구현하기전 테스트
Alarm Clock까지 진행한 상태의 코드에서
mlfqs부분을 제외하고 테스트를 진행했다.
pass tests/threads/alarm-single
pass tests/threads/alarm-multiple
pass tests/threads/alarm-simultaneous
FAIL tests/threads/alarm-priority
pass tests/threads/alarm-zero
pass tests/threads/alarm-negative
FAIL tests/threads/priority-change
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-one
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple2
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-nest
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-sema
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-lower
FAIL tests/threads/priority-fifo
FAIL tests/threads/priority-preempt
FAIL tests/threads/priority-sema
FAIL tests/threads/priority-condvar
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-chain
구현 step 1
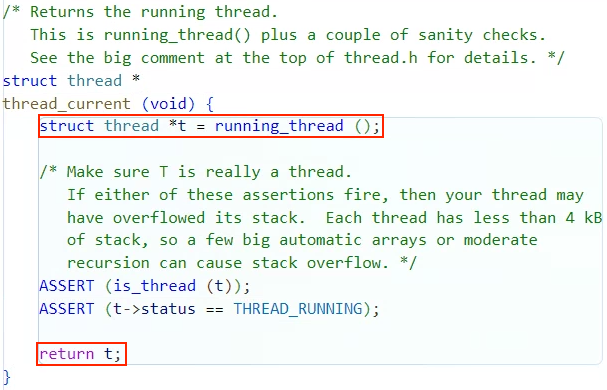
thread.c
void check_preemption(void)
ready_list에 최고 우선순위와 현재 실행 중인 스레드의 우선순위 확인하는
함수를 만들었다 워낙 자주 쓰기 때문에 함수로 따로 만들어서 작성했다.
// ready_list에 최고 우선순위와 현재 실행 중인 스레드의 우선순위 확인
void
check_preemption(void){
int highest_priority = list_entry(list_begin(&ready_list), struct thread, elem)->priority;
if(!list_empty(&ready_list) && highest_priority > thread_current()->priority){
thread_yield();
}
}bool get_higher_priority(...)
두 스레드의 우선순위를 비교해서 첫번째 스레드가 더 크면 true를 출력하도록 했다.
이렇게 구현하면 list_insert_ordered(...)에 사용하면 내림차순이 되도록 삽입하고
list_sort(...) 비교함수로 사용하면 '내림차순'으로 정렬이 된다.
맨위에 아래 코드처럼 초기화를 해주자.
static bool get_higher_priority(const struct list_elem *a_, const struct list_elem *b_, void *aux UNUSED);bool
get_higher_priority(const struct list_elem *a_, const struct list_elem *b_, void *aux UNUSED){
const struct thread *a = list_entry(a_, struct thread, elem);
const struct thread *b = list_entry(b_, struct thread, elem);
return a->priority > b->priority;
}tid_t thread_create(...)
새로 생성한 스레드의 우선순위가 현재 실행 중인 스레드보다 우선순위가 높다면 양도를 하도록
함수를 추가해주었다.
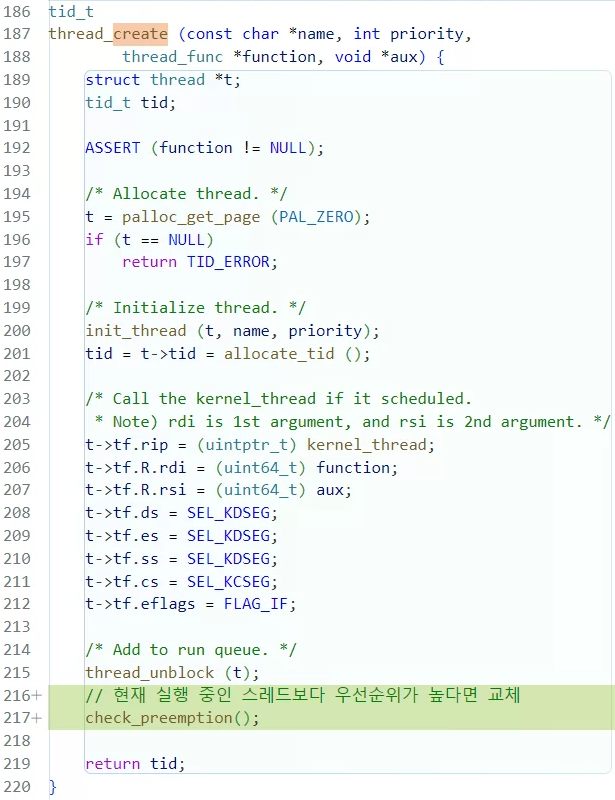
tid_t
thread_create (const char *name, int priority,
thread_func *function, void *aux) {
struct thread *t;
tid_t tid;
ASSERT (function != NULL);
/* Allocate thread. */
t = palloc_get_page (PAL_ZERO);
if (t == NULL)
return TID_ERROR;
/* Initialize thread. */
init_thread (t, name, priority);
tid = t->tid = allocate_tid ();
/* Call the kernel_thread if it scheduled.
