클래스
클래스란?
객체와 클래스
- 객체(Object)
- 실생활에 존재하는 실제적인 물건 또는 개념
- 속성(Attribute)
- 객체가 가지고 있는 특성
- 메서드(Method)
- 객체가 동작(행동)할 수 있도록 하는 함수
- 클래스(Class)
- 객체가 가져야 할 기본적인 정보를 담은 코드
- 객체를 효율적으로 생성하기 위해 만들어진 구문
- 일종의 설계도
생성자 함수 vs 클래스
- 생성자 함수
- new 키워드가 생략되면 일반 함수로 호출됨
- function 키워드로 정의
- 클래스
- new 키워드 생략 시, 타입 에러 발생
- class 키워드로 정의
클래스 선언 및 객체 생성
- 클래스 선언 방식
class 클래스 이름 { // 클래스 내용 }-
예시
class Rectangle { // 클래스 내용 }
-
- 객체 생성
let 객체이름 = new 클래스이름();-
예시
class Rectangle { // 클래스 내용 } let rec1 = new Rectangle();
-
클래스 함수
클래스에 함수 추가하기
- 클래스 내부 함수 종류
- 생성자 메서드
- 프로토타입 메서드
- 정적 메서드
생성자 메서드
- 객체를 생성하고 초기화하는 메서드
- 클래스 내에 최대 1개만 존재
- 생략 가능
- 생략 시, 빈 생성자가 만들어짐
- 예시
class Rectangle {
constructor() {
// 객체 초기화
}
}- 클래스 외부에서 객체의 초기 프로퍼티 값 전달
class Rectangle {
// 생성자 메서드에 매개변수 선언
constructor(**w, h**) {
// 인스턴스 프로퍼티
this.width = w;
this.height = h;
}
}
// 객체 생성 시, 초기값 전달
let rec1 = new Rectangle(100, 200);- 생성자 메서드의 return문
-
return문은 생략해야 함
-
new 연산자가 클래스와 함께 호출되면 암묵적으로 객체를 반환해주기 때문
-
new가 return을 포함하고 있음
class Rectangle { constructor(w, h) { this.width = w; this.height = h; ~~return object;~~ } } // 객체 생성 시, 초기값 전달 let rec1 = new Rectangle(100, 200);
-
-
명시적으로 객체를 리턴하는 경우
- 객체를 만들었기 때문에 객체를 returnclass Rectangle { constructor(w, h) { this.width = w; this.height = h; **return {};** } } let rec1 = new Rectangle(100, 200); console.log(rec1); // 결과 : {} 빈 객체 리턴 -
명시적으로 다른 값을 반환하는 경우
- return값이 반환되지 않고 Rectangle이 반환
- return을 쓰나 안 쓰나 결과값 동일class Rectangle { constructor(w, h) { this.width = w; this.height = h; **return “soo”;** } } let rec1 = new Rectangle(100, 200); console.log(rec1); // 결과 : Rectangle { width: 100, height: 200 }
-
객체 값 사용하기
- 객체 값 접근
객체이름.프로퍼티이름- 예시) rec1 객체의 width 속성의 값에 접근
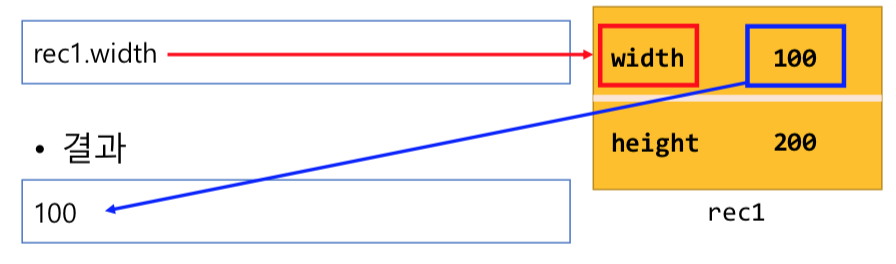
프로토타입 메서드
- 클래스 내부에서 명시적으로 정의한 메서드
