PCAP Programming
C언어로 PCAP API를 이용하여 패킷의 정보를 출력하는 프로그램을 만들어보자
출력 요소는 다음과 같다
- Ethernet 헤더에서
src mac / dst mac - IP 헤더에서
src ip / dst ip - TCP 헤더에서
src port / dst portPCAP API
PCAP(packet capture) API는 운영체제의 패킷 캡처 기능에 효율적으로 액세스 하기 위한 플랫폼이다. 기존 소켓 프로그래밍은 운영체제마다의 이식성이 낮고, 구현이 복잡하다. C언어에서 이를 사용하기 위해 libpcap 라이브러리를 사용한다.
설계하기
네트워크 패킷을 캡처하기 위해 다음과 같이 설계한다.
- 네트워크 디바이스 열기
- 패킷 캡처 시작
- pcap 핸들 닫기
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pcap.h>
void packet_capture(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet){
// 코드 작성
}
int main() {
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
pcap_t *handle;
// 네트워크 디바이스 열기
handle = pcap_open_live("eth0", BUFSIZ, 1, 1000, errbuf);
if (handle == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "디바이스 열기 실패: %s\n", errbuf);
return 1;
}
// 패킷 캡처 시작
pcap_loop(handle, 0, packet_handler, NULL);
// pcap 핸들 닫기
pcap_close(handle);
return 0;
}
pcap_open_live(device, snaplen, promisc, to_ms, ebuf)
- device : 패킷 캡처를 위해 열려는 네트워크 디바이스의 이름
- snaplen : 패킷당 캡처할 최대 바이트 수 지정
- promisc : 디바이스가 무차별 모드로 전환되도록 지정(0 또는 1)
- to_ms : 읽기 제한시간 지정
- ebuf : 오류 텍스트를 리턴하며 pcap_open_live 서브루틴이 실패하는 경우에만 설정
pcap_loop(p, cnt, callback, user)
- p : pcap_open_live에서 반환된 패킷 캡쳐 디스크립터
- cnt : 리턴하기 전 처리할 최대 패킷 수 지정. 음수 값을 사용하면 영원히 루프되거나 EOF에 도달하기 전까지 처리함
- callback : 각 패킷 읽기에 대해 호출되는 사용자 제공 루틴(사용자 지정 함수)
- user : 콜백 루틴에 전달할 첫 번째 인수 지정
Ethernet
Ethernet 구조체

- DA(Destination Address) : 목적지 MAC 주소
- SA(Source Address) : 출발지 MAC 주소
- Type : IP등의 네트워크 계층 프로토콜 타입
Ethernet Header in C
/* Ethernet header */
struct ethheader {
u_char ether_dhost[6]; // destination host address
u_char ether_shost[6]; // source host address
u_short ether_type; // IP? ARP? RARP? etc
};MAC Address 출력하기
Ethernet의 MAC 정보를 받기 위해서, Ethernet 헤더 구조체를 선언한 후 Ethernet 헤더 내의 source mac 주소와 destination mac 주소를 파싱하여 출력한다.