* Note) rdi is 1st argument, and rsi is 2nd argument. */
t->tf.rip = (uintptr_t) kernel_thread;
t->tf.R.rdi = (uint64_t) function;
t->tf.R.rsi = (uint64_t) aux;
t->tf.ds = SEL_KDSEG;
t->tf.es = SEL_KDSEG;
t->tf.ss = SEL_KDSEG;
t->tf.cs = SEL_KCSEG;
t->tf.eflags = FLAG_IF;
/* Add to run queue. */
thread_unblock (t);
// 현재 실행 중인 스레드보다 우선순위가 높다면 교체
check_preemption();
return tid;
}void thread_unblock (struct thread *t)
스레드를 unblock을 하고 ready_list에 넣을 때
우선순위에 따라 정렬해서 삽입하도록 변경했다.
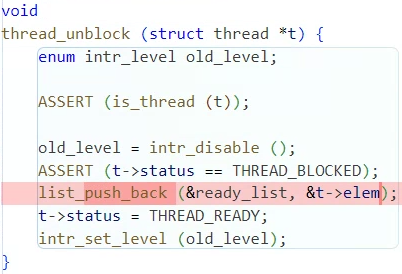
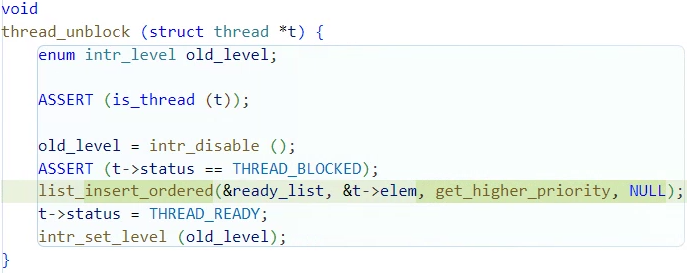
void
thread_unblock (struct thread *t) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (is_thread (t));
old_level = intr_disable ();
ASSERT (t->status == THREAD_BLOCKED);
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, &t->elem, get_higher_priority, NULL);
t->status = THREAD_READY;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}void thread_yield (void)
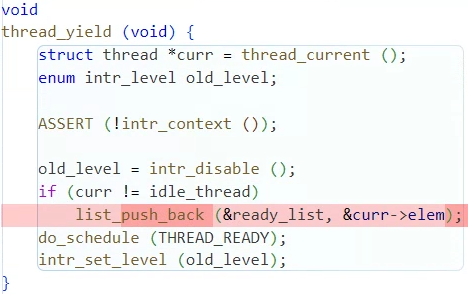
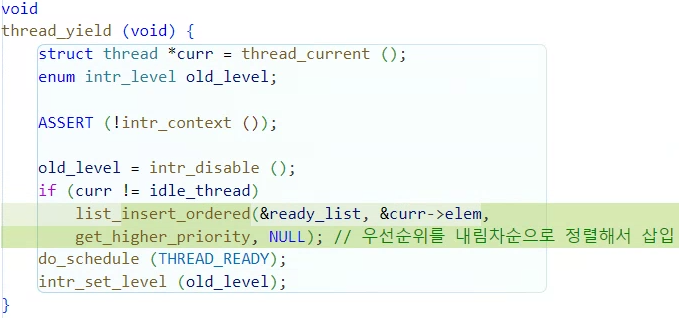
void
thread_yield (void) {
struct thread *curr = thread_current ();
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (curr != idle_thread)
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, &curr->elem,
get_higher_priority, NULL); // 우선순위를 내림차순으로 정렬해서 삽입
do_schedule (THREAD_READY);
intr_set_level (old_level);
}void thread_set_priority(...)
우선순위를 바꾸고 ready_list에 최고 우선순위보다 높은지 확인하고
양보해준다.
이 코드를 추가하면 "pass tests/threads/priority-fifo" 테스트가 통과하게 된다.
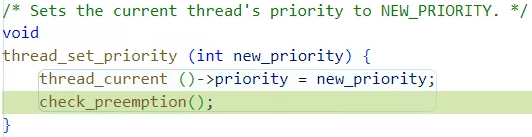
/* Sets the current thread's priority to NEW_PRIORITY. */
void
thread_set_priority (int new_priority) {
thread_current ()->priority = new_priority;
check_preemption(); // 바뀐 우선순위가 ready_list의 최고 우선순위보다 낮으면 양도
}구현 step 1 - 테스트 결과
pass tests/threads/alarm-single
pass tests/threads/alarm-multiple
pass tests/threads/alarm-simultaneous
pass tests/threads/alarm-priority
pass tests/threads/alarm-zero
pass tests/threads/alarm-negative
pass tests/threads/priority-change
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-one
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple2
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-nest
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-sema
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-lower
pass tests/threads/priority-fifo
pass tests/threads/priority-preempt
FAIL tests/threads/priority-sema
FAIL tests/threads/priority-condvar
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-chain
구현 step 2
tests/threads/priority-sema를 구현해보자
thread.c 컴파일 오류 해결
thread.c/earliest_wakeup_time 초기화
지난 alarm clock에서는 발견되지 않았던 컴파일 오류가 발생해서 수정해줬다.
