08. 예외 처리
08-1. 구문 오류와 예외
- 구문 오류 : 괄호 개수를 잘못 입력하는 등의 오류로 코드가 실행조차 되지 않는 오류
- 예외(런타임 오류) : 문법적 오류를 제외하고 코드 실행 중간에 발생하는 오류
2-1) 예외 처리 : 예외가 난 것을 처리하는 것
오류의 종류
구문 오류
구문 오류가 발생시 웹 브라우저가 코드를 분석조차 하지 못하므로 실행 되지 않습니다.
<!-- 구문 요류가 발생하는 코드 -->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
console.log("# 프로그램이 시작되었습니다!")
console.log("# 괄호를 닫지 않는 실수를 했습니다."
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>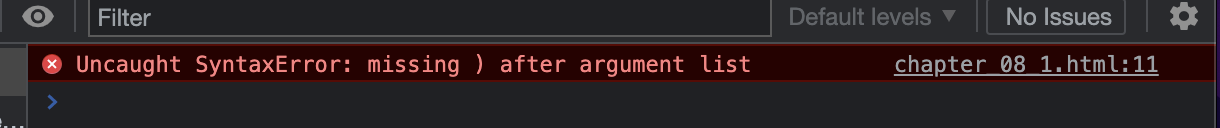
해석을 하자면,
"제가 코드를 읽어봤는데 이런 곳에 문제가 있어서 실행조차 안됩니다. 해결해주면 좋겠습니다"
따라서, 2번째 console.log()에 괄호를 추가하면 구문 오류를 해결할 수 있다.
예외
예외(런타임 오류)는 실행 중에 발생하는 오류를 의미합니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
console.log("# 프로그램이 시작되었습니다!")
console.rog("# 괄호를 닫지 않는 실수를 했습니다.")
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>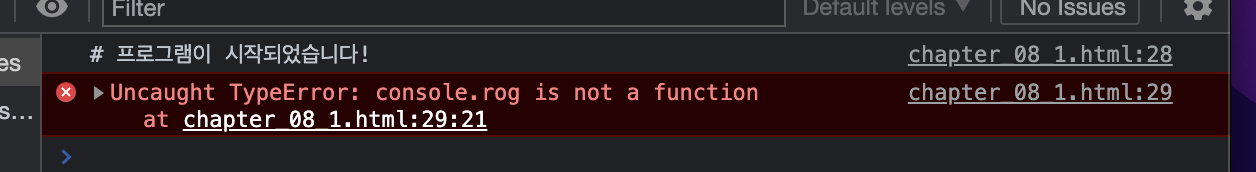
해석을 하면,
"console.rog는 함수가 아니에요"
이처럼 실행 중에 발생하는 오류가 예외입니다. 자바스크립트에서는 SyntaxError라고 출력되는 오류 이외의 모든 오류(TypeError, ReferenceError, RangeError)가 예외로 분류됩니다.
기본 예외 처리
조건문을 사용하여 예외처리를 하는 것을 기본 예외 처리라고 합니다.
아래와 같은 상황을 보면,
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
document.addEventListener('DOCContentLoaded', () =>{
const h1 = document.querySelector('h1')
h1.textContent = '안녕하세요'
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>발생 오류,
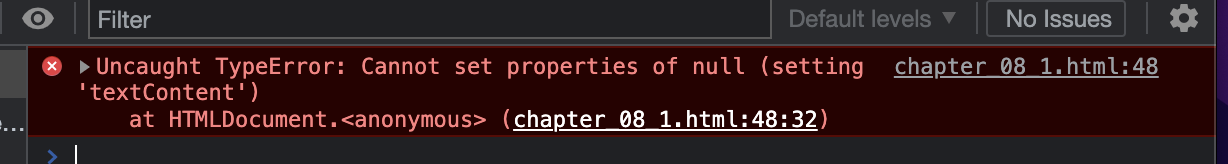
<h1> 태그가 존재하지 않는 경우에 대한 내용이 없어 오류가 발생 하였다.
이를 해결하기 위해서는 조건문으로 해결을 할 수 있다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', () =>{
const h1 = document.querySelector('h1')
if(h1) {
h1.textContent = '안녕하세요'
} else {
console.log('h1 태그를 추출할 수 없습니다.')
}
})
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>배열의 undefined
대부분의 프로그래밍 언어는 배열의길이를 넘는 위치를 선택할 경우 오류를 발생하지만, 자바스크립트는 undefined를 출력을 한다.
고급 예외 처리
예외를 조금 더 쉽게 잡을 수 있는 기능으로 'try catch finally' 구문이 있습니다.
<script>
try{
// 예외가 발생할 가능성이 있는 코드
} catch {
// 예외가 발생했을 때 실행할 코드
} finally {
무조건 실행할 코드
}
</script>try 구문 안에서 예외를 발생하면 이를 catch 구문에서처리합니다. finally 구문은 필수 사항은 아니며, 예외 발생 여부와 상관없이 수행해야 하는 작업이 있을 때 사용합니다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
try{
willExcpt.byeBye()
console.log("try 구문의 마지막 줄")
} catch (excption) {
console.log("catch 구문의 마지막 줄")
} finally {
// 무조건 실행할 코드
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>finally 구문을 사용하는 경우는 아래와 같이 출력이 된다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
try{
willExcpt.byeBye()
console.log("try 구문의 마지막 줄")
} catch (excption) {
console.log("catch 구문의 마지막 줄")
} finally {
console.log("finally 구문의 마지막 줄")
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>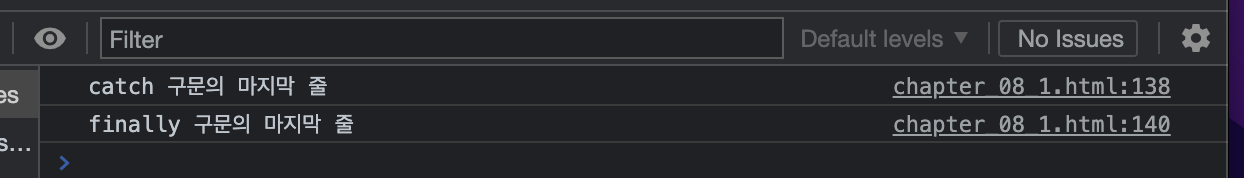
08-2. 예외 처리 고급
- 예외 객체 : 프로그래밍 언어에서도 예외가 발생하면 예외아 발생된 정보를 확인할 수 있게 해주는 것
자바스크립트는 유연한 언어이므로 예외가 잘 발생하지 않는다. 그렇기 때문에 강제로 예외를 발생 시킬 때 throw 키워드를 사용한다.
예외 강제 발생
상황에 따라서 예외를 강제로 발생시켜야 하는 경우가 있다. 이럴때 throw 키워드를 사용한다.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script>
function divide(a, b){
if (b===0) {
throw '0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.'
}
return a/b
}
console.log(divide(10,2))
console.log(divide(10,0))
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>