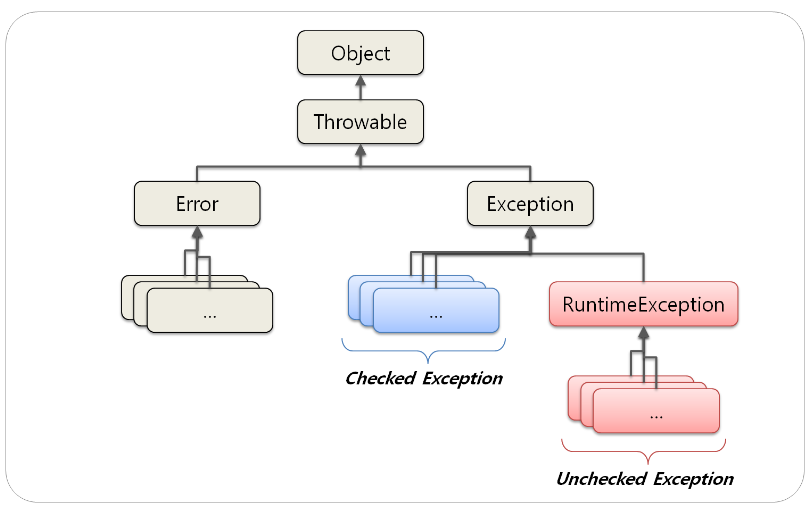
Java의 Exception에는 Unchecked Exception 과 Checked Exception 두 가지 예외로 구분이 된다.
Exception은 위와 같은 상속 구조를 가지는데, RuntimeException을 상속하는 Exception들은 모두 Unchecked Exception으로 분류된다. 그 외의 Exception들은 Checked Exception으로 분류된다.
Unchecked Exception
- 런타임 단계에서 확인이 가능해
Runtime Time Exception이라고도 부른다. - 예외 처리를 강제하지 않는다. 하지만 처리해도 무방하다.
Unchecked Exception은 컴파일 시 컴파일러에서 확인하지 않는 예외이다.
우리가 자주 마주치는 Unchecked Exception으로 NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 이 있다.
예시 코드로 확인해 보자.
public class UncheckedException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3};
int index = 10;
System.out.println("number = " + numbers[index]);
}
}index가 2까지 밖에 존재하지 않는 배열의 10번째 index에 접근하려고해
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException 에러가 발생하는 코드이다.
만약 Unchecked Exception에서 예외 처리를 강제한다면 try/catch문을 사용하면 된다. 하지만 RuntimeException은 개발자들에 의한 실수로 발생하는 것들이기 때문에 에러를 강제하지 않는 것이다.
Checked Exception
- 컴파일 시점에 컴파일러에서 확인하는 예외로 Compile Time Exception 이라고도 부른다.
- 컴파일 시점에 Exception을 확인한다. 컴파일 시점에 Exception에 대한 처리(try/catch)를 수행하지 않을 경우 컴파일 에러를 발생시킨다.
Checked exception은 Unchecked Exception과는 다르게 컴파일 시 예외를 체크한다.
예시 코드로 확인해보자.
public class CheckedException {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
File file = new File("example.txt");
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(file);
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
String line = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("line = " + line);
}
scanner.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("An error occurred while reading the file: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}위 코드는 존재하지 않는 example.txt라는 파일을 읽는 코드이다. 그래서 example.txt 파일을 읽으려고 하면 예외처리(FileNotFoundException)를 진행한다.
즉, catch 안의 코드를 실행한다.
Checked Exception와 Unchecked Exception의 Rollback 여부
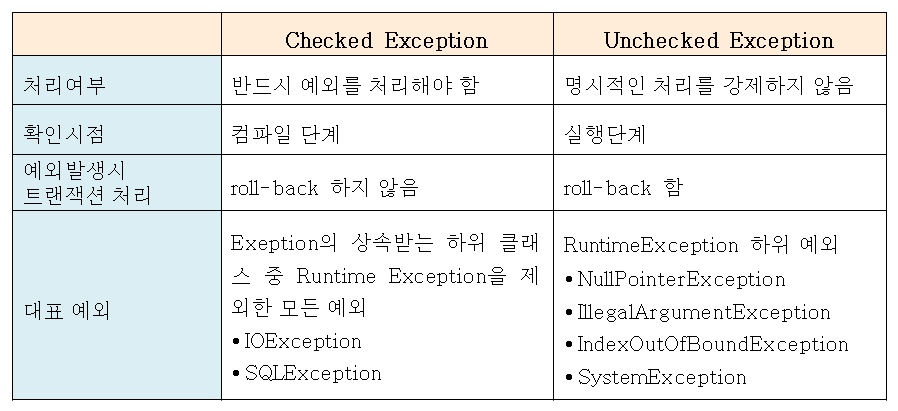
체크 예외와 언체크 예외의 차이점 중에 같이 보아야 할 점은 Rollback의 여부이다.
Checked Exception : Rollback이 되지 않고 트랜잭션이 commit까지 완료된다.
Unchecked Exception : Rollback이 된다.
올바른 예외 처리 방식
- 무책임하게 상위 메서드에 throw로 예외를 던지는 것은 상위 메서드의 책임이 증가하기 때문에 좋지 않다
- 복구가 불가능한 Checked Exception이 발생하면 더 구체적인 Unchecked Exception을 발생시키고 예외에 대한 메시지를 명확하게 전달하는 것이 좋다.
- 예외 복구 전략이 명확하고 복구가 가능하다면 Checked Exception을 try-catch로 잡아서 예외를 복구하는 것이 좋다.
참고
- https://cheese10yun.github.io/checked-exception/#null
Checked Exception을 대하는 자세