2022.6.15 torch
학습한 내용
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
import cv2
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
from torchvision import transforms, utils
from PIL import Image
import torch.optim as optim
import torch.nn as nn
import torchvision
from torchvision import datasets, models, transforms
from timeit import default_timer as timer
classes = ['Downdog', 'Goddess', 'Plank', 'Tree', 'Warrior2']
"""1. 데이터 비율 확인 체크"""
def data_check(path="./dataset/YogaPoses"):
count_dit = {}
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
if files != [] and str(root.split("\\")[-1]) in classes:
#파일이 존재하고 root.split한값중에 마지막값이 classes에 있으면
count_dit[str(root.split('\\')[-1])] = len(files)
#files의 갯수를 count_dit에 넣는다 key:value
#각 클래스별로 파일이 몇개씩 있는지 확인
return count_dit
counts = data_check()
#{'Downdog': 196, 'Goddess': 199, 'Plank': 197, 'Tree': 198, 'Warrior2': 198}
"""2. 데이터 train val"""
def data_split(path="./dataset/YogaPoses", split_predictions=0.1):
train_dict = {}
valid_dict = {}
counts = data_check(path)
for root, dirs, files in os.walk(path):
if files != [] and str(root.split('\\')[-1]) in classes:
file_paths = [os.path.join(root, files[i])
for i in range(len(files))]
#파일경로 지정
vaild_idex = np.random.randint(
low=0, high=len(files), size=int(len(files)*split_predictions))
#최대최소사이에서 정수를 파일개수의 10%만큼
#[ 79 122 171 155 76 63 154 72 49 94 114 23 37 17 154 156 152 192 108]
train_idex = list(set(range(0, len(files))) - set(vaild_idex))
# valid에서 뽑아간것 제외 나머지 90%
train_dict[str(root.split('\\')[-1])] = [file_paths[idx]
for idx in train_idex]
valid_dict[str(root.split('\\')[-1])] = [file_paths[idx]
for idx in vaild_idex]
return train_dict, valid_dict
# train_dict,val_dict에 key:value형식으로 file_path를 넣어줌
train_dict, valid_dict = data_split()
# values() -> 딕셔너리 값만 가져오는 방법
print('training data sizes : ', [len(l) for l in train_dict.values()])
print('validation data sizes : ', [len(l) for l in valid_dict.values()])
# dataset class
class YogaData(Dataset):
"""Chess Piece Dataset class"""
def __init__(self, data_dict, transform=None):
"""
Args:
data_dict (dict): dictionary with class as key and the corresponding paths to the data of that class
"""
self.data_dict = data_dict
self.transform = transform
def __len__(self):
return sum([len(l) for l in self.data_dict.values()])
def __getitem__(self, idx):
counts = [len(l) for l in self.data_dict.values()]
#data_dict에 각 key별로 몇개씩 데이터가 있는지
#[179, 180, 179, 180, 180]
sum_counts = list(np.cumsum(counts))
#[179, 359, 538, 718, 898] 누적합
sum_counts = [0] + sum_counts + [np.inf]
#데이터의 처음과 끝에 0과 inf추가
#[0, 179, 359, 538, 718, 898, inf]
for c, v in enumerate(sum_counts):
if idx < v:
i = (idx - sum_counts[c - 1]) - 1
break
#idx 894 i 177
#idx 895 i -1
#idx는 총 이미지 개수고 idx가 몇인지에 따라 몇번째폴더의 몇번째 이미지인지 i에 저장
label = list(self.data_dict.keys())[c - 1]
img = Image.open(self.data_dict[str(label)][i]).convert('RGB')
#for문 밖인데 c랑i는 어떻게 동작하는거지
#data_dict에들어있는 label(key)에 대한 i번째파일 이미지주소
if self.transform:
img = self.transform(img)
#transform이 존재하면 변환하는건가?