void mac_capture(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet){
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
// Ethernet 정보 출력
printf("Source MAC: %s\n", ether_ntoa((struct ether_addr *)eth->ether_shost));
printf("Destination MAC: %s\n", ether_ntoa((struct ether_addr *)eth->ether_dhost));
printf("\n");
}
ether_ntoa(const struct ether_addr *__addr)
network 바이트 주소를 아스키 코드로 변환 (network to ascii)
ether_addr변수를 사용하려면<netinet/ether.h>헤더를 포함시켜주어야 한다
IP
IP 구조체
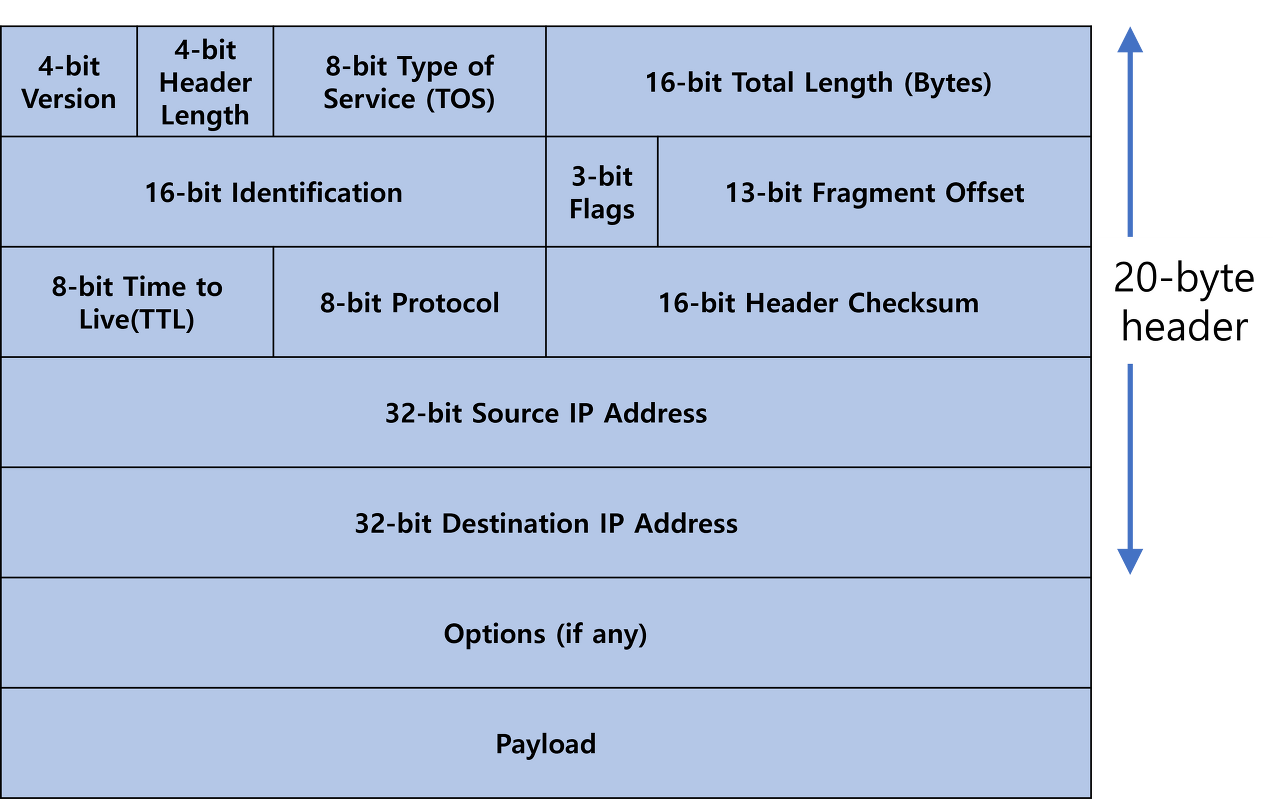
- Version : IP 버전
- Header Length : IP 헤더 길이(보통 20byte)
- TOS(Type Of Service) : 패킷 우선순위(QoS, Quality of Service를 만족시키기 위함)
- Length : 패킷의 총 길이(header + payloads)
- Identification : 데이터가 크면 단편화가 일어남. 이때 같은 데이터임을 나타내는 값
- Flag : 단편화가 일어났는지 확인하기 위한 값
- Fragment Offset : 단편화 시 패킷이 몇 번째 패킷인지 나타내는 값
- TTL(Time To Live) : 패킷의 생존 시간
- Protocol Type : TCP 등의 상위 전송 계층 타입
- Source IP : 출발지 IP 주소
- Destination IP : 목적지 IP 주소
IP Header in C
/* IP Header */
struct ipheader {
unsigned char iph_ihl:4, // IP header length
iph_ver:4; // IP version
unsigned char iph_tos; // Type of service
unsigned short int iph_len; // IP Packet length (data + header)
unsigned short int iph_ident; // Identification
unsigned short int iph_flag:3, // Fragmentation flags
iph_offset:13; // Flags offset
unsigned char iph_ttl; // Time to Live
unsigned char iph_protocol; // Protocol type
unsigned short int iph_chksum; // IP datagram checksum
struct in_addr iph_sourceip; // Source IP address
struct in_addr iph_destip; // Destination IP address
};
char val:4에서:4는 char형 4비트를 할당받는 C언어 문법이다
IP Address 출력하기
IP 정보를 받기 위해서, IP 헤더 구조체를 선언한 후 IP 헤더 내의 source IP 주소와 destination IP 주소를 파싱하여 출력한다.
