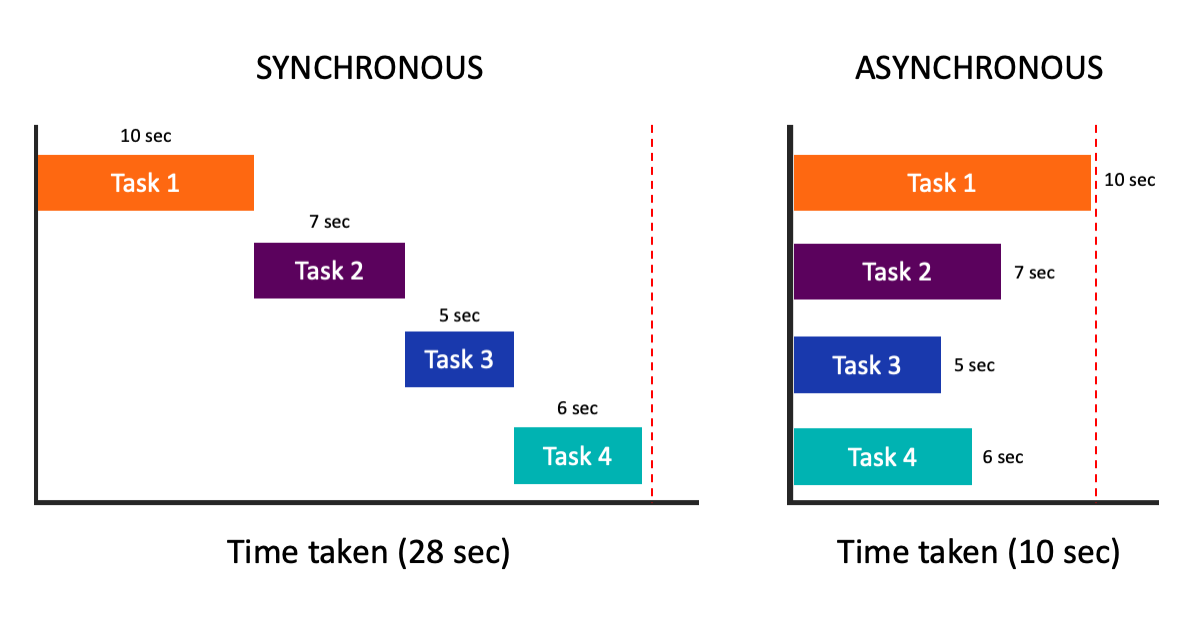
- 비동기란?
// 동기적 코드
console.log('시작');
const data = fetchData(); // 이 작업이 끝날 때까지 다음 코드로 진행되지 않음
console.log('완료');
// 비동기적 코드
console.log('시작');
fetchData().then(data => {
console.log('데이터 도착');
});
console.log('완료'); // fetchData가 완료되기 전에 실행됨- 비동기가 필요한 상황들:
- 서버에서 데이터를 가져올 때
- 대용량 파일을 처리할 때
- 타이머 기능을 구현할 때
- 사용자 입력을 기다릴 때
- 콜백 함수를 이용한 비동기 처리:
// 콜백 지옥의 예
getData(function(a) {
getMoreData(a, function(b) {
getMoreData(b, function(c) {
console.log(c);
});
});
});
// 개선된 방식 (Promise)
getData()
.then(a => getMoreData(a))
.then(b => getMoreData(b))
.then(c => console.log(c));- Promise를 사용한 비동기 처리:
const myPromise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 비동기 작업 수행
const success = true;
if (success) {
resolve('성공!');
} else {
reject('실패!');
}
});
myPromise
.then(result => console.log(result))
.catch(error => console.error(error));- 실제 사용 예시:
// 이미지 로딩
function loadImage(url) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const img = new Image();
img.onload = () => resolve(img);
img.onerror = () => reject(new Error(`이미지 로드 실패: ${url}`));
img.src = url;
});
}
// 타이머 함수
function delay(ms) {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
}
// 사용 예시
async function showImageWithDelay() {
try {
await delay(1000); // 1초 대기
const img = await loadImage('example.jpg');
document.body.appendChild(img);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}- async/await를 사용한 현대적인 비동기 처리:
async function fetchUserData() {
try {
const response = await fetch('https://api.example.com/user');
const userData = await response.json();
// 추가 데이터 병렬로 가져오기
const [posts, comments] = await Promise.all([
fetch(`/api/posts/${userData.id}`).then(r => r.json()),
fetch(`/api/comments/${userData.id}`).then(r => r.json())
]);
return {
user: userData,
posts,
comments
};
} catch (error) {
console.error('데이터 가져오기 실패:', error);
throw error;
}
}- 비동기 작업의 상태 처리:
async function loadData() {
const loadingElement = document.querySelector('.loading');
const contentElement = document.querySelector('.content');
try {
loadingElement.style.display = 'block';
contentElement.style.display = 'none';
const data = await fetchData();
contentElement.innerHTML = data;
contentElement.style.display = 'block';
} catch (error) {
console.error('에러:', error);
} finally {
loadingElement.style.display = 'none';
}
}- 이벤트 리스너와 비동기:
const button = document.querySelector('#submitButton');
const form = document.querySelector('#myForm');
form.addEventListener('submit', async (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const formData = new FormData(form);
try {
const response = await fetch('/api/submit', {
method: 'POST',
body: formData
});
if (!response.ok) throw new Error('제출 실패');
alert('성공적으로 제출되었습니다!');
} catch (error) {
alert('제출 중 오류가 발생했습니다.');
}
});비동기 프로그래밍은 사용자 경험을 향상시키고 성능을 최적화하는데 필수적!
