구현할 것
Spring Boot 3과 Next.js 14 간에
HTTPS CORS 통신을 주고받는 과정에서 어려움을 겪어
기록을 남겨 반복된 시행착오를 줄이려고 한다.
준비물
두 서버가 CORS 정책을 만족시키면서 HTTPS 통신을
HTTPS 통신을 위한 인증 파일이 필요하다.
[Next.js 14]
- .key 파일
- .cert 파일
[spring boot 3]
- keystore.p12
Spring
HTTPS 설정
HTTPS 통신을 하기위해서는 keystore.p12와
application.yml설정이 필요하다.
키 파일 발급은 아래글을 참고하자
https://velog.io/@penloo/%EB%82%B4%EB%B6%80%EB%A7%9D-HTTPS-%EC%9D%B8%EC%A6%9D%EC%84%9C-%EB%B0%9C%EA%B8%89%ED%95%98%EA%B8%B0
.gitignore
keystore.p12 파일이 깃에 올라가지 않도록 설정해주자.
### Local HTTPS ###
application-local.yml
keystore.p12application.yml
로컬에서만 사용할 인증서이기 때문에
spring.profiles.active=local로
application-local.yml파일 설정을 가져와주자.
spring:
thymeleaf:
cache: false
application:
name: {프로젝트명}
profiles:
active: localapplication-local.yml
# local HTTPS Configuration
server:
ssl:
enabled: true
key-store: classpath:keystore.p12
key-store-password: {p12 키 비밀번호}
key-store-type: PKCS12
key-alias: {p12 키 별명}
client:
server:
domain1: https://localhost:3000/
domain2: https://{클라이언트 도메인1}/
domain3: https://{클라이언트 도메인2}/keystore.p12파일을
../src/main/resources/keystore.p12 경로에 두면
key-store: classpath:keystore.p12
이 설정에서 인식할 수 있다.
CORS 설정
CorsConfig
package com.myweapon.hourglass.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.CorsRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
// 클라이언트 서버 도메인 주소
@Value("${client.server.domain1}")
private String clientServerDomain1;
@Value("${client.server.domain2}")
private String clientServerDomain2;
@Value("${client.server.domain3}")
private String clientServerDomain3;
// 전역 CORS 설정
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
registry.addMapping("/api/**")
.allowedOrigins(clientServerDomain1) // 필요한 도메인 추가
.allowedOrigins(clientServerDomain2)
.allowedOrigins(clientServerDomain3)
.allowedMethods("*")
.allowedHeaders("*")
.allowCredentials(true);
}
}SecurityConfig
package com.myweapon.hourglass.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configurers.AbstractHttpConfigurer;
import org.springframework.security.config.http.SessionCreationPolicy;
import org.springframework.security.web.SecurityFilterChain;
import org.springframework.web.cors.CorsConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.cors.UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {
@Value("${client.server.domain1}")
private String clientServerDomain1;
@Value("${client.server.domain2}")
private String clientServerDomain2;
@Value("${client.server.domain3}")
private String clientServerDomain3;
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
return http.csrf(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.httpBasic(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.cors(cors -> cors.configurationSource(corsConfigurationSource())) // CORS 설정 추가
.sessionManagement(sessionManagementConfig ->
sessionManagementConfig
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS))
.authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize
.anyRequest().permitAll()
)
.formLogin(AbstractHttpConfigurer::disable)
.build();
}
@Bean
public UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource corsConfigurationSource() {
UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource source = new UrlBasedCorsConfigurationSource();
CorsConfiguration config = new CorsConfiguration();
config.setAllowCredentials(true);
config.addAllowedOrigin(clientServerDomain1);
config.addAllowedOrigin(clientServerDomain2);
config.addAllowedOrigin(clientServerDomain3);
config.addAllowedHeader("*");
config.addAllowedMethod("*");
source.registerCorsConfiguration("/**", config);
return source;
}
}WebSocketConfig
package com.myweapon.hourglass.config;
import com.myweapon.hourglass.webchat.util.SignalSocketHandler;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketHandler;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketHandlerRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.standard.ServletServerContainerFactoryBean;
@Configuration
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketConfigurer {
// 클라이언트 서버 도메인 주소
@Value("${client.server.domain1}")
private String clientServerDomain1;
@Value("${client.server.domain2}")
private String clientServerDomain2;
@Value("${client.server.domain3}")
private String clientServerDomain3;
@Override
public void registerWebSocketHandlers(WebSocketHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addHandler(signalHandler(), "/signal")
.setAllowedOrigins(clientServerDomain1, clientServerDomain2, clientServerDomain3)
.withSockJS();
}
@Bean
public WebSocketHandler signalHandler() {
return new SignalSocketHandler();
}
@Bean
public ServletServerContainerFactoryBean createWebSocketContainer() {
ServletServerContainerFactoryBean container = new ServletServerContainerFactoryBean();
container.setMaxTextMessageBufferSize(8192);
container.setMaxBinaryMessageBufferSize(8192);
return container;
}
}테스트 API Controller
Next.js와 Spring Boot 간에 통신을 주고받을 수 있는지
CORS 정책에 막히지 않는지 확인하기 위한 테스트용 API다.
package com.myweapon.hourglass.webchat.controller;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController
public class RestController {
@GetMapping("/api/hello")
public ResponseEntity<String> hello() {
ResponseEntity<String> response = ResponseEntity.ok("Hello, World!");
return response;
}
}Next.js 14
Next.js HTTPS 통신을 위해
dev.cert, dev.key를 생성하고 챙겨주자.