return img, classes.index(str(label))
data_transform = transforms.Compose([
transforms.RandomVerticalFlip(),
transforms.RandomAdjustSharpness(sharpness_factor=1.5),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ColorJitter(),
transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor()])
data_train = YogaData(train_dict, transform=data_transform)
data_valid = YogaData(valid_dict, transform=data_transform)
t_idx = np.random.randint(0, len(data_train))
v_idx = np.random.randint(0, len(data_valid))
print("Total Number of training images : ", len(data_train))
print("Total Number of validation images : ", len(data_valid))
t_img, t_label = data_train[t_idx]
v_img, v_label = data_valid[v_idx]
# # show train image check
# plt.figure(figsize=(8, 3))
# plt.subplot(121)
# plt.imshow(t_img.numpy().transpose(1, 2, 0))
# plt.title(f'Traning Data; class = {classes[t_label]}')
# plt.subplot(122)
# plt.imshow(v_img.numpy().transpose(1, 2, 0))
# plt.title(f'Validation Data; class = {classes[v_label]}')
# plt.show()
# definning data loader
train_loader = DataLoader(data_train, batch_size=50, shuffle=True)
valid_loader = DataLoader(data_valid, batch_size=50, shuffle=False)
# for i_batch, sample_batched in enumerate(train_loader):
# # print(i_batch, sample_batched[0].size(),sample_batched[1])
# # sample_batched[0]은 이미지 feature batch_size가 50이므로 torch.size는 50
# # sample_batched[1]은 label
# # print(type(sample_batched[0]))
# break
# specify loss function (categorical cross-entropy)
criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# Load the pretrained model from pytorch
# vgg16 = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
# # Freeze training for all "features" layers
# for param in vgg16.features.parameters():
# param.requires_grad = False
# n_inputs = vgg16.classifier[6].in_features
# # add last linear layer (n_inputs -> 5 flower classes)
# # new layers automatically have requires_grad = True
# last_layer = nn.Linear(n_inputs, len(classes))
# vgg16.classifier[6] = last_layer
# # 마지막layer 의 입출력값 변경
# # if GPU is available, move the model to GPU
# train_on_gpu = torch.cuda.is_available()
# if train_on_gpu:
# print("training on gpu...")