void ip_capture(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet){
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader));
// IP 정보 출력
printf("Source IP: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_sourceip));
printf("Destination IP: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_destip));
printf("\n");
}
(struct ipheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader));
ethernet 헤더 부분을 제외한 부분부터 ip header 이므로, 다음과 같은 연산 실행
TCP
TCP 구조체
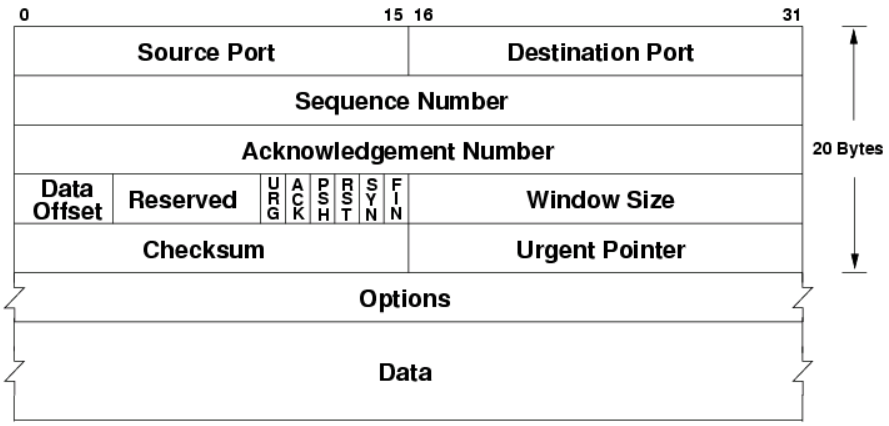
- Source Port : 출발지 포트 번호
- Destination Port : 목적지 포트 번호
- Sequence Number : 송신자가 보내는 데이터의 시작 바이트
- Acknowledgement Number : 송신자에게 받은 데이터 바이트의 +1
- Data Offset(4비트) : 헤더 길이. 4byte단위로 표현됨(일반적으로 20byte)
- Reserved(6비트) : 예약 필드. 0으로 채워짐
- flag(6비트) : 특정 동작을 나타내는 제어 플래그
- URG : 긴급 데이터, Urgent
- ACK : 데이터 수신 확인, Acknowledgment
- PSH : 버퍼의 데이터 즉시 송신, Push
- RST : 연결 초기화 또는 오류, Reset
- SYN : TCP 연결 설정, Synchronize
- FIN : TCP 연결 종료, Finish
- ECE : 네트워크 혼잡 상태를 나타냄, ECN-Echo, (ECN, Explicit Congestion Notification)
- CWR : 수신자가 혼잡 상태를 해결했음을 나타냄, Congestion Window Reduced
- Window Size : 수신가능한 데이터의 양
- Checksum : 오류 검출 필드
- Urgent Pointer : 긴급 데이터를 처리하거나 신호를 보내는 데 사용되는 필드
TCP Header in C
/* TCP Header */
struct tcpheader {
u_short tcp_sport; // source port
u_short tcp_dport; // destination port
u_int tcp_seq; // sequence number
u_int tcp_ack; // acknowledgement number
u_char tcp_offx2; // data offset, rsvd
u_char tcp_flags;
#define TH_FIN 0x01
#define TH_SYN 0x02
#define TH_RST 0x04
#define TH_PUSH 0x08
#define TH_ACK 0x10
#define TH_URG 0x20
#define TH_ECE 0x40
#define TH_CWR 0x80
#define TH_FLAGS (TH_FIN|TH_SYN|TH_RST|TH_ACK|TH_URG|TH_ECE|TH_CWR)
u_short tcp_win; // window
u_short tcp_sum; // checksum
u_short tcp_urp; // urgent pointer
};일반적으로
Flags필드는 6비트로 정의되어야 하지만ECE,CWR을 포함하는 확장된 TCP 플래그를 다루기 때문에 8비트Flags필드를 갖는다
Port Number 출력하기
void tcp_capture(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet){
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader));
struct tcpheader *tcp = (struct tcpheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader) + ip->iph_ihl * 4);
// TCP 포트 정보 출력
printf("Source Port: %d\n", ntohs(tcp->tcp_sport));
printf("Destination Port: %d\n", ntohs(tcp->tcp_dport));
printf("\n");
}
(struct tcpheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader) + ip->iph_ihl * 4);
IP 헤더의 길이를 나타내는 필드(iph_ihl)를 사용하여 TCP 헤더의 시작부분을 가르키도록 함
ntohs함수는 TCP/IP 네트워크 바이트 순서에서 호스트 바이트 순서(Intel 프로세서의 little-endian)로 변환함
최종