원래 변수 earliest_wakeup_time을 초기화하지 않고 사용했었는데
컴파일 에러가 발생해서 int64_t의 최대값 9223372036854775807으로 수정해줬다.
최대값으로 해준 이유는 void check_thread_sleep_list(int64_t os_ticks)
이 함수에서 매 ticks마다 thread sleep_list을 확인할지를 earliest_wakeup_time을 기준으로 정하는데
sleep_list가 비어있는 경우 earliest_wakeup_time=9223372036854775807로 할당해주기 때문이다.
이렇게 할당하면 check_thread_sleep_list(...)를 호출하더라도 sleep_list를 확인하지 않기 때문에 자원이 절약된다.

static int64_t earliest_wakeup_time = 9223372036854775807; // 가장 일찍 기상하는 시간thread.c/void check_preemption(void) 원형 선언
thread.c에 작성된 check_preemption(...) 함수가 synch.c에서 호출되니
prototype이 선언되지 않았다는 컴파일 오류가 발생했다.
그래서 함수 원형 선언을 해주었다.
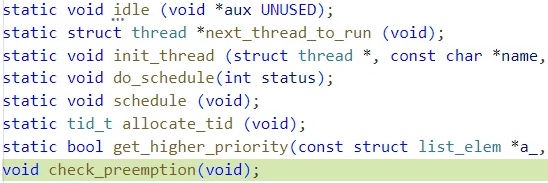
void check_preemption(void);thread.c/void thread_sleep(...)
sleep_list에 저장된 스레드가 없다면 earliest_wakeup_time는 int64_t의 최대값일 것이다. 그래서 조건을 변경해줬다.
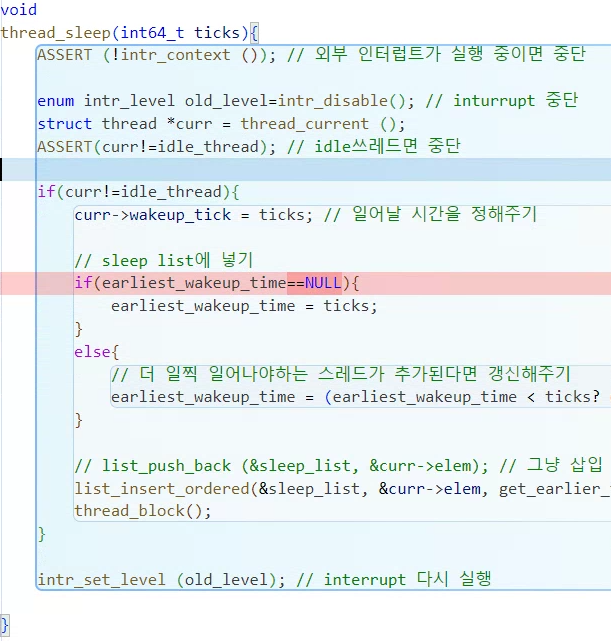

void
thread_sleep(int64_t ticks){
ASSERT (!intr_context ()); // 외부 인터럽트가 실행 중이면 중단
enum intr_level old_level=intr_disable(); // inturrupt 중단
struct thread *curr = thread_current ();
ASSERT(curr!=idle_thread); // idle쓰레드면 중단
if(curr!=idle_thread){
curr->wakeup_tick = ticks; // 일어날 시간을 정해주기
// sleep list에 넣기
if(earliest_wakeup_time == 9223372036854775807){
earliest_wakeup_time = ticks;
}
else{
// 더 일찍 일어나야하는 스레드가 추가된다면 갱신해주기
earliest_wakeup_time = (earliest_wakeup_time < ticks? earliest_wakeup_time: ticks);
}
// list_push_back (&sleep_list, &curr->elem); // 그냥 삽입
list_insert_ordered(&sleep_list, &curr->elem, get_earlier_time, NULL); // 정렬해서 sleep list에 삽입
thread_block();
}
intr_set_level (old_level); // interrupt 다시 실행
}synch.c
컴파일 오류도 수정했겠다 본격적으로 sema를 구현해보자.
synch.c/bool get_higher_priority()
thread.c에 이미 구현해놓았던 스레드 우선순위를 내림차순으로 정렬해주는 비교함수
get_higher_priority(...)와 원형을 작성했다.
bool get_higher_priority(const struct list_elem *a_, const struct list_elem *b_, void *aux UNUSED);
bool
get_higher_priority(const struct list_elem *a_, const struct list_elem *b_, void *aux UNUSED){
const struct thread *a = list_entry(a_, struct thread, elem);
const struct thread *b = list_entry(b_, struct thread, elem);
return a->priority > b->priority;
}synch.c/void sema_down (...)
sema_down은 공유자원에 접근할 수 있는 여부를 확인하는 함수다.
sema->value==0이면 공유자원에 접근할 수 없다는 의미이고,
sema->waiters 리스트에 elem을 넣어서 다른 스레드가 끝나기를 기다리게 된다.
