문제링크 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1927
Heap이란 반정렬된 이진트리 구조를 가진 자료구조이다.
따라서 삽입, 삭제가 빠른 장점을 가지고 있으며 시간복잡도는 log(n)이다.
보통 여러 데이터를 저장하되 최소, 최대 순으로 추출해야하는 상황에서 적합한 자료구조이다.
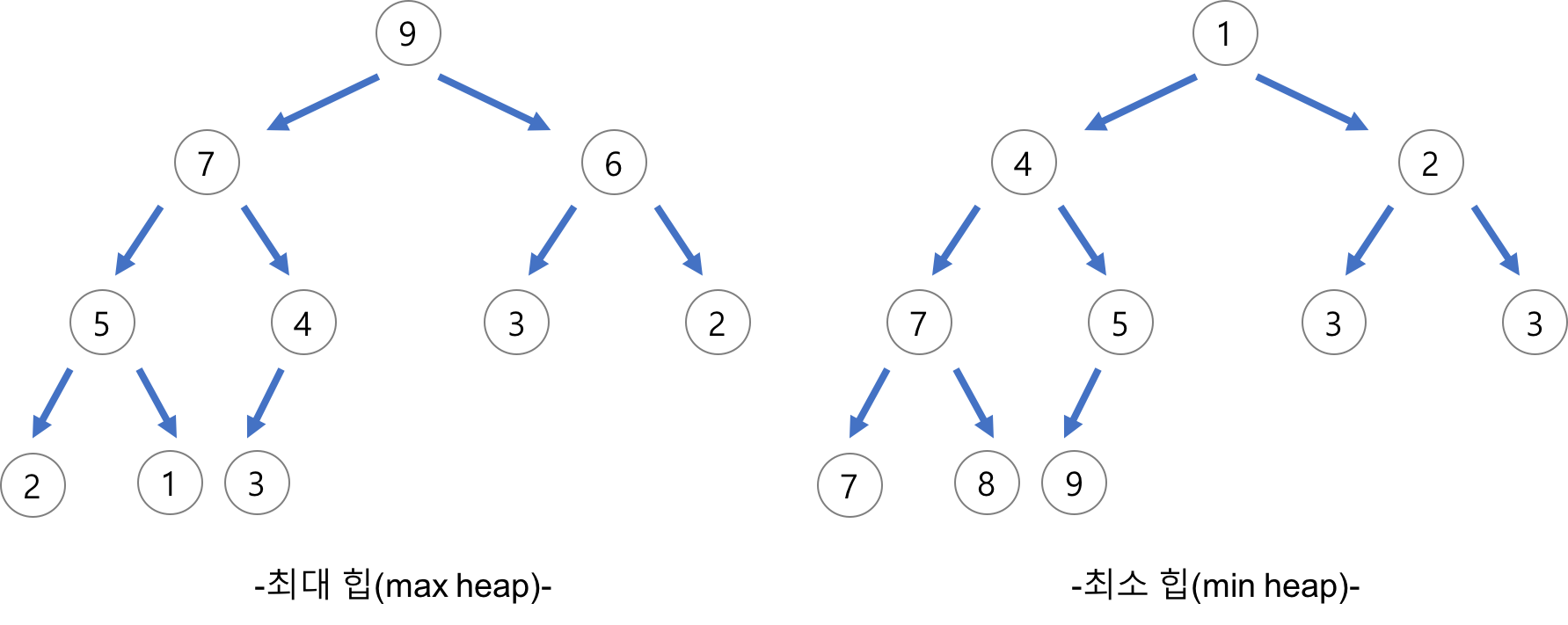
가장 상위인 루트노드로 갈수록 값이 작아지는 최소 힙과
가장 상위인 루트노드로 갈수록 값이 커지는 최대 힙이 있다.
TreeSet과 비슷한 자료구조이지만 Set은 집합으로 중복값을 허용하지 않지만
Heap은 ArrayList로 구현되기에 중복값이 허용된다.
보통 우선순위 큐(Priority Queue)를 구현할 때 Heap 구조가 이용된다.
이번 문제에서는 라이브러리를 사용하지 않고 최소 힙을 직접 클래스로 만들어
Heap 객체 생성, Heap에 값 삽입, 삭제 등을 구현하였다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
Heap heap = new Heap();
int n = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
for( int test = 1 ; test <= n ; test++){
int command = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
if(command == 0) sb.append(heap.delete()+"\n");
else heap.insert(command);
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
//최소 Heap 클래스
class Heap{
private ArrayList<Integer> heap; //Heap은 ArrayList를 이용한다.
public Heap(){
heap = new ArrayList<>();
heap.add(0); // 인덱스를 1번부터 편하게 이용하기 위해 0번 인덱스를 미리 채워둔다.
}
//삽입
public void insert(int value){
//ArrayList의 마지막 위치에 값을 넣는다.
heap.add(value);
int index = heap.size()-1;
//새로 들어온 값을 부모노드와 비교하여 부모노드보다 값이 작다면 자리를 바꿔준다(반복)
//어떤 값의 부모노드 index는 항상 index/2이다.
while(index>1 && value < heap.get(index/2)){
int pValue = heap.get(index/2);
heap.set(index/2, heap.get(index));
heap.set(index, pValue);
index /= 2;
}
}
//삭제
public int poll(){
if(heap.size() == 1) return 0; //삭제시 값이 남아있지않다면 0을 반환한다.
int deleted_value = heap.get(1); // index가 1인 값이 최소이므로 반환값으로 설정
heap.set(1, heap.get(heap.size()-1)); // ArrayList의 가장 뒤에 있던 값을 맨 앞으로 채워넣고
heap.remove(heap.size()-1); //맨 뒤에 있던 값을 제거
//맨 뒤에 있던 값을 맨 앞으로 가져왔으므로 정렬을 해주어야한다
int index = 1;
while(2*index < heap.size()){ //루트노드에서부터 (index 1부터) 하위노드로 가면서 반복
//먼저 왼쪽자식노드를 후보군으로 삼고
int childValue = heap.get(2*index);
int childIndex = 2*index;
//만약 오른쪽 자식노드가 존재하는데 오른쪽 자식노드가 왼쪽 자식노드보다 더 작으면
//오른쪽 노드와 부모노드를 교체할 준비
if(2*index+1<heap.size() && childValue > heap.get(2*index+1)){
childValue = heap.get(2*index+1);
childIndex = 2*index+1;
}
//그런데 만약 부모노드가 교체할 자식노드보다 같거나 작으면
//교체할 필요가 없으므로 break;
if(heap.get(index) <= childValue) break;
//부모와 자식 교체
heap.set(childIndex, heap.get(index));
heap.set(index, childValue);
index = childIndex;
}
return deleted_value; //최소값(index가 1이었던 값) 반환
}
}