- 사용자가 직접 정의한 함수
class Rectangle {
constructor(w, h) {
this.width = w;
this.height = h;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
area() {
console.log('사각형의 넓이를 구합니다.');
}
}- 프로토타입 메서드 호출
let rec1 = new rectangle(100, 200);
// 클래스 내부의 area() 메서드 호출
rec1.area();- 프로토타입 메서드 - 화살표 함수
class Rectangle {
constructor(w, h) {
this.width = w;
this.height = h;
}
area = () => {
console.log("사각형의 넓이를 구합니다.");
}
}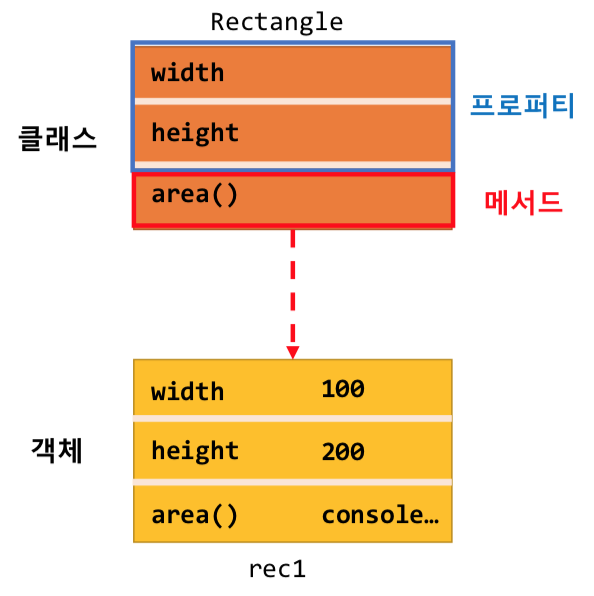
클래스는 프로퍼티(값)와 메서드(함수)로 이루어져 있다
정적 메서드
- 정적 프로퍼티와 정적 메서드
-
클래스 자체에 선언된 프로퍼티 또는 메서드
-
객체를 생성하지 않아도 호출 가능
-
객체가 아닌 클래스 자체가 갖는 값
-
선언 방법
- static 키워드를 붙여서 생성class Rectangle { **static** color = “red”; constructor(w, h) { this.width = w; this.height = h; } **static** area = () => { console.log("사각형의 넓이를 구합니다."); } }
-
- 정적 메서드 호출
-
객체가 호출하지 않고, 클래스로 호출해야 함
-
클래스.정적메서드()
Rectangle.area();
-
- 프로토타입 메서드와의 차이
구분 정적 메서드 프로토타입 메서드 프로토타입 체인 클래스 인스턴스(객체) 호출 방식 클래스로 호출 인스턴스로 호출 인스턴스 프로퍼티 참조 가능 여부
(this에 접근 가능한가)불가능 가능
접근 제어
클래스 접근 제어(캡슐화)
- 캡슐화(Encapsulation)
- 클래스 내부의 특정 프로퍼티나 메소드를 외부에서 참조하지 못하도록 숨기는 것
- 클래스 외부
- 제한된 접근 권한을 제공
- 클래스 내부
- 원하지 않은 외부의 접근에 대해 내부를 보호
- 방법
- 캡슐화를 원하는 프로퍼티나 메서드 앞에 # 기호를 붙임
- #color 변수는 rec1.color 방식으로 접근 불가
class Rectangle { **#color = "red";** constructor(w, h) { this.width = w; this.height = h; } area = () => { console.log("사각형의 넓이를 구합니다."); } } var rec1 = new Rectangle(100, 200); console.log(**rec1.color**); // 결과 : undefined - 에러 : SyntaxError: Private field '#color' must be declared in an enclosing class
class Rectangle { **#color = "red";** constructor(w, h) { this.width = w; this.height = h; } area = () => { console.log("사각형의 넓이를 구합니다."); } } var rec1 = new Rectangle(100, 200); console.log(**rec1.#color**); - 결과
-
Rectangle { width: 100, height: 200, area: [Function: area] }