이때 waiters 리스트에 스레드의 priority의 내림차순으로 정렬해서 삽입을 하도록
변경해주면 된다.
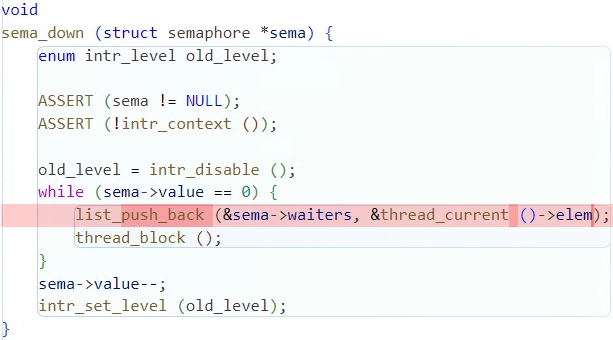
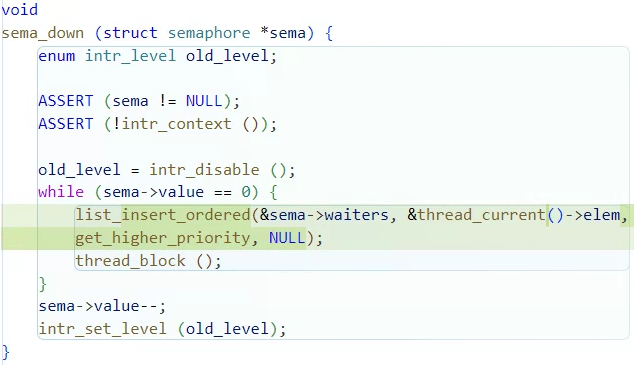
void
sema_down (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
while (sema->value == 0) {
list_insert_ordered(&sema->waiters, &thread_current()->elem,
get_higher_priority, NULL);
thread_block ();
}
sema->value--;
intr_set_level (old_level);
}synch.c/void sema_up (...)
sema_up은 사용했던 공유자원을 반환하고 다음 실행할 함수를 확인하는 함수이다.
공유자원을 사용을 마치고 자원을 반환하면 sema->value를 +1해준다.
이후 실행할 스레드를 찾아야하는데 현재 실행 중인 스레드의 우선순위와
ready_list의 맨 앞 스레드의 우선순위 즉 ready_list의 최고 우선순위와 비교해서
더 높은 스레드가 있다면 CPU 사용을 양도해줘야한다.
기존에 check_preemption()함수를 재사용해서 구현했다.
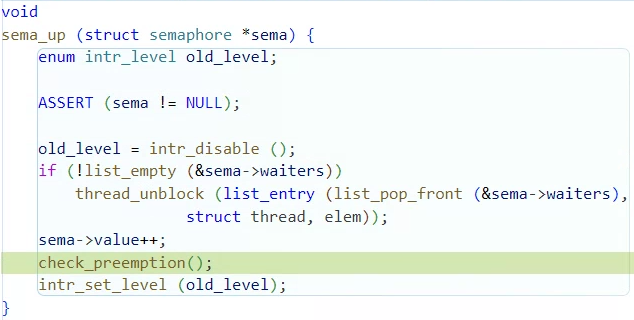
void
sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters))
thread_unblock (list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters),
struct thread, elem));
sema->value++;
check_preemption();
intr_set_level (old_level);
}구현 step 2 테스트
여기까지 잘 따라왔다면 tests/threads/priority-sema가 통과한다.
이어서 condition variable도 구현해보자.
pass tests/threads/alarm-single
pass tests/threads/alarm-multiple
pass tests/threads/alarm-simultaneous
pass tests/threads/alarm-priority
pass tests/threads/alarm-zero
pass tests/threads/alarm-negative
pass tests/threads/priority-change
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-one
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple2
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-nest
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-sema
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-lower
pass tests/threads/priority-fifo
pass tests/threads/priority-preempt
pass tests/threads/priority-sema
FAIL tests/threads/priority-condvar
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-chain
구현 step 3
tests/threads/priority-condvar를 구현해보자.
우선 condition 변수가 어떻게 쓰이는 지를 알고 싶다면 condition 구조체를 이해해야한다.
구조체가 꽤 복잡한 편이기 때문에 차근차근 알아보도록 하자.
condition 변수 안에는 waiters라는 list가 들어간다.
list에 어떤 원소가 들어가는지는 cond_wait(...)함수를 보면 알 수 있는데
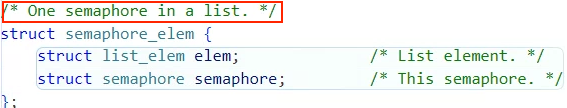
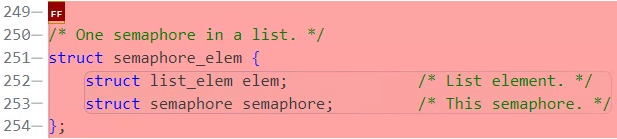
struct semaphore_elem 타입 원소가 들어간다.