.gitignore
# local HTTPS
dev.key
dev.cert
server-local.js로컬 테스트환경에서만 쓸 파일이 깃에 올라가지 않도록 설정해주자.
package.json
{
"name": "your_project_name",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"scripts": {
"dev": "next dev",
"build": "next build",
"lint": "next lint",
"local": "node server-local.js",
"start": "next start -p 3000"
},
"dependencies": {
"@types/date-fns": "^2.6.0",
"date-fns": "^3.6.0",
"dotenv": "^16.4.5",
"env-cmd": "^10.1.0",
"http-proxy-middleware": "^3.0.0",
"js-cookie": "^3.0.5",
"jwt-decode": "^4.0.0",
"next": "14.2.4",
"react": "^18",
"react-dom": "^18",
"yarn": "^1.22.22",
"zustand": "^4.5.4"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@types/js-cookie": "^3.0.6",
"@types/node": "^20",
"@types/react": "^18",
"@types/react-dom": "^18",
"eslint": "^8",
"eslint-config-next": "14.2.4",
"postcss": "^8",
"tailwindcss": "^3.4.1",
"typescript": "^5"
}
}"local": "node server-local.js",
npm run local 명령어를 실행하면 server-local.js 파일이
실행되도록 파일 내용을 수정했다.
테스트 할 때 Next.js Server를
npm run local로 켜주도록 하자.
.env.localhost
NEXT_PUBLIC_RUN_MODE=localserver-local.js
const { createServer } = require('https');
const { parse } = require('url');
const next = require('next');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
require('dotenv').config({ path: '.env.localhost' }); // 환경 변수 로드
const dev = process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production';
const app = next({ dev });
const handle = app.getRequestHandler();
// 인증서 파일 경로 설정
const httpsOptions = {
key: fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(__dirname, 'dev.key')),
cert: fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(__dirname, 'dev.cert')),
};
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000; // 로컬에서는 3000 포트 사용
app.prepare().then(() => {
const server = createServer(httpsOptions, (req, res) => {
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', 'https://localhost:3000');
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Methods', 'GET,POST,PUT,DELETE,OPTIONS');
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers', 'Content-Type, Authorization');
res.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Credentials', 'true');
if (req.method === 'OPTIONS') {
res.writeHead(204);
res.end();
return;
}
const parsedUrl = parse(req.url, true);
handle(req, res, parsedUrl);
});
server.listen(port, (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log(`> Ready on https://localhost:${port}/`);
});
});// 인증서 파일 경로 설정
const httpsOptions = {
key: fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(__dirname, 'dev.key')),
cert: fs.readFileSync(path.resolve(__dirname, 'dev.cert')),
};이 파일로 하면 루트 디렉토리에 있는 dev.key, dev.cert파일을
인식할 수 있다.
page.tsx
테스트 API 요청할 버튼을 만들어서 클릭하면
API 요청을 하고 콘솔에 메시지를 출력하도록 설정하자.
'use client'
import { useState, useEffect } from "react";
export default function TestPage() {
async function test() {
try {
const response = await fetch('https://localhost:8081/api/hello', {
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json'
}
});
const data = await response.text(); // 텍스트 형식의 응답을 받음
console.log(data);
} catch (error) {
console.error('Error fetching data:', error);
}
}
useEffect (() => {
},[])
return (
<div className="flex">
<button onClick={test}>Test</button>
</div>
);
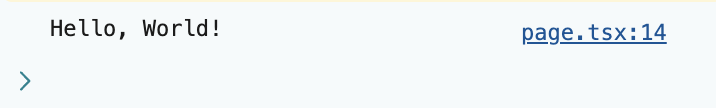
}테스트
무사히 출력된다.
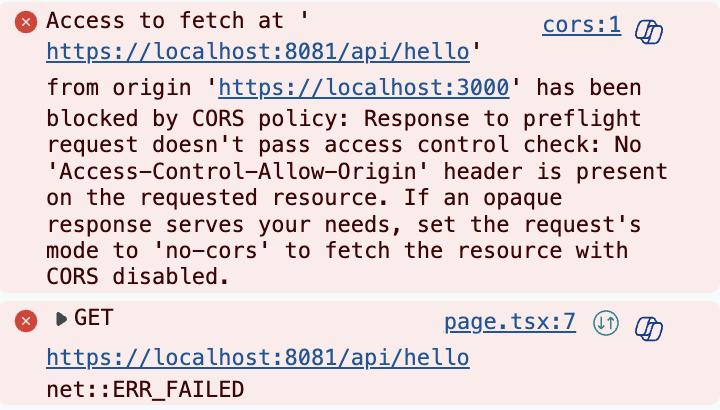
만약 설정을 잘못 건드려서 CORS가 막혀있다면
아래 같은 메시지가 나온다.
정리
Next.js서버와 Spring서버가 HTTPS 통신을 해서
데이터를 잘 주고받으려면 CORS 설정이 잘 되어있어야한다.
- Spring의 경우 웹소켓까지 사용한다면
3개의 설정 파일이 있어야한다.
public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer
: 글로벌 허용
public class SecurityConfig
: 보안설정 허용
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketConfigurer
3개 중에 중복이 되는줄 알고 CorsConfig이 파일을 지웠더니
글로벌 허용이 안되서 CORS 에러가 발생했다. -_-
POST Man 같은 API테스트로는 요청을 해도 잘 될 수 있다.
하지만 Next.js에서 렌더링한 버튼으로 요청을 하면 안 될 수 있는데
왜냐하면 PostMan-Spring 간의 통신은 브라우저-서버 통신이라 CORS 정책과 무관하지만
Next.js-Spring 간의 통신은 서버-서버 통신이라 CORS 정책이 허용되어있어야하기 때문이다.
이걸 잘 모르는 팀원들에게 왜 포스트맨 되는데 Next.js 안 되는지를 설명하느라
애를 먹었었다.
그래도 무사히 연결이 되서 다행이고
이제 AWS 배포해서 맞춰봐야겠다.