# device = torch.device('mps')
# vgg16.to(device)
# # vgg16.cuda()
# else:
# vgg16
# print("no gpu found.")
# # check to see that your last layer produces the expected number of outputs
# print(vgg16.classifier[6].out_features)
# print(vgg16)
train_on_gpu = torch.cuda.is_available()
def base_model_build():
# Load the pretrained model from pytorch
vgg16 = models.vgg16(pretrained=True)
# print out the model structure
# print(vgg16)
# Freeze training for all "features" layers
for param in vgg16.features.parameters():
param.requires_grad = False
import torch.nn as nn
n_inputs = vgg16.classifier[6].in_features
# add last linear layer (n_inputs -> 5 flower classes)
# new layers automatically have requires_grad = True
last_layer = nn.Linear(n_inputs, len(classes))
vgg16.classifier[6] = last_layer
# if GPU is available, move the model to GPU
if train_on_gpu:
print("training on gpu...")
vgg16.cuda()
else:
vgg16
print("no gpu found.")
# check to see that your last layer produces the expected number of outputs
# print(vgg16.classifier[6].out_features)
# print(vgg16)
return vgg16
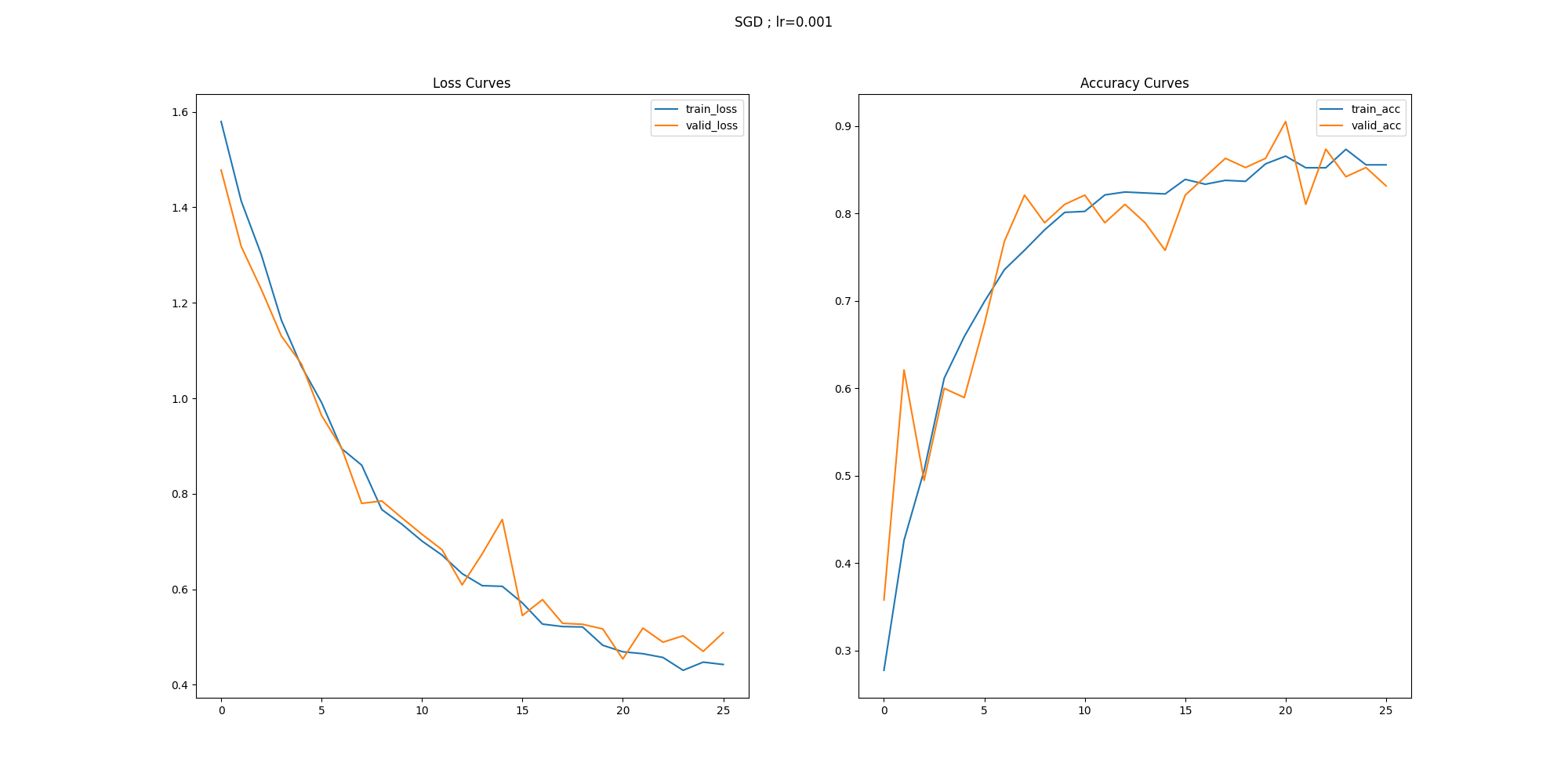
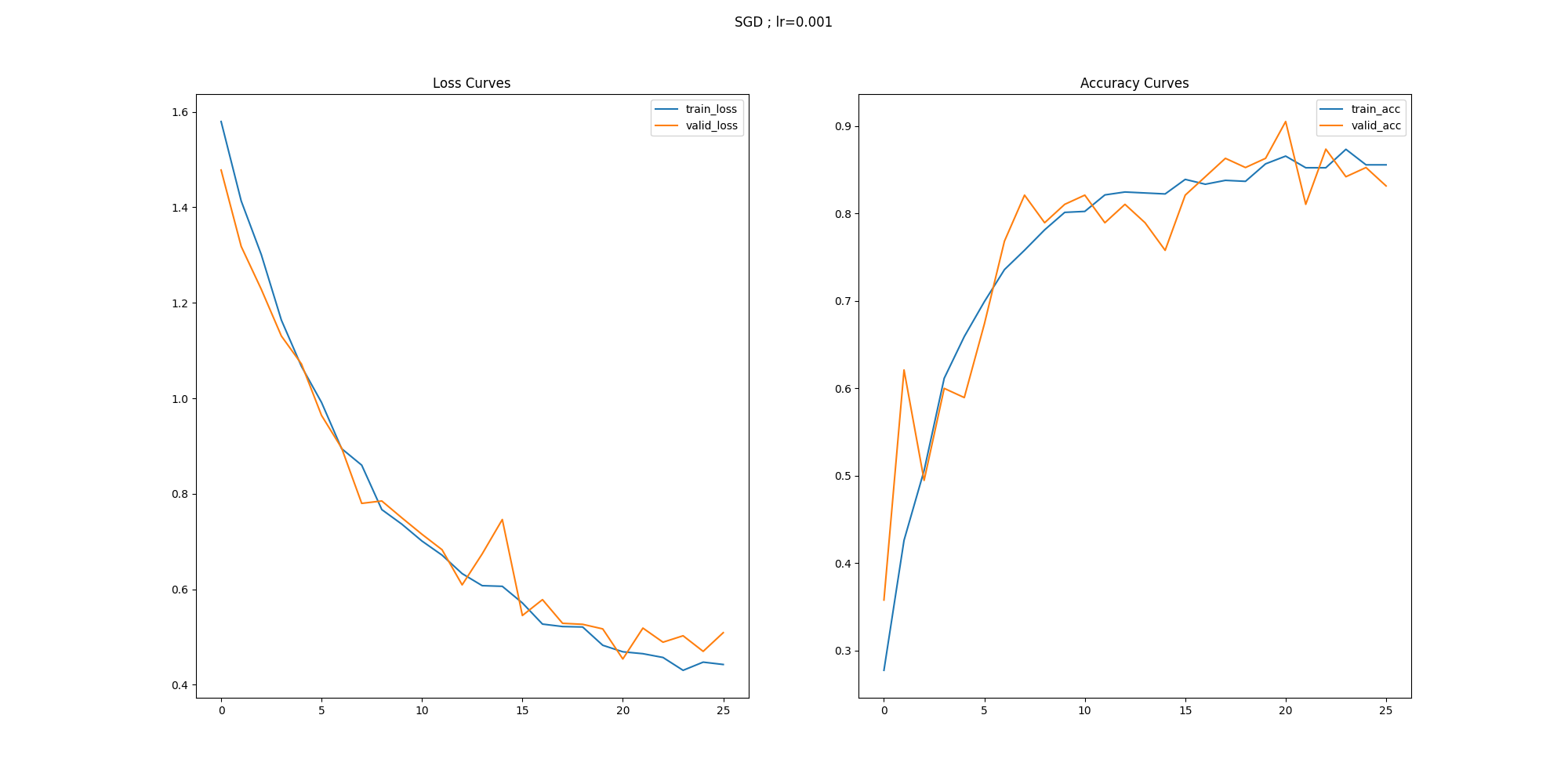
def loss_acc_visuaize(history, optim, path):
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
plt.suptitle(str(optim))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.plot(history['train_loss'], label='train_loss')
plt.plot(history['valid_loss'], label='valid_loss')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Loss Curves')
plt.subplot(122)
plt.plot(history['train_acc'], label='train_acc')
plt.plot(history['valid_acc'], label='valid_acc')
plt.legend()
plt.title('Accuracy Curves')
plt.savefig(str(path) + 'loss_acc.png')
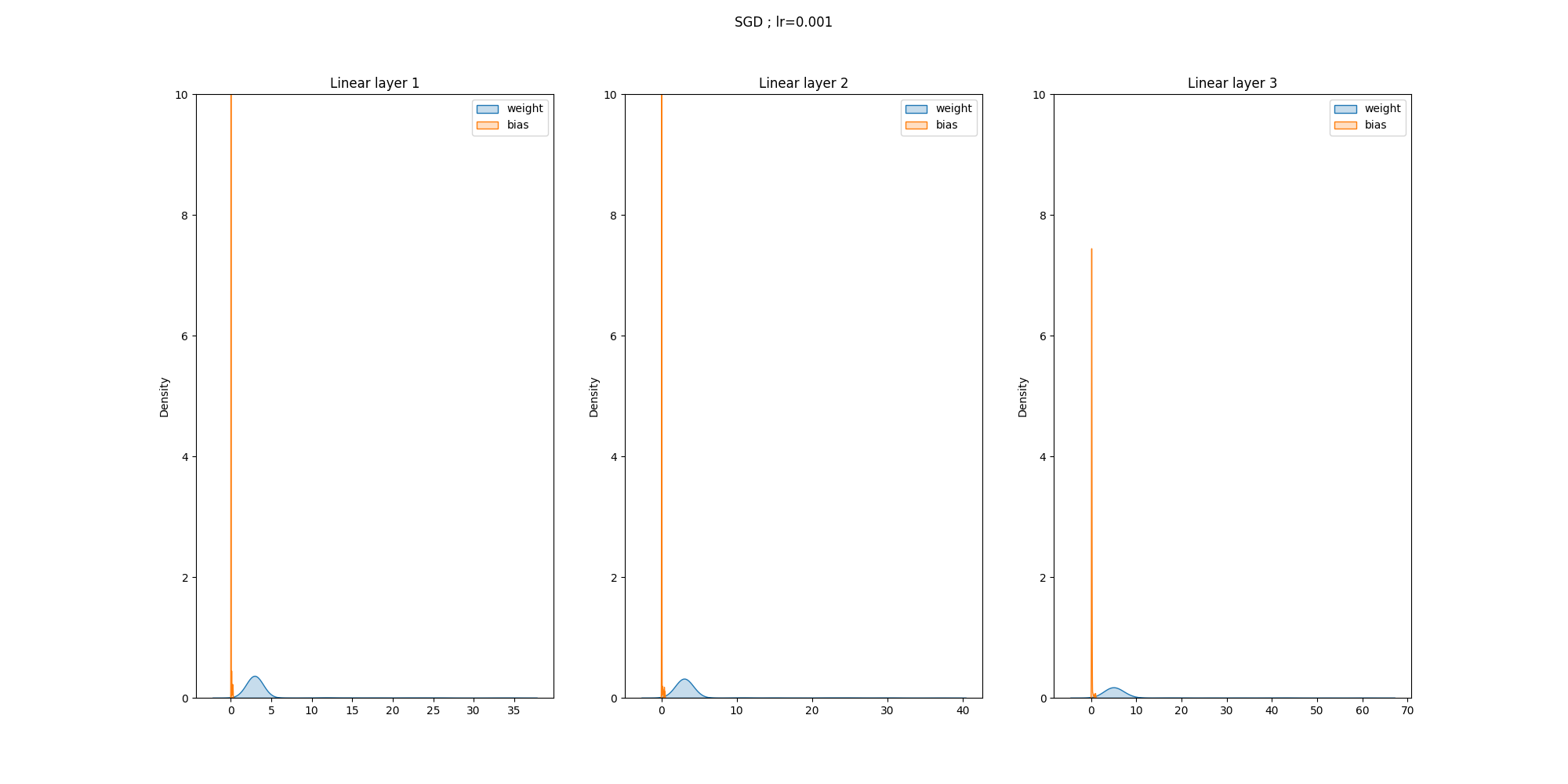
def grad_visualize(history, optim, path, ylimit=10):
# gadient norm distribution
import seaborn as sns
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
plt.suptitle(str(optim))
plt.subplot(131)
sns.kdeplot(weight_grads1, shade=True)
sns.kdeplot(bias_grads1, shade=True)
plt.legend(['weight', 'bias'])