코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pcap.h>
#include <netinet/ether.h>
/* Ethernet header */
struct ethheader {
u_char ether_dhost[6]; // destination host address
u_char ether_shost[6]; // source host address
u_short ether_type; // IP? ARP? RARP? etc
};
/* IP Header */
struct ipheader {
unsigned char iph_ihl:4, //IP header length
iph_ver:4; //IP version
unsigned char iph_tos; //Type of service
unsigned short int iph_len; //IP Packet length (data + header)
unsigned short int iph_ident; //Identification
unsigned short int iph_flag:3, //Fragmentation flags
iph_offset:13; //Flags offset
unsigned char iph_ttl; //Time to Live
unsigned char iph_protocol; //Protocol type
unsigned short int iph_chksum; //IP datagram checksum
struct in_addr iph_sourceip; //Source IP address
struct in_addr iph_destip; //Destination IP address
};
/* TCP Header */
struct tcpheader {
u_short tcp_sport; // source port
u_short tcp_dport; // destination port
u_int tcp_seq; // sequence number
u_int tcp_ack; // acknowledgement number
u_char tcp_offx2; // data offset, rsvd
u_char tcp_flags;
#define TH_FIN 0x01
#define TH_SYN 0x02
#define TH_RST 0x04
#define TH_PUSH 0x08
#define TH_ACK 0x10
#define TH_URG 0x20
#define TH_ECE 0x40
#define TH_CWR 0x80
#define TH_FLAGS (TH_FIN|TH_SYN|TH_RST|TH_ACK|TH_URG|TH_ECE|TH_CWR)
u_short tcp_win; // window
u_short tcp_sum; // checksum
u_short tcp_urp; // urgent pointer
};
void packet_capture(u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet){
struct ethheader *eth = (struct ethheader *)packet;
struct ipheader *ip = (struct ipheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader));
struct tcpheader *tcp = (struct tcpheader *)(packet + sizeof(struct ethheader) + ip->iph_ihl * 4);
// Ethernet 정보 출력
printf("Source MAC: %s\n", ether_ntoa((struct ether_addr *)eth->ether_shost));
printf("Destination MAC: %s\n", ether_ntoa((struct ether_addr *)eth->ether_dhost));
// IP 정보 출력
printf("Source IP: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_sourceip));
printf("Destination IP: %s\n", inet_ntoa(ip->iph_destip));
// TCP 포트 정보 출력
printf("Source Port: %d\n", ntohs(tcp->tcp_sport));
printf("Destination Port: %d\n", ntohs(tcp->tcp_dport));
printf("\n");
}
int main(){
pcap_t *handle;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
handle = pcap_open_live("eth0", BUFSIZ, 1, 1000, errbuf);
pcap_loop(handle, 0, packet_capture, NULL);
pcap_close(handle);
return 0;
}실행
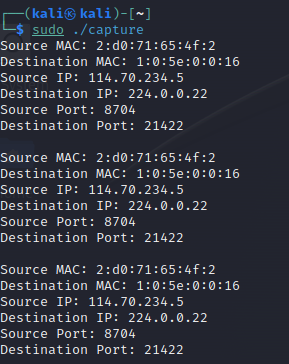
잘 동작함을 확인할 수 있다.
