[BFS / DFS] [백준 / 2178 ] 실버1 - 미로 탐색 (java/자바)
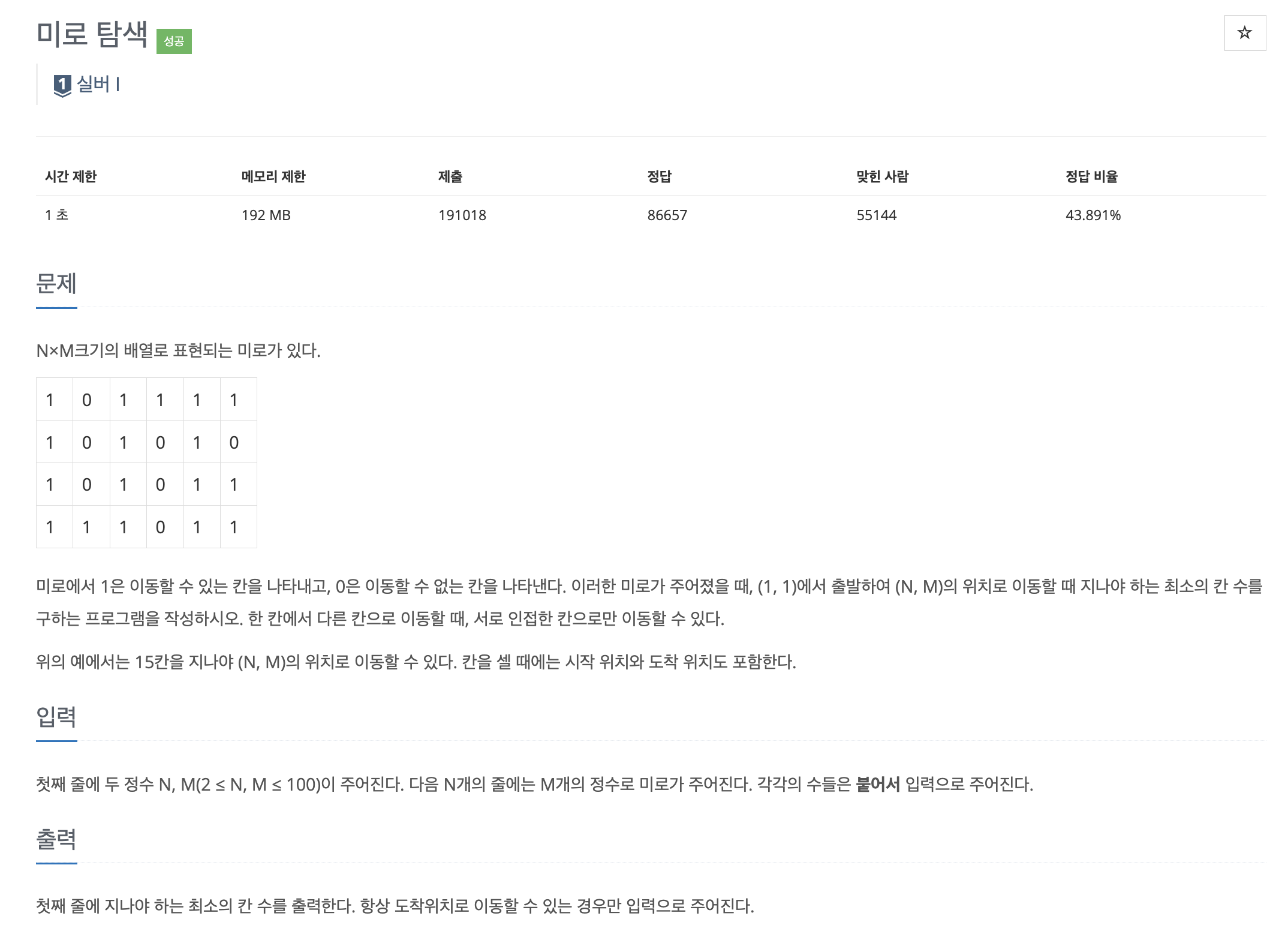
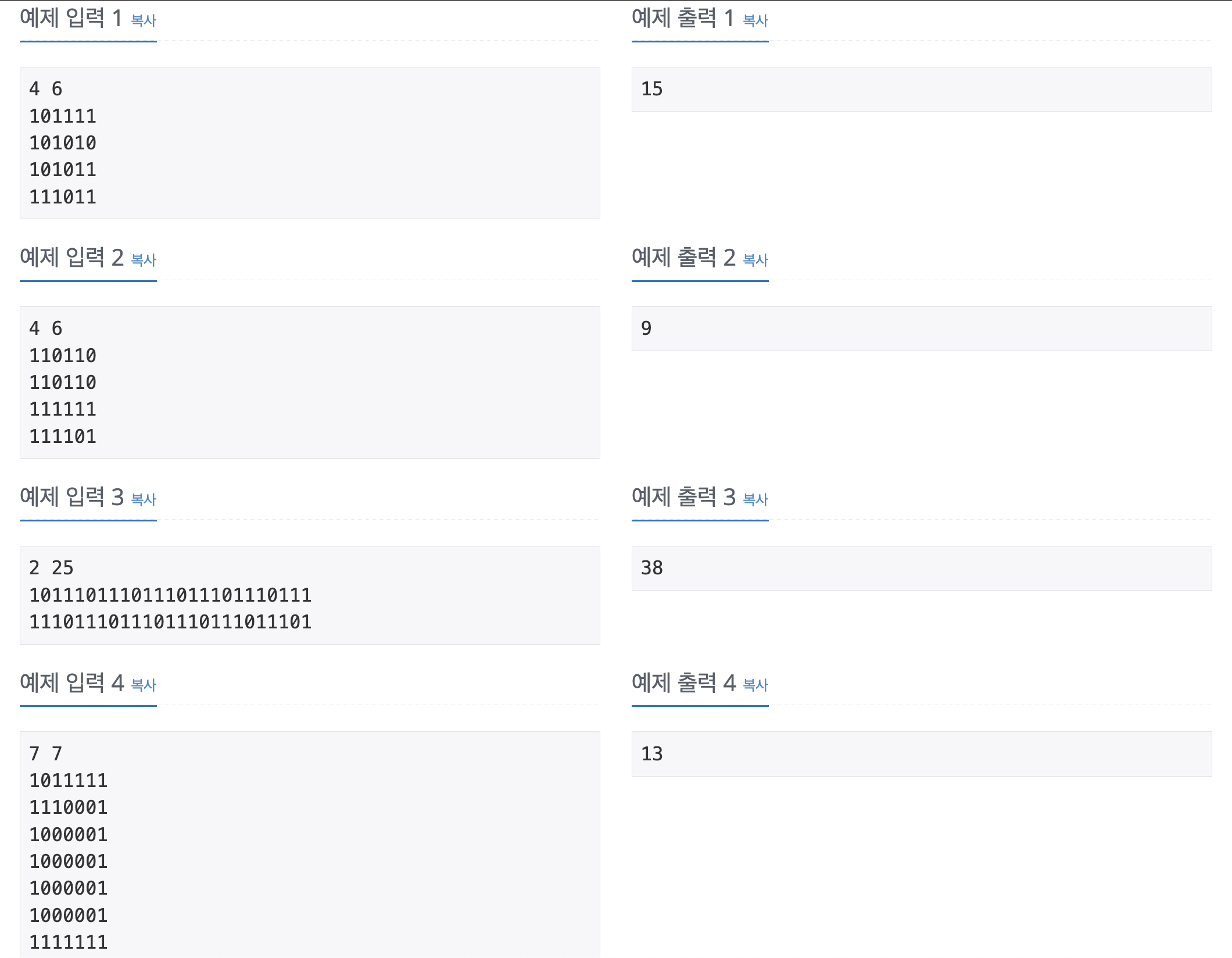
문제
성공 코드
package newboj;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class boj_2178 {
static int N,M;
static int[][] map;
static boolean[][] isVisited;
static int[] dx =new int[]{-1,1,0,0};
static int[] dy =new int[]{0,0,1,-1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader r = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(r.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[N+1][M+1];
isVisited = new boolean[N+1][M+1];
for(int i=1; i<N+1; i++){
int[] array = Arrays.stream(r.readLine().split("")).mapToInt(Integer::parseInt).toArray();
for(int j=1;j<M+1; j++){
map[i][j]= array[j-1];
}
}
bfs(new Point(1,1,1));
}
static void bfs(Point start){
// bfs를 시작하기전 첫 시작점 방문 초기화를 합니다.
isVisited[start.y][start.x] =true;
// 큐를 생성합니다. 앞으로 순회할때 순회가능한 포인트를 저장합니다.