plt.title('Linear layer 1')
# plt.gca().set_xlim(left=0)
plt.ylim(0, ylimit)
plt.subplot(132)
sns.kdeplot(weight_grads2, shade=True)
sns.kdeplot(bias_grads2, shade=True)
plt.legend(['weight', 'bias'])
plt.title('Linear layer 2')
# plt.gca().set_xlim(left=0)
plt.ylim(0, ylimit)
plt.subplot(133)
sns.kdeplot(weight_grads3, shade=True)
sns.kdeplot(bias_grads3, shade=True)
plt.legend(['weight', 'bias'])
plt.title('Linear layer 3')
# plt.gca().set_xlim(left=0)
plt.ylim(0, ylimit)
plt.savefig(str(path) + 'grad_norms.png')
def visual_predict(model, data=data_valid):
c = np.random.randint(0, len(data))
img, label = data[c]
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
# Model outputs log probabilities
out = model(img.view(1, 3, 224, 224))
out = torch.exp(out)
print(out)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
plt.subplot(121)
plt.imshow(img.numpy().transpose((1, 2, 0)))
plt.title(str(classes[label]))
plt.subplot(122)
plt.barh(classes, out.cpu().numpy()[0])
plt.show()
plt.savefig('./vp.png')
def class_accuracies(model, data_dict=valid_dict, classes=classes):
accuracy_dict = {}
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval()
for c in data_dict.keys():
correct_count = 0
total_count = len(data_dict[str(c)])
gt = classes.index(str(c))
for path in data_dict[str(c)]:
# print(path)
im = Image.open(path).convert('RGB')
# im.show()
im = transforms.ToTensor()(im)
im = transforms.Resize((224, 224))(im)
out = model(im.view(1, 3, 224, 224))
# print(out)
out = torch.exp(out)
pred = list(out.cpu().numpy()[0])
# print(pred)
pred = pred.index(max(pred))
# print(pred,gt)
if gt == pred:
correct_count += 1
print(f"Accuracy for class {str(c)} : ",
correct_count / total_count)
accuracy_dict[str(c)] = correct_count / total_count
return accuracy_dict
vgg16 = base_model_build()
optimizer_sgd = optim.SGD(vgg16.classifier.parameters(), lr=0.001)
model = vgg16
criterion = criterion
optimizer = optimizer_sgd
train_loader = train_loader
valid_loader = valid_loader
save_file_name = './vgg16-transfer-sgd-lr=0.001'
max_epochs_stop = 2
n_epochs = 10
print_every = 1
"""Train a PyTorch Model
Params