class Rectangle { **#color = "red";** constructor(w, h) { this.width = w; this.height = h; } area = () => { console.log("사각형의 넓이를 구합니다."); } } var rec1 = new Rectangle(100, 200); console.log(**rec1**);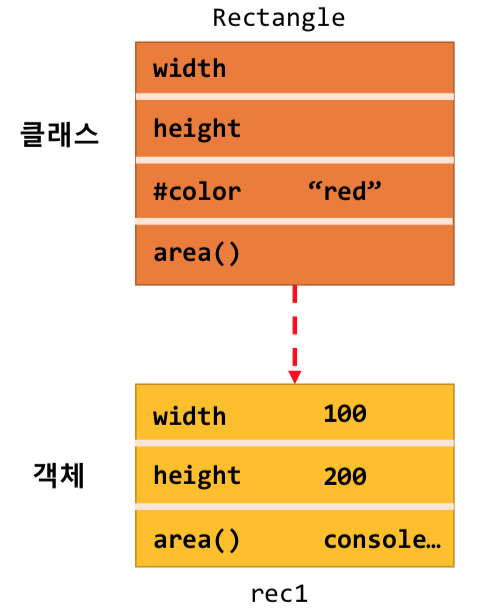
-
접근자 프로퍼티
데이터 프로퍼티
- 키와 값으로 구성된 일반적인 프로퍼티
접근자 프로퍼티
- 자체적으로는 값을 갖지 않고 다른 데이터 프로퍼티의 값을 읽거나 저장할 때 호출되는 접근자 함수로 구성된 프로퍼티
| 종류 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| get | 접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 데이터 프로퍼티의 값을 가져와서 읽을 때 호출되는 접근자 함수 getter 함수가 호출되고 그 결과가 프로퍼티 값으로 반환 |
| set | 접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 데이터 프로퍼티의 값을 받아서 저장할 때 호출되는 접근자 함수 setter 함수가 호출되고 그 결과가 프로퍼티 값으로 저장 |
- getter 함수
-
캡슐화한 프로퍼티에 접근할 수 있음
- 같은 class 내부 안에 있기 때문
-
get 키워드로 선언
**get** display() { return `가로는 ${this.width}, 세로는 ${this.height}입니다.`; } -
호출 방법
-
함수 호출 방식이 아닌 프로퍼티 호출 방식으로 호출
객체이름.display
-
-
- setter 함수
-
캡슐화한 프로퍼티에 접근할 수 있음
- 같은 class 내부 안에 있기 때문
-
set 키워드로 선언
**set** changeWidth(value) { console.log(value); } -
값 저장 방법
-
값 할당 방식으로 저장
객체이름.changeWidth = 100;
-
-
상속
클래스 상속
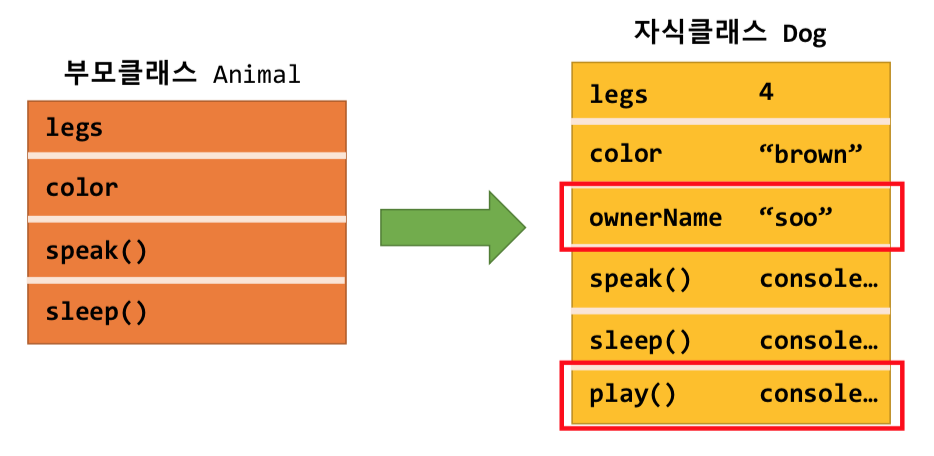
- 한 클래스가 다른 클래스에서 정의된 속성 및 함수를 모두 물려받아 그대로 사용
- 상속받아 만들어진 클래스의 특징 (자식 클래스)
- 물려받은 기능에 필요한 기능을 추가하여 정의할 수 있음
- 클래스 상속 방법
class 클래스이름 extends 부모클래스이름 {
// 클래스 구현
}
코드 재사용 가능
오버라이딩(overriding)
- 부모 클래스로부터 상속받은 메서드를 자식 클래스에서 재정의
- 부모가 물려준 함수의 이름과 동일한 이름의 함수를 가지고 와서 값을 추가함
- cf) 오버로딩(overloading)
- 함수 이름이 똑같고 똑같은 함수를 또 구현 단, 파라미터 개수가 다름
- cf) 오버로딩(overloading)
sleep() {
super.sleep();
console.log('많이 잔다');
}- 실행 결과
잔다. // 부모 클래스로부터 상속
많이 잔다. // 자식 클래스에서 추가instanceof 연산자
- 객체가 특정 클래스에 속하는지 아닌지를 확인해주는 연산자
-
해당하면 true 리턴
-
해당하지 않으면 false 리턴
console.log(dog instanceof Animal); // true console.log(cat instanceof Animal); // false
-
새싹DT 기업연계형 프론트엔드 실무 프로젝트 과정 4주차 블로그 포스팅