Queue<Point> q = new LinkedList<>();
// 첫번째 시작점을 q에 넣습니다.
q.add(start);
//--- 이제 순회를 시작합니다. ---//
while(!q.isEmpty()){
Point currentPoint = q.poll();
// 목적지에 도달했을 때 거리 반환 및 함수 종료
if (currentPoint.y == N && currentPoint.x == M) {
System.out.println(currentPoint.d);
return;
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nextY = currentPoint.y + dy[i];
int nextX = currentPoint.x + dx[i];
if(!(1<=nextY && nextY<=N && 1<=nextX && nextX<=M)) continue;
if(map[nextY][nextX]!=1) continue;
if(isVisited[nextY][nextX] == true) continue;
isVisited[nextY][nextX] =true;
q.add(new Point(nextY,nextX, currentPoint.d+1));
}
}
// 순회를 마치면 bfs를 종료합니다.
}
static class Point{
int y;
int x;
int d;
Point(int y, int x, int d){
this.y=y;
this.x=x;
this.d=d;
}
}
}
생각하기
(1,1) -> (N,M)까지 이동하기 위한 최소의 거리를 구해야 합니다.
NxM의 각각의 칸을 포인트라고 하겠습니다.
한칸씩 이동할 때마다 지금까지 온 거리에 +1을 더하고
(N,M)에 도달한 포인트가 있으면 이 포인트의 거리를 출력하고 종료합니다.
BFS는 가장 먼저 (N,M)에 도달하는 경로를 찾을 때, 그 경로가 최소 이동 거리를 가진 경로임을 보장합니다. 따라서 (N,M)에 도달한 첫 번째 포인트의 거리가 바로 답입니다.