--------
model (PyTorch model): cnn to train
criterion (PyTorch loss): objective to minimize
optimizer (PyTorch optimizier): optimizer to compute gradients of model parameters
train_loader (PyTorch dataloader): training dataloader to iterate through
valid_loader (PyTorch dataloader): validation dataloader used for early stopping
save_file_name (str ending in '.pt'): file path to save the model state dict
max_epochs_stop (int): maximum number of epochs with no improvement in validation loss for early stopping
n_epochs (int): maximum number of training epochs
print_every (int): frequency of epochs to print training stats
Returns
--------
model (PyTorch model): trained cnn with best weights
history (DataFrame): history of train and validation loss and accuracy
"""
# Early stopping intialization
epochs_no_improve = 0
valid_loss_min = np.Inf
valid_max_acc = 0
history = []
bias_grads1 = []
weight_grads1 = []
bias_grads2 = []
weight_grads2 = []
bias_grads3 = []
weight_grads3 = []
# Number of epochs already trained (if using loaded in model weights)
try:
print(f'Model has been trained for: {model.epochs} epochs.\n')
except:
model.epochs = 0
print(f'Starting Training from Scratch.\n')
overall_start = timer()
# Main loop
for epoch in range(n_epochs):
# keep track of training and validation loss each epoch
train_loss = 0.0
valid_loss = 0.0
train_acc = 0
valid_acc = 0
# Set to training
model.train()
start = timer()
# Training loop
for ii, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
# Tensors to gpu
if train_on_gpu:
data, target = data.cuda(), target.cuda()
# Clear gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Predicted outputs are log probabilities
output = model(data)
# Loss and backpropagation of gradients
loss = criterion(output, target)
loss.backward()
# Update the parameters
optimizer.step()
weight_grads1.append(np.linalg.norm(
model.classifier[0].weight.grad.cpu().numpy()))
bias_grads1.append(np.linalg.norm(
model.classifier[0].bias.grad.cpu().numpy()))
weight_grads2.append(np.linalg.norm(
model.classifier[3].weight.grad.cpu().numpy()))
bias_grads2.append(np.linalg.norm(