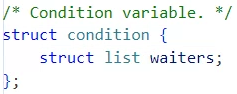
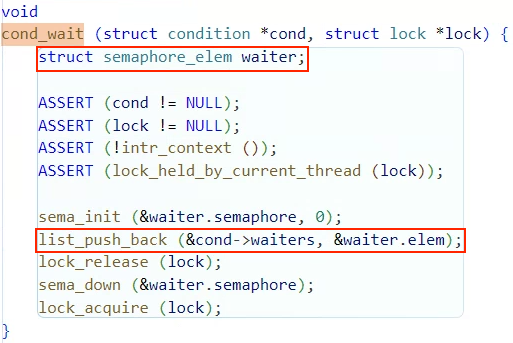
waiters 리스트 원소로 semaphore_elem가 들어가며
아래와 같은 구조체와 멤버 변수가 존재한다.
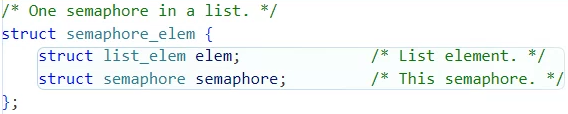
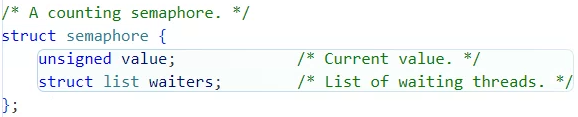
semaphore의 멤버 struct list waiters에는 어떤 원소가 들어가는지를 알려면
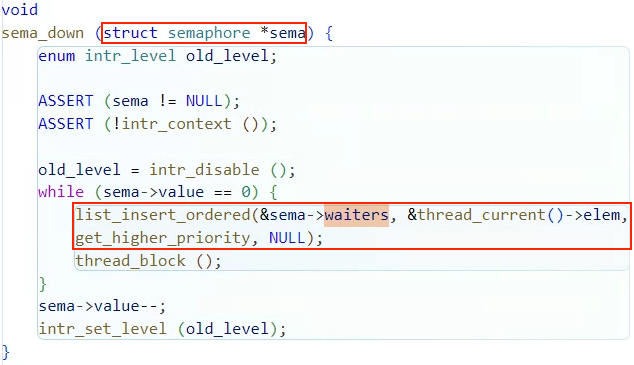
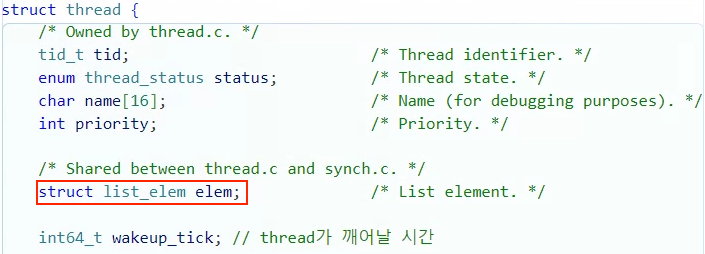
sema_down(...)함수를 보면 알 수 있는데 struct thread의 struct list_elem elem이 들어간다.
아래 코드 사진을 보면 더 확실하게 알 수 있을 것이다.
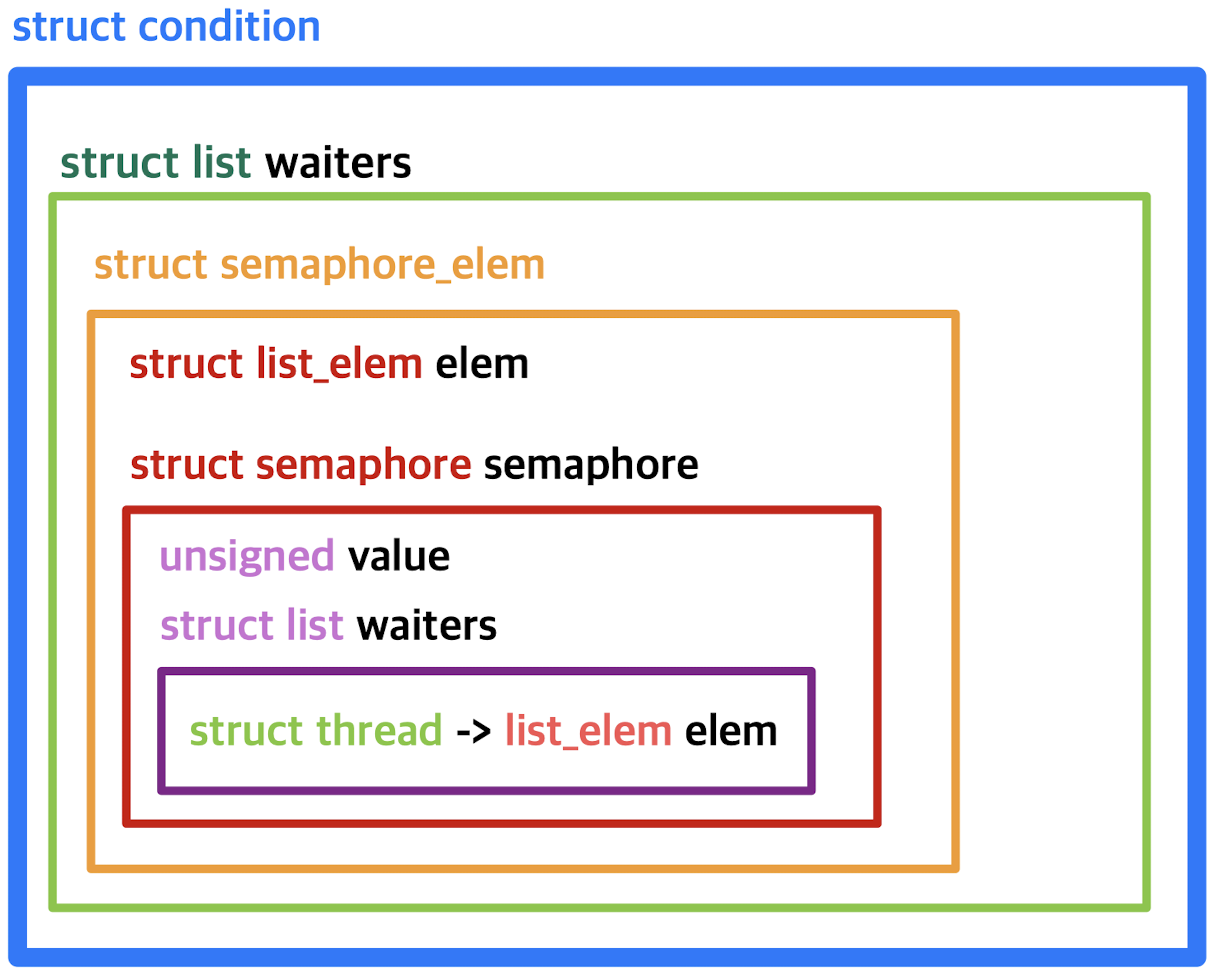
지금까지 condition 구조체의 list의 원소를 정리해보자면
- struct list &condition->waiters: semaphore_elem이 원소
- struct list &semaphore->waiters: &thread->list_elem 이 원소
그래서 구조를 그림으로 정리해보자면
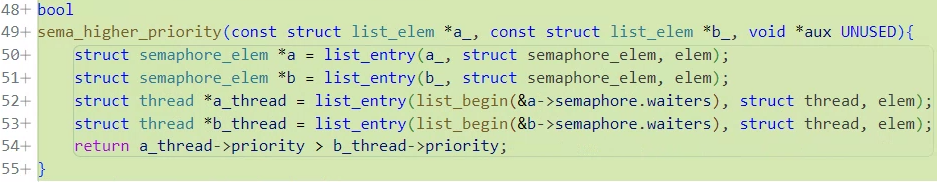
synch.c/bool sema_higher_priority(...)
cond_wait(...)에서 &cond->waiters.elem인 struct semaphore_elem를
&semaphore->waiters.elem에 들어있는 thread의 elem에 따라 정렬해야한다.
