객체를 생성할 때 호출하면 컴파일러에 의해 자동으로 생성되는 것이 디폴트 생성자 이다. (용도는 초기화)
직접 생성자 함수를 만들지 않았어도, 객체 생성 시 생성자 함수를 호출하게 되어있다.
어떻게 만들지 않은 생성자 함수를 사용할 수 있을까?
모든 클래스의 인스턴스 생성은 생성자 호출을 동반한다. 생성자 함수를 만들지 않으면 컴파일러에 의해 디폴트 생성자가 자동으로 생성된다. 그래서 생성자 함수를 만들지 않아도 호출해서 사용할 수 있는것.
8. null
null은 참조 변수에 대입 했을 때 비어 있음을 의미한다.
참조 변수에는 주소값이 들어가는데 그곳이 비어 있다는 의미는 아무 곳도 가리키고 있지 않음을 의미한다. (ref가 참조하는 객체가 있었다면 그 관계를 끊는 것을 의미함) 참조 변수를 초기화 할 때 사용한다.
9. java의 명명 규칙
1) 클래스
- 첫 문자는 대문자 CirclePoint
- 합성어는 주로 Camel Case를 사용한다.
CirclePoint (Camel Case) ← 더 많이씀 / Circle_point (snake case)
2) 메소드와 변수
- 첫 문자 소문자로 시작
- 합성어는 주로 Camel Case를 사용한다.addYourMoney
3) 상수
- 상수는 전체 대문자
- 합성어에 snake case사용 : 전체가 대문자 이기 때문에 둘 이상의 단어로 쓸 때 구분해서 보여주기 위해 언더바로 표현(final COLOR_RAINBOW)
4) camel case
- 둘 이상의 문자가 결합된 합성어를 이름으로 사용 시에 두 번째 단어부터 첫 글자를 대문자로 사용한다.
- 낙타의 등처럼 생겼다고 해서 camel case라고 부른다.
- 클래스, 메소드, 변수명은 주로 camel case를 사용한다.
(예)
메소드,변수의 cammel case: addYourMoney, yesOrNo, countMoney
클래스의 cammel case: CircleArea, RectangleArea, StarPoint5) snake case
- 둘 이상의 문자가 결합된 합성어를 이름으로 사용 시에 문자와 문자 사이를 _(언더바)로 이어준다.
- 상수는 전체를 대문자로 작성하기 때문에 합성어로 이름 지을 경우 sanke case를 사용한다.
(예)
메소드, 변수의 snake case: add_your_money, yes_or_no, count_money
클래스의 snake case: Circle_area, Rectangle_area, Star_point
상수의 snake case: final COLOR_RAINBOW10. 문제04
노래 한 곡을 나타내는 Song 클래스를 작성하라.
Song은 다음 필드로 구성된다.
- 노래의 제목을 나타내는 title
- 가수를 나타내는 artist
- 노래가 발표된 연도를 나타내는 year
- 국적을 나타내는 country
또한 Song 클래스에 다음 생성자와 메소드를 작성하라.
- 생성자 2개: 기본 생성자와 매개변수로 모든 필드를 초기화하는 생성자
- 노래 정보를 출력하는 show() 메소드
- main() 메소드에서는 1978년, 스웨덴 국적의 ABBA가 부른 "Dancing Queen"을
song 객체로 생성하고 show()를 이용하여 노래의 정보를 다음과 같이 출력하라.
1978년 스웨덴국적의 ABBA가 부른 Dancing Queen1)
public class Song {
String title;
String artist;
int year;
String country;
public Song() {
}
public Song(String title, String artist, int year, String country) {
this.title = title;
this.artist = artist;
this.year = year;
this.country = country;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println("노래 정보");
System.out.println("제목: " + title);
System.out.println("가수: " + artist);
System.out.println("발표연도: " + year);
System.out.println("국적: " + country);
}
}2)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Song song = new Song(
"Dancing Queen",
"ABBA",
1978,
"Sweden"
);
song.show();
}
}11. 문제05
Grade me = new Grade(90, 70, 100);
System.out.println("평균은 "+me.average());public class Grade {
int sub1;
int sub2;
int sub3;
public Grade (int sub1, int sub2, int sub3) {
this.sub1 = sub1;
this.sub2 = sub2;
this.sub3 = sub3;
}
public void show() {
int avg;
avg = (sub1 + sub2 + sub3) / 3;
System.out.println("평균은 "+ avg);
}
}
public class GradeResult {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Grade me = new Grade(90,70,100);
me.show();
}
}
12. 문제06
public static void main(String[] args) {
TV myTV = new TV("LG", 2017, 32); //LG에서 만든 2017년 32인치
myTV.show();
}
LG에서 만든 2017년형 32인치 TVpublic class LG {
String brand;
int year;
int inch;
public LG(String brand, int year, int inch) {
this.brand = brand;
this.year = year;
this.inch = inch;
}
public void show() {
System.out.println(brand + "에서 만든 " + year + "년형 " + inch + "인치 TV");
}
}public class LG_Result {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LG myTV = new LG("LG", 2017, 32); //LG에서 만든 2017년 32인치
myTV.show();
}
}13. 문제07
아래의 BankAccount 객체에 대하여 그림을 그리시오.
BankAccount ref1 = new BankAccount();
BankAccount ref2 = ref1;14. 문제08
Gugudan gugudan = new Gugudan();
gugudan.printGugu(10); //1단부터 10단까지 출력
gugudan.printGugu(20); //1단부터 20단까지 출력public class GuguDan {
public void printGugu(int num) {
for(int i = 1; i <= num; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j < 10; j++) {
System.out.println(i + " x " + j + " = " + (i*j));
}
}
}
}public class GugudanResult {
public static void main (String[] args) {
GuguDan gugudan = new GuguDan();
gugudan.printGugu(10); //1단부터 10단까지 출력
gugudan.printGugu(20); //1단부터 20단까지 출력
}
}