model.classifier[3].bias.grad.cpu().numpy()))
weight_grads3.append(np.linalg.norm(
model.classifier[6].weight.grad.cpu().numpy()))
bias_grads3.append(np.linalg.norm(
model.classifier[6].bias.grad.cpu().numpy()))
# Track train loss by multiplying average loss by number of examples in batch
train_loss += loss.item() * data.size(0)
# Calculate accuracy by finding max log probability
_, pred = torch.max(output, dim=1)
correct_tensor = pred.eq(target.data.view_as(pred))
# Need to convert correct tensor from int to float to average
accuracy = torch.mean(correct_tensor.type(torch.FloatTensor))
# Multiply average accuracy times the number of examples in batch
train_acc += accuracy.item() * data.size(0)
# Track training progress
print(
f'Epoch: {epoch}\t{100 * (ii + 1) / len(train_loader):.2f}% complete. {timer() - start:.2f} seconds elapsed in epoch.',
end='\r')
# After training loops ends, start validation
else:
model.epochs += 1
# Don't need to keep track of gradients
with torch.no_grad():
# Set to evaluation mode
model.eval()
# Validation loop
for data, target in valid_loader:
# Tensors to gpu
if train_on_gpu:
data, target = data.cuda(), target.cuda()
# Forward pass
output = model(data)
# Validation loss
loss = criterion(output, target)
# Multiply average loss times the number of examples in batch
valid_loss += loss.item() * data.size(0)
# Calculate validation accuracy
_, pred = torch.max(output, dim=1)
correct_tensor = pred.eq(target.data.view_as(pred))
accuracy = torch.mean(
correct_tensor.type(torch.FloatTensor))
# Multiply average accuracy times the number of examples
valid_acc += accuracy.item() * data.size(0)
# Calculate average losses
train_loss = train_loss / len(train_loader.dataset)
valid_loss = valid_loss / len(valid_loader.dataset)
# Calculate average accuracy
train_acc = train_acc / len(train_loader.dataset)
valid_acc = valid_acc / len(valid_loader.dataset)
history.append([train_loss, valid_loss, train_acc, valid_acc])
print(history)
# Print training and validation results
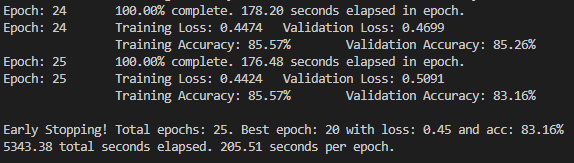
if (epoch + 1) % print_every == 0:
print(
