쓰레드의 동기화(synchronization)
- 멀티 쓰레드 프로세스에서는 다른 쓰레드의 작업에 영향을 미칠 수 있다.
- 진행중인 작업이 다른 쓰레드에게 간섭받지 않게 하려면 '동기화'가 필요
(동기화 - 한 쓰레드가 진행중인 작업을 다른 쓰레드가 간섭하지 못하게 막는 것) - 동기화 하려면 간섭받지 않아야 하는 문장들을 '임계 영역'으로 설정
- 임계영역은 락(Lock)을 얻은 단 하나의 쓰레드만 출입가능(객체 1개에 Lock 1개)
synchronized를 이용한 동기화
- synchronized로 임계영역(lock이 걸리는 영역)을 설정하는 방법 2가지
1. 메서드 전체를 임계영역으로 지정
public synchronized void calcSum(){
// ...
}
2. 특정한 영역을 임계 영역으로 지정
synchronized(객체의 참조변수){
// ...
}※ 임계영역은 한 번에 한 쓰레드만 사용할 수 있기 때문에, 영역을 최소화 해야한다. 임계영역이 많을수록 성능이 떨어진다. (멀티 쓰레드의 장점이 동시에 여러 쓰레드가 돌아가는 건데 이 장점이 없어짐)
따라서, 임계영역은 가능하면 개수도 최소화 해야하고, 영역도 좁아야한다. 가능하다면 메서드 전체로 하지 않는 것이 좋고, 그럴 때는 위의 2번째 예시와 같이 하면 된다.
Case
class Account2{
private int balance = 1000; // private으로 해야 동기화가 의미가 있다.(외부 접근 방지)
// 메서드를 동기화(임계 영역)
public synchronized void withdraw(int money){
if(balance >= money){
try{
Thread.sleep(1000); // sleep은 결과를 보기 쉽게 하려고 넣은것 뿐(신경쓰지말자)
}catch(InterruptedException e) {}
balance -= money;
}
} // withdraw
}
class RunnableEx22 implements Runnable{
Account2 acc = new Account2();
public void run(){
while(acc.getBalance() > 0){
// 100, 200, 300 중의 한 값을 임의로 선택해서 출금(withdraw)
int money = (int)(Math.random() * 3 + 1) * 100;
acc.withdraw(money);
System.out.println("balance:"+acc.getBalance());
}
} // run()
}
class ThreadEx22{
public static void main(String args[]){
Runnable r = new RunnableEx22();
new Thread(r).start();
new Thread(r).start();
}
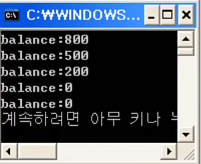
}위의 예시에서 withdraw 메서드에 synchronized가 없다면, 음수의 결과가 나올 수 있다.
- synchronized 없을 때
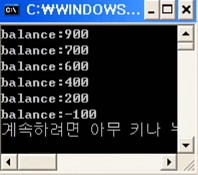
- synchronized 있을 때