이때 &semaphore->waiters.elem은 오직 하나만 들어갈 수 있다.
그래서 위의 저 복잡한 구조에서 list_entry로 스레드 포인터를 구해서 우선순위를 비교해서
semaphore_elem를 정렬해줘야하는데
이 때 list_insert_ordered(..)함수의 인자로 들어갈 비교함수를 구현해야한다.
그 비교함수에 쓰일 함수가 바로 bool sema_higher_priority(...)이다.
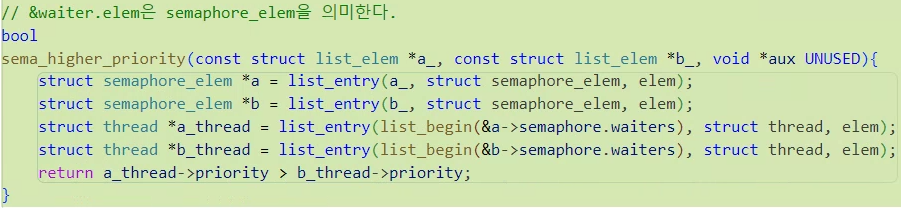
// &waiter.elem은 semaphore_elem을 의미한다.
bool
sema_higher_priority(const struct list_elem *a_, const struct list_elem *b_, void *aux UNUSED){
struct semaphore_elem *a = list_entry(a_, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
struct semaphore_elem *b = list_entry(b_, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
struct thread *a_thread = list_entry(list_begin(&a->semaphore.waiters), struct thread, elem);
struct thread *b_thread = list_entry(list_begin(&b->semaphore.waiters), struct thread, elem);
return a_thread->priority > b_thread->priority;
}함수 원형도 잊지말고 해주자.