f'\nEpoch: {epoch} \tTraining Loss: {train_loss:.4f} \tValidation Loss: {valid_loss:.4f}'
)
print(
f'\t\tTraining Accuracy: {100 * train_acc:.2f}%\t Validation Accuracy: {100 * valid_acc:.2f}%'
)
# Save the model if validation loss decreases
if valid_loss < valid_loss_min:
# Save model
torch.save(model.state_dict(), save_file_name)
# Track improvement
epochs_no_improve = 0
valid_loss_min = valid_loss
valid_best_acc = valid_acc
best_epoch = epoch
# Otherwise increment count of epochs with no improvement
else:
epochs_no_improve += 1
# Trigger early stopping
if epochs_no_improve >= max_epochs_stop:
print(
f'\nEarly Stopping! Total epochs: {epoch}. Best epoch: {best_epoch} with loss: {valid_loss_min:.2f} and acc: {100 * valid_acc:.2f}%'
)
total_time = timer() - overall_start
print(
f'{total_time:.2f} total seconds elapsed. {total_time / (epoch + 1):.2f} seconds per epoch.'
)
# Load the best state dict
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(save_file_name))
# Attach the optimizer
model.optimizer = optimizer
# Format history
history = pd.DataFrame(
history,
columns=[
'train_loss', 'valid_loss', 'train_acc',
'valid_acc'
])
break
# Attach the optimizer
model.optimizer = optimizer
# Record overall time and print out stats
total_time = timer() - overall_start
print(
f'\nBest epoch: {best_epoch} with loss: {valid_loss_min:.2f} and acc: {100 * valid_acc:.2f}%'
)
print(
f'{total_time:.2f} total seconds elapsed. {total_time / (epoch + 1):.2f} seconds per epoch.'
)
# Format history
history = pd.DataFrame(
history,
columns=['train_loss', 'valid_loss', 'train_acc', 'valid_acc'])
loss_acc_visuaize(history, optim='SGD ; lr=0.001', path='./')
grad_visualize(history, optim='SGD ; lr=0.001', path='./')
model = base_model_build()
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("./vgg16-transfer-sgd-lr=0.001"))
visual_predict(model=model)
sgd_lr001_dict = class_accuracies(model=model)
데이터를 나누고 file path를 연결하고 transform으로 필요한 변환을 하고 vgg16모델로 output layer의 크기를 label종류인 5로 변경 loss, accuracy , gradient 그래프
실행결과
학습한 내용 중 어려웠던 점 또는 해결못한 것들
코드가 길어지면서 이해하기가 어렵다
해결방법 작성
한줄씩 print해가며 이해하는중
학습 소감
gpu가 없어서 너무 느리다 ㅜㅜ;