-
기본적인 함수의 형태와 현대적인 함수의 형태.
//객체 기본값을지정. 코드를 명확하게 작성해서 보기 편하게 하기 위해서 const test = function (name, age, color) { return `${name} : ${age} : ${color}` } console.log(test('구름', 8, '빨강')) //아래와 같이 코딩을 하기 시작. 읽기가 훨씬 편함. const test = function (object) { return `${object.name} : ${object.age} : ${object.color}` } console.log(test({ name: '구름', age: 8, color: '빨강' })) -
객체 기본 매개변수 도입.
const test = function (name, age, color, status = '이상없음') { return `${name} : ${age} : ${color} : ${status}` } console.log(test('구름', 8, '빨강')) //>> 구름 : 8 : 빨강 : 이상없음그럼 현대적 형태의 함수에선 어떻게 표현할까?
const test = function (object) { // 과거(1) object.status = object.status !== undefined ? object.status : '이상없음' // 과거(2) object.status = object.status ? object.status : '이상없음' // 과거(3) object.status = object.status || '이상없음' // 현대(1) object = {status: '이상없음', ...object} // 현대(2) fun = function ({name, age, color, status = '이상없음'}){ return `${name} : ${age} : ${color} : ${status}` } return `${object.name} : ${object.age} : ${object.color} : ${object.status}` } console.log(test({ name: '구름', age: 8, color: '빨강', status: '이상없음' // 어떤 데이터가 거의 일정한 값을 가지고 간다고 할 때, 이 값을 고정시켜주는 게 좋다. }))<과거 1>
객체의 속성에 값이 없으면 undefined를 출력하는 것에 착안하여 아래와 같이 만들었음.const cloud = { name: '구름', age: 8, color: '빨강', } console.log(cloud.status) // >>undefined 없는 값을 찾으려면 unde를 출력. //이를 바탕으로 cloud.status = cloud.status !== undefined? cloud.status : '이상없음'<과거 2>
cloud.status에 빈문자열이나 0과 같은 false로 변환되는 값이 오지않을 때 사용가능.
'cloud.status 가 있는가? 있으면 cloud.status를 넣고 아니면 이상없음을 넣어라.'cloud.status = cloud.status ? cloud.status : '이상없음'<과거 3>
짧은 조건문.cloud.status = cloud.status || '이상없음'
※짧은 조건문 다시 알아보기.
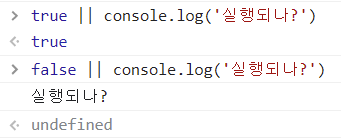
<논리합>
불 표현식 || 불 표현식이 거짓일 때 실행할 문장
>> 불 표현식이 참이면 우변을 실행하지 않고, 불 표현식이 거짓이면 우변이 참인지 거짓인지 확인하여 참이면 실행.
<논리곱>
양변이 모두 참일 때만 참이기 때문에false && 000는 항상 거짓.
즉, 좌변이 거짓이면, 우변을 실행하지 않는다.
<현재 1>
전개 연산자로 객체 기본 매개변수 지정하기.object = {status: '이상없음', ...object}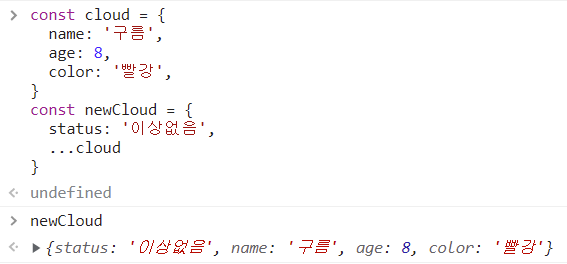
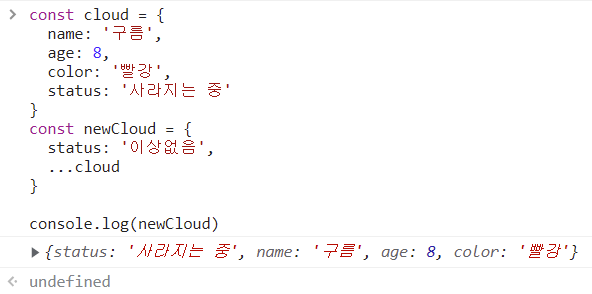
...cloud가 status보다 위에 있으면 다른 값이 나오기 때문에 위치에 신경써야함.
<현재 2>
기본 객체 매개변수 함수const test = function ({ name, age, color, status = '이상없음' }) { return `${name} : ${age} : ${color} : ${status}` } console.log(test({ name: '구름', age: 8, color: '빨강', }))<추가>
/// 현재 1번을 사용한다면 이런 형식이 된다. const test = function (object) { object = {status: '이상없음', ...object} return `${object.name} : ${object.age} : ${object.color} : ${object.status}` } console.log(test({ name: '구름', age: 8, color: '빨강', })) //////////// 아래처럼 변환 const test = function (object) { const {name, age, color, status} = {status: '이상없음', ...object} return `${name} : ${age} : ${color} : ${status}` } console.log(test({ name: '구름', age: 8, color: '빨강', }))