bool sema_higher_priority(const struct list_elem *a_, const struct list_elem *b_, void *aux UNUSED);
void check_preemption(void);void sema_up(...)
sema_down으로 자원을 얻고 sema_up으로 자원을 반환하는 과정에서
lock이 걸리고 풀고를 반복하는 과정에서 정렬이 제대로 되어있지 않을 수 있다고 한다.
그래서 thread_unblock을 하기 전에 sema->waiters를 정렬하는 코드를 추가했다.
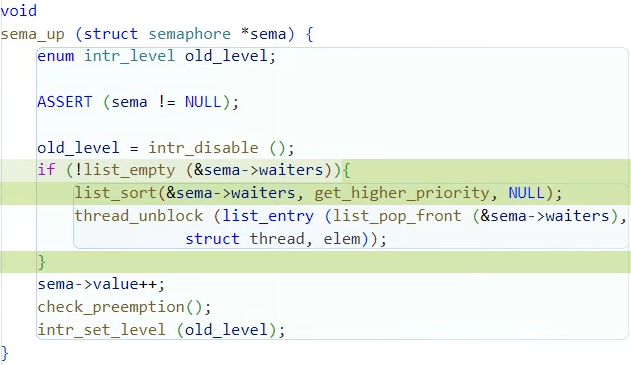
void
sema_up (struct semaphore *sema) {
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (sema != NULL);
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (!list_empty (&sema->waiters)){
list_sort(&sema->waiters, get_higher_priority, NULL);
thread_unblock (list_entry (list_pop_front (&sema->waiters),
struct thread, elem));
}
sema->value++;
check_preemption();
intr_set_level (old_level);
}void cond_wait(...)
위에서 작성한 sema_higher_priority을 사용해
cond->waiters속 semaphore_elem를
저장된 스레드의 우선순위를 기준으로 내림차순이 되도록 삽입하자.
기존 코드"list_push_back (&cond->waiters, &waiter.elem);"는
주석처리로 지웠음을 표시했다.
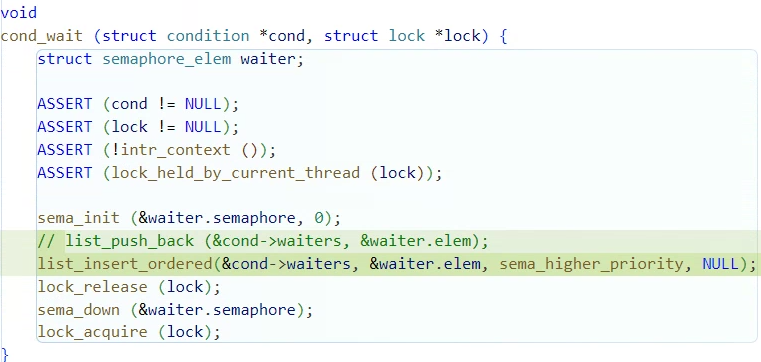
void
cond_wait (struct condition *cond, struct lock *lock) {
struct semaphore_elem waiter;
ASSERT (cond != NULL);
ASSERT (lock != NULL);
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
ASSERT (lock_held_by_current_thread (lock));
sema_init (&waiter.semaphore, 0);
list_insert_ordered(&cond->waiters, &waiter.elem, sema_higher_priority, NULL);
lock_release (lock);
sema_down (&waiter.semaphore);
lock_acquire (lock);
}void cond_signal(...)
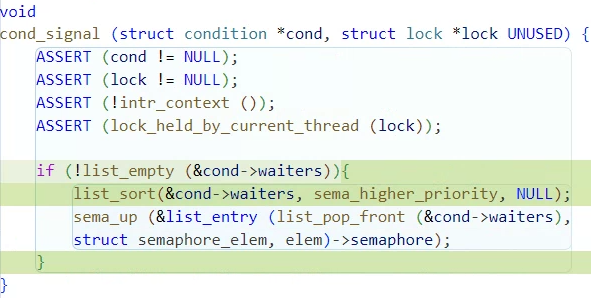
condition 포인터변수 cond가 자원 사용을 마치고 sema_up을 실행해 자원을 반환하기 전에
list_sort에 sema_higher_priority를 사용해서 우선순위를 내림차순에 따라
정렬해줘야한다. 대부분의 경우 괜찮지만 간혹 정렬하지 않으면 sema_down으로
공유자원을 차지한 unblock된 스레드와 기존 waiters의 스레드와 우선순위가 바뀌어
오류가 발생할 수 있다고 한다.
정렬을 빼면 어떻게 되는지는 구체적으로 정렬을 왜 해야하는지는
나중에 더 자세히 알아보도록 하자.
오류 1 error: dereferencing pointer to incomplete type
컴파일하려고 보니 에러가 발생했다.
