
이번 포스팅은 annotation을 사용하여 Spring에서 제공하는 validation을 사용하는 방법을 사용해 볼 것이다.
Important Java bean validations
| NO. | annotation | 뜻 | 예시 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | @NotNull | value의 값이 NUll일 수 없다. (but "", ' '은 허용하기 때문에 Null이 아닐경우에만 사용) | @NotNull(message = "이름은 Null 일 수 없습니다!") |
| 2 | @Size | value의 길이를 설정한다. ( String, Collection, Map, Array 속성에 적용 가능) | @Size(min = 3, max = 15) |
| 3 | @Min | 값의 최소값을 설정한다. | @Min(1) |
| 4 | @Max | 값의 최대값을 설정한다. | @Max(10) |
| 5 | 이메일 주소의 값설정, @Email 은 이메일 형식이 아닌경우 예외를 던지도록 설정 (@Email은 null을 유효하다고 판단) | @Email private String email; | |
| 6 | @NotEmpty | null 과 "" 둘다 금지 (but " "(공백) 허용 | |
| 7 | @NotBlank | null 과 "" 과 " " 모두 허용하지 않는다 |
@NotNull, @NotEmpty, @NotBlank 차이점
- 강도가 높은것 @NotNull< @NotEmpty < @NotBlank
- 이들 중 어떤 것을 허용하는 가? => null, "", " "(공백)
| @NotNull | @NotEmpty | @NotBlank |
|---|---|---|
| "", " "(공백) 허용 | " "(공백) 허용 | 모두 허용하지 않음 |
@Test
public void 사용자_이름_DTO_NotNull_체크() {
UserLoginRequestDto user = UserLoginRequestDto.builder()
.name(null)
.email("")
.phone(" ")
.build();
Set<ConstraintViolation<UserLoginRequestDto>> violations = validator.validate(user);
assertThat(violations.size()).isEqualTo(3);
}이 코드에서 어떤 어노테이션을 사용하는지에 따라서 허용하는 항목을 말하시오
- @NotNull
- @NotEmpty
- @NotBlank
개발 단계
- Maven 애플리케이션 생성
- 의존성 추가 - pom.xml
- 프로젝트 구조
- Spring 구성 - MVCConfig.java
- Servlet Container 선언 - SpringMvcDispatcherServletInitializer.java
- Model Class -Customer.java
- Controller Class - CustomerController.java
- Views -customer-form & customer-confirmation.jsp
- 실행 (Tomcat)
- 결과
단계 설명
1. Maven 애플리케이션 생성
인텔리제이에서 Maven프로젝트의 webapp 선택수 프로젝트 생성
2. 의존성 추가 - pom.xml
<project
xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>net.javaguides.springmvc</groupId>
<artifactId>springmvc5-form-validation</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springmvc5-form-validation Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<failOnMissingWebXml>false</failOnMissingWebXml>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Hibernate Validator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hibernate</groupId>
<artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId>
<version>5.4.1.Final</version>
</dependency>
<!-- JSTL Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp.jstl-api</artifactId>
<version>1.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>taglibs</groupId>
<artifactId>standard</artifactId>
<version>1.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- JSP Dependency -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.1</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.30</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>hibernate-validator를 의존성 추가하여 <form:errors>를 사용하여 에러 메세지 설정하여 출력할 수 있다.
3. 프로젝트 구조
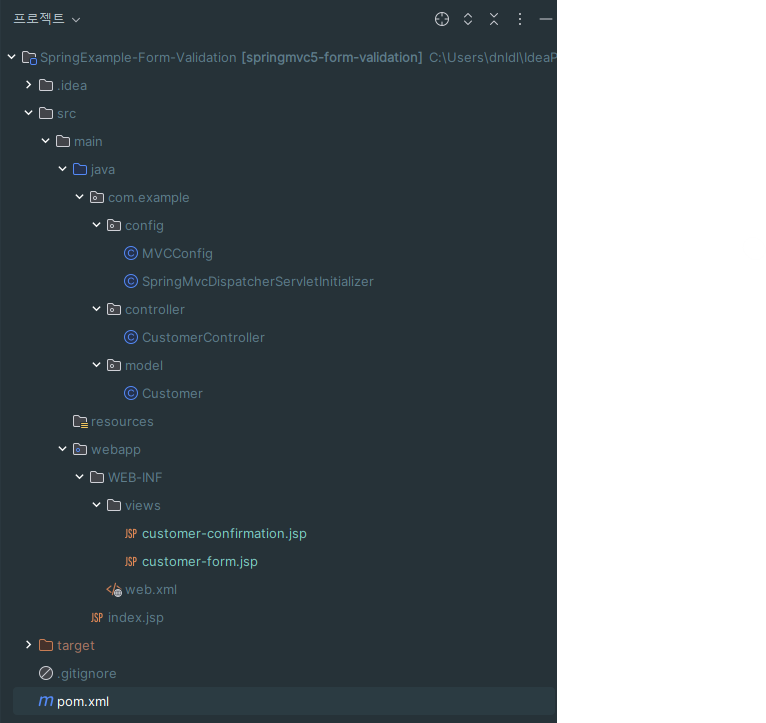
4. Spring 구성 - MVCConfig.java
이전 포스팅과 같은 코드 ViewResolver에서 view의 경로를 설정해준다.