- 포인트는 y좌표 , x좌표, 이동거리를 알고 있어야 합니다.
-
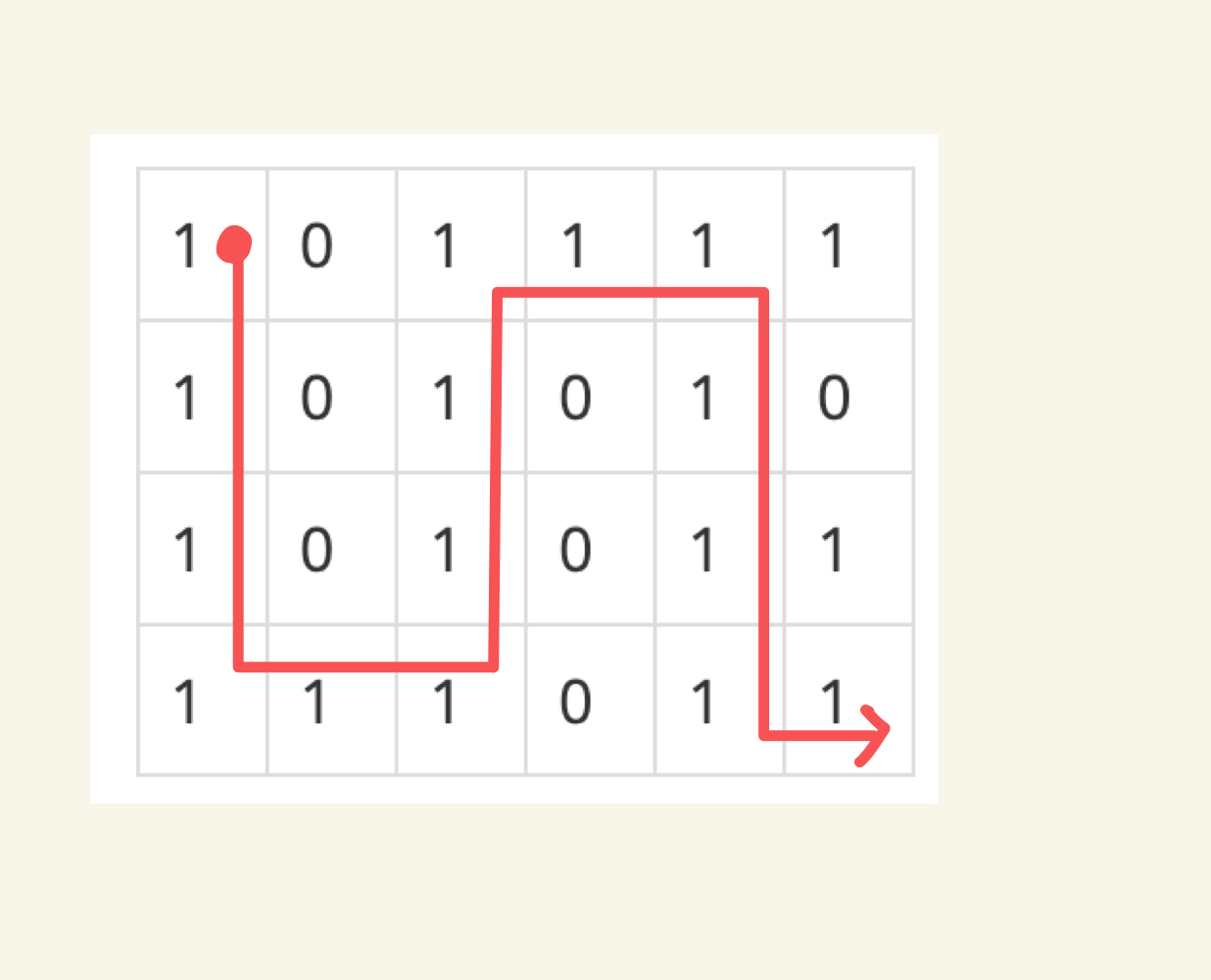
다음과 같이 이동하면 최소의 거리를 구할 수 있습니다.
-
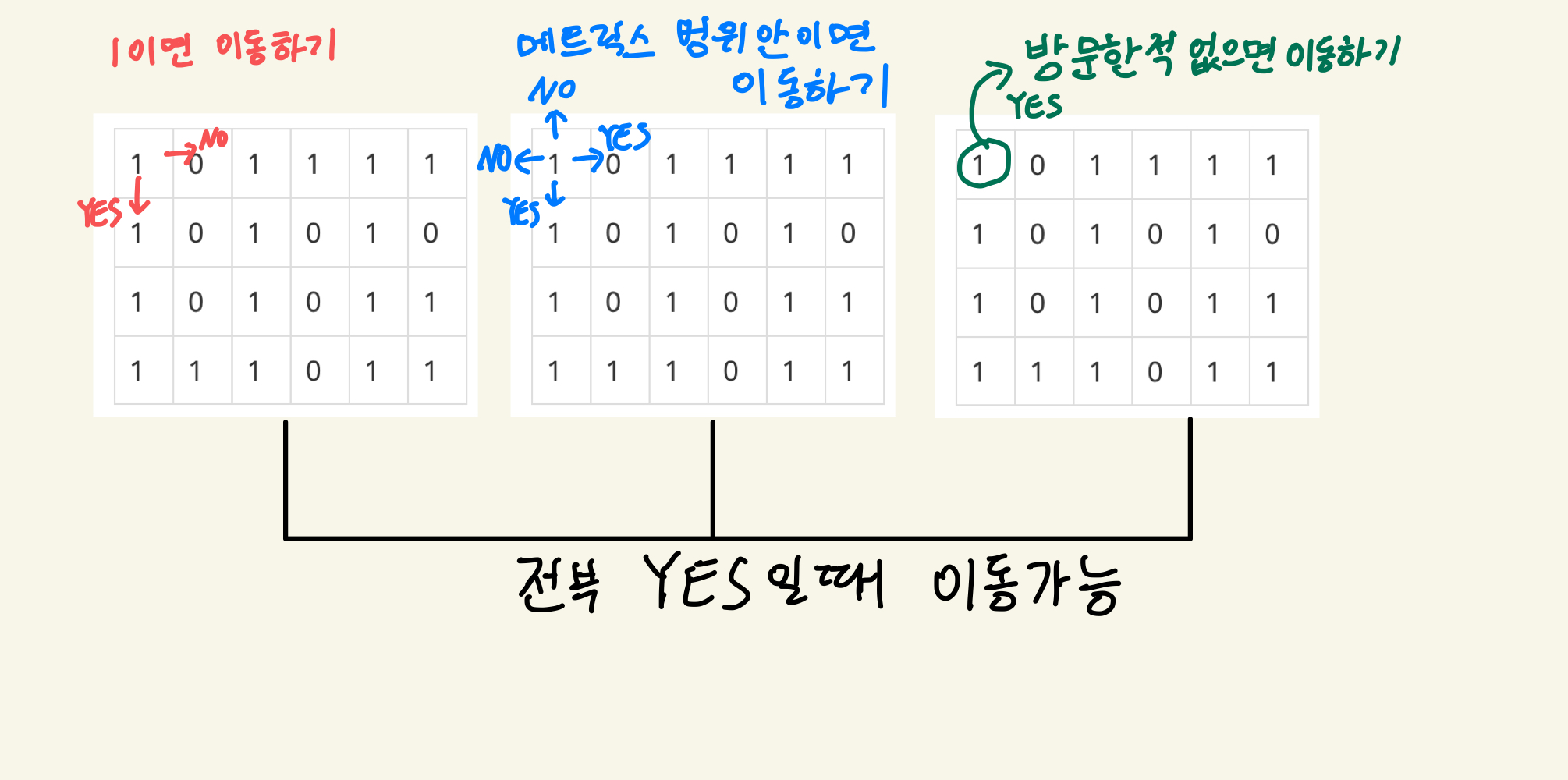
이동할 수 있는 경우는 다음 3가지를 만족할 때 입니다.
DFS로는 실패하는 이유
만약 dfs 코드를 만든다면 다음과 같이 만들 수 있습니다
static void dfs(Point currentPoint){
isVisited[currentPoint.y][currentPoint.x] =true;
// 목적지에 도달했을 때 거리 반환 및 함수 종료
if (currentPoint.y == N && currentPoint.x == M) {
System.out.println(currentPoint.d);
return;
}
for(int i=0; i<4; i++){
int nextY = currentPoint.y+dy[i];
int nextX = currentPoint.x+dx[i];
if(!(1<=nextY && nextY<=N && 1<=nextX && nextX<=M)) continue;
if(map[nextY][nextX]!=1) continue;
if(isVisited[nextY][nextX] == true) continue;
dfs(new Point(nextY,nextX, currentPoint.d+1));
}
}DFS(깊이 우선 탐색) 알고리즘을 사용하여 이 문제를 푸는 것은 BFS에 비해 직관적이지 않습니다. DFS는 모든 가능한 경로를 탐색하여 (N, M)에 도달하는 데 필요한 경로를 찾지만, BFS와 달리 첫 번째로 찾은 경로가 최소 거리를 보장하지 않습니다. 따라서, DFS를 사용할 때는 모든 경로를 탐색하고 그 중 최소 거리를 찾아야 합니다.
그럼에도 DFS로 풀어보기