../../include/lib/stddef.h:5:55: error: dereferencing pointer to incomplete type ‘struct semaphore_elem’

../../include/lib/stddef.h:5:55: error: dereferencing pointer to incomplete type ‘struct semaphore_elem’
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *) 0)->MEMBER)
^
../../include/lib/kernel/list.h:105:5: note: in expansion of macro ‘offsetof’
- offsetof (STRUCT, MEMBER.next)))
^~~~~~~~
../../threads/synch.c:51:29: note: in expansion of macro ‘list_entry’
struct semaphore_elem *a = list_entry(a_, struct semaphore_elem, elem);
^~~~~~~~~~
../../Make.config:33: recipe for target 'threads/synch.o' failederror: dereferencing pointer to incomplete type ‘struct semaphore_elem’
semaphore_elem 구조체가 불완전하게 선언되어있다는 건데
아무래도 synch.c/struct semaphore_elem가 선언되기 전에
위에 정렬하기 위해 작성한 비교함수 sema_higher_priority(...)에서
호출되기 때문에 에러가 발생한 거라 생각했다.
그래서 구조체 원형을 미리 선언하는 등 별의별 시도를 다했지만 여전히 에러가 발생해서
결국 synch.c파일의 struct semaphore_elem를 synch.h파일로 옮겨줬다.
synch.c와 synch.h 둘다 적으면 redefinition type 에러가 발생한다.
synch.c 맨위나 synch.h에 적어놓도록 하자.
그리고 보통 구조체는 .h 헤더파일에 적어놓지 않나 싶은데
PintOS 처음 받을 때부터 synch.c파일에 250줄 근처에 적혀있었다.

오류 수정 2 - thread.c/void check_preemption(void)
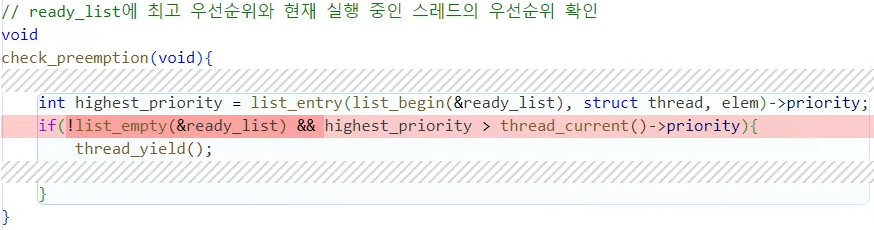
우선순위를 조정해줘야하는 경우에 확인하는 함수인데 논리적 오류가 있어서 수정했다.
기존 방식은 만약 ready_list가 비어있는 경우 highest_priority를 구하는 과정에서
에러가 발생할 여지가 있었다.
그래서 ready_list가 비어있지 않은 경우에만 동작하도록 변경해줬다.
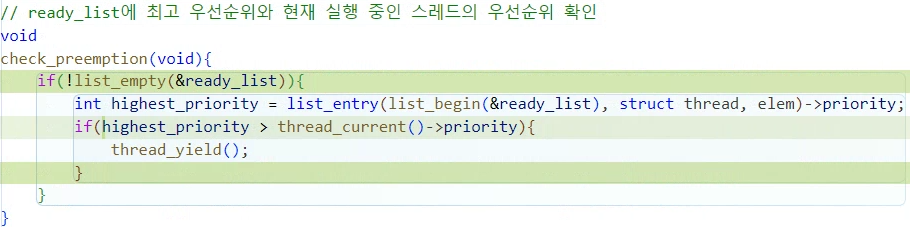
// ready_list에 최고 우선순위와 현재 실행 중인 스레드의 우선순위 확인
void
check_preemption(void){
if(!list_empty(&ready_list)){
int highest_priority = list_entry(list_begin(&ready_list), struct thread, elem)->priority;
if(highest_priority > thread_current()->priority){
thread_yield();
}
}
}오류 수정 3 - thread.c/함수 prototype 선언
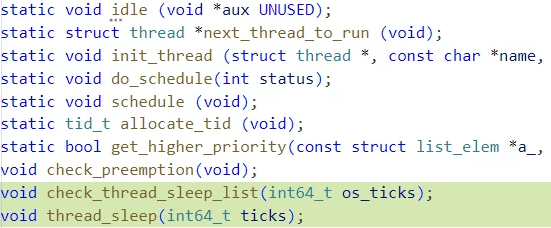
thread.c파일에 함수 원형을 선언하지 않아서 컴파일 에러가 발생했다.
추가 해주도록 하자.
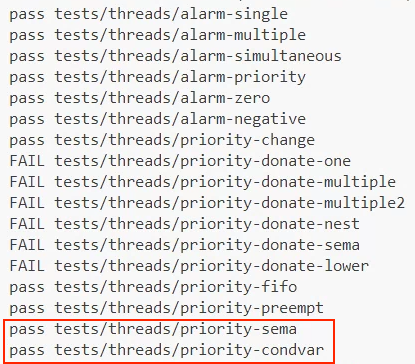
구현 step 2 테스트 결과
이번에도 마찬가지로 mlfqs는 제외하고 테스트를 진행했다.
sema와 condvar가 성공적으로 통과했다!!
다음 글
이제 다음 글에서 남은 priority donnation을 구현해보도록 하자.