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.EnableWebMvc;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.view.JstlView;
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.example"})
public class MVCConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Bean
public InternalResourceViewResolver resolver(){
InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver();
resolver.setViewClass(JstlView.class);
resolver.setPrefix("/WEB-INF/views/");
resolver.setSuffix(".jsp");
return resolver;
}
}
5. Servlet Container 선언 - SpringMvcDispatcherServletInitializer.java
이전 포스팅의 코드와 동일 : DispatcherServlet을 생성하여 지정해준다.
package com.example.config;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.support.AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer;
public class SpringMvcDispatcherServletInitializer extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer {
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() {
return null;
}
//getRootConfigClasses() 메소드에서는 ContextLoaderListener가 생성한 애플리케이션 컨텍스트를 설정하는 데 사용된다.
@Override
protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() {
return new Class[]{
MVCConfig.class
};
}
//getServletConfigClasses()는 DispatcherServlet이 애플리케이션 컨텍스트를 WebConfig 설정 클래스(java 설정)에서 정의된 Bean으로 로딩하도록 되어있다.
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{
"/"
};
}
// getServletMapping()는 DispatcherServlet이 매핑되기 위한 하나 혹은 여러 개의 패스를 지정한다. => 현재 "/"만 설정되어 있으며 애플리케이션으로 들어오는 모든 요청을 처리
}
6. Model Class -Customer.java
이번 포스팅에서 가장 많이 추가된 부분 annotation를 적용하여 값의 길이와 허용값을 정함
package com.example.model;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import org.hibernate.validator.constraints.Email;
import javax.validation.constraints.*;
@Getter
@Setter
public class Customer {
private String firstName;
@NotNull (message = "is required")
@Size(min =1 , message = "is required")
private String lastName;
@NotNull(message = "is required")
@Min(value=0 , message= "must be greater that or equal to zero")
@Max(value =10, message = "must be less than or equal to 10")
private Integer freePasses;
@Pattern(regexp = "^[a-zA-Z0-9]{5}", message = "only 5 chars/digits")
private String postalCode;
@NotNull(message = "is required")
@Email(message = "Invalid email! Please enter valid email")
private String email;
}
- @Pattern을 보면 regexp (정규 표현식) -> a~z,A~Z,0~9로 구성되어야하며 5글자여야한다.
- 만약 형식에 맞지않는 다면 message를 설정하여 에러에 따라서 다른 메세지가 출력되게 설정한다.
7. Controller Class - CustomerController.java
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.model.Customer;
import org.springframework.beans.propertyeditors.StringTrimmerEditor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.validation.BindingResult;
import org.springframework.web.bind.WebDataBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.InitBinder;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import javax.validation.Valid;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/customer")
public class CustomerController {
@InitBinder
public void initBinder(WebDataBinder dataBinder){
StringTrimmerEditor stringTrimmerEditor = new StringTrimmerEditor(true);
dataBinder.registerCustomEditor(String.class ,stringTrimmerEditor);
}
@RequestMapping("/showForm")
public String showForm(Model theModel){
theModel.addAttribute("customer", new Customer());
return "customer-form";
}
@RequestMapping("/processForm")
public String processForm(
@Valid @ModelAttribute("customer") Customer theCustomer,
BindingResult theBindingResult) {
if (theBindingResult.hasErrors()) {
return "customer-form";
} else {
return "customer-confirmation";
}
}
}
@Valid
-> 객체를 검증하는 annotation
코드에서의 내용은 @ModelAttribute("customer")가 유효한 객체인지 검사한다.