DFS로 이 문제를 풀려면, 각 경로를 따라 (N, M)에 도달할 때까지 탐색을 진행하고, 각 경로의 길이를 기록해야 합니다. 모든 가능한 경로를 탐색한 후, 가장 짧은 경로의 길이를 결과로 반환합니다.
그리고 미로의 크기가 크거나 경로의 수가 많을 때는 탐색에 많은 시간이 소요될 수 있습니다.
static int N, M;
static int[][] map;
static boolean[][] visited;
static int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 최소 거리를 저장할 변수
static int currentDistance = 0; // 현재 경로의 거리
static void dfs(int y, int x, int distance) {
if (y == N && x == M) { // (N, M)에 도달했다면
minDistance = Math.min(minDistance, distance); // 최소 거리 업데이트
return;
}
int[] dx = {-1, 1, 0, 0};
int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nextY = y + dy[i];
int nextX = x + dx[i];
if (1 <= nextY && nextY <= N && 1 <= nextX && nextX <= M && map[nextY][nextX] == 1 && !visited[nextY][nextX]) {
visited[nextY][nextX] = true;
dfs(nextY, nextX, distance + 1);
visited[nextY][nextX] = false; // 경로 복원
}
}
}이 문제를 DFS로 풀 때는, 모든 경로를 탐색하면서 각 경로에 대한 거리를 계산하고, 가장 짧은 거리를 찾아야 합니다. 이 과정에서 최소 거리를 갱신하는 방식을 사용합니다.
하지만 DFS는 이 문제에 최적의 해법이 아니며, 특히 최소 거리를 찾는 문제에서는 BFS가 더 적합합니다.