- spring boot version이 2.3 이상이라면 validation 의존성을 따로 추가해야 사용 가능
8. Views customer-form & customer-confirmation.jsp
customer-form (정보 입력)
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Customer Registration Form</title>
<style>
.error {
color: red
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1> Spring MVC 5 - Form Validation Example</h1>
<i>Fill out the form. Asterisk (*) means required.</i>
<br><br>
<form:form action="processForm" modelAttribute="customer">
First name:
<form:input path="firstName" />
<br><br> Last name (*):
<form:input path="lastName" />
<form:errors path="lastName" cssClass="error" />
<br><br> Free passes (*):
<form:input path="freePasses" />
<form:errors path="freePasses" cssClass="error" />
<br><br> Email (*):
<form:input path="email" />
<form:errors path="email" cssClass="error" />
<br><br> Postal Code:
<form:input path="postalCode" />
<form:errors path="postalCode" cssClass="error" />
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit" />
</form:form>
</body>
</html>cssClass = 스타일 시트에서 설정한 css 를 가져오거나 설정한다. -> 만약 에러가 뜬다면 글자를 빨간색으로 바꾼다.
customer-confirmation (결과 출력)
<%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" prefix="c" %>
<%@page isELIgnored="false" language="java" pageEncoding="UTF-8" %>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Customer Confirmation</title>
</head>
<body>
The customer is confirmed: ${customer.firstName} ${customer.lastName}
<br><br> Free passes: ${customer.freePasses}
<br><br> Email: ${customer.email}
<br><br> Postal Code: ${customer.postalCode}
</body>
</html>9. 실행 (Tomcat)
실행 경로
http://localhost:8080/springmvc5_form_validation_war/customer/showForm
10. 결과
초기 출력화면
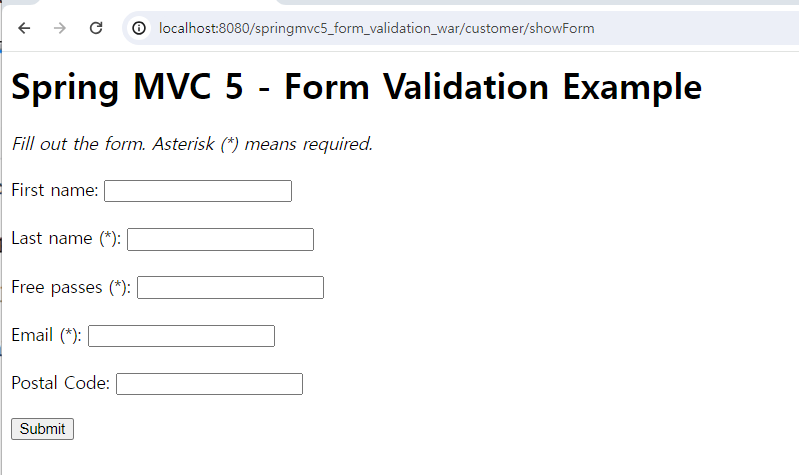
유효성 검사를 적용
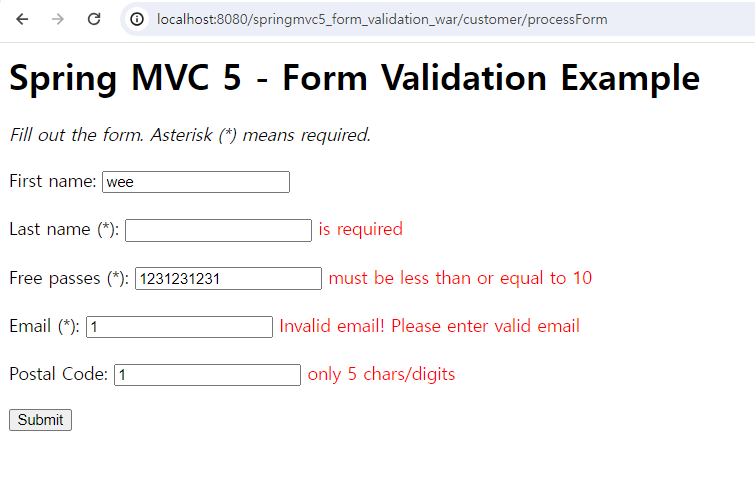
결과 페이지
참고 자료
https://www.javaguides.net/2018/10/spring-mvc-form-validation-with-annotations-tutorial.html
https://sanghye.tistory.com/36
https://offbyone.tistory.com/281
