1. 메소드 (Method)
메소드 (Method):
반복되는 코드, 내용, 재사용해야할 코드들을 한 뭉치로 묶어서
따로 메소드로 만들은 다음(정의) 이를 필요할때마다 사용(호출)한다.
※ 자바는 '함수(function)' 가 따로 없으나, 혼용하여 사용 가능.메소드 정의:
메소드는 main 메소드 바깥에서!!, class 안에서 정의!!
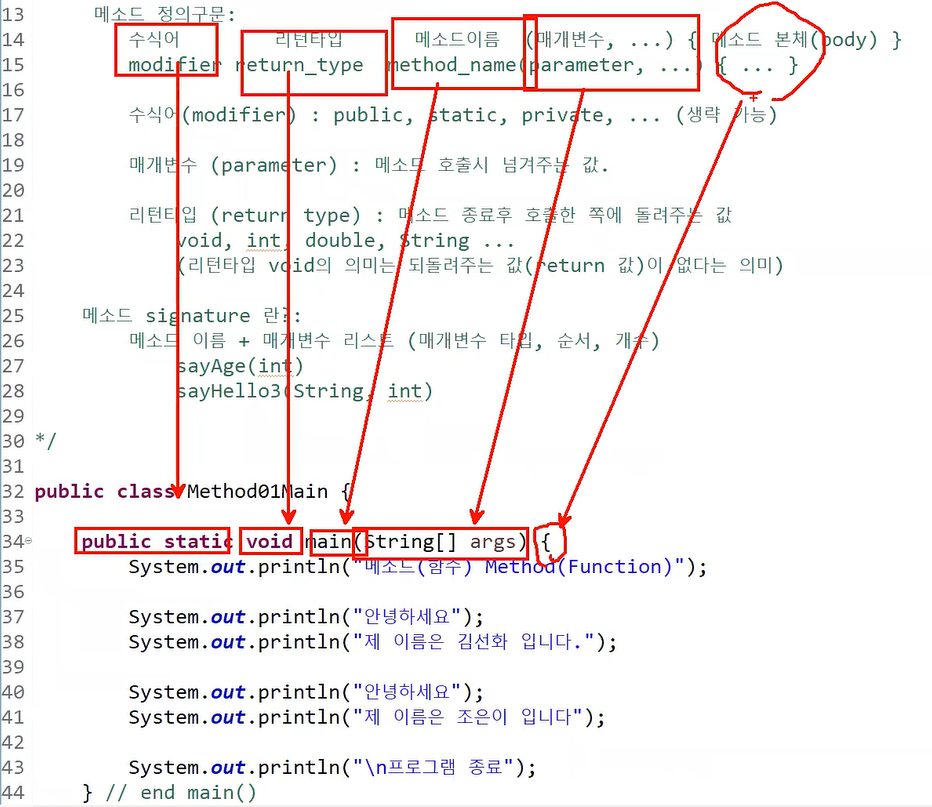
메소드 정의구문:
수식어 리턴타입 메소드이름(매개변수, ...) { 메소드 본체(body) }
modifier return_type method_name(parameter, ...) { ... }
- 수식어(modifier) : public, static, private, ... (생략 가능)
- 매개변수 (parameter) : 메소드 호출시 넘겨주는 값.
- 리턴타입 (return type) : 메소드 종료후 호출한 쪽에 돌려주는 값
ex) void, int, double, String ...
(리턴타입 void의 의미는 되돌려주는 값(return 값)이 없다는 의미)
메소드 signature 란?:
- 메소드 이름 + 매개변수 리스트 (매개변수 타입, 순서, 개수)
sayAge(int)
sayHello3(String, int)
[메소드 signature]
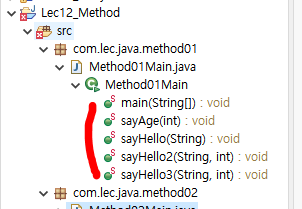
package com.lec.java.method01;
public class Method01Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("메소드(함수) Method(Function)");
System.out.println("안녕하세요");
System.out.println("제 이름은 김선화 입니다.");
System.out.println("안녕하세요");
System.out.println("제 이름은 조은이 입니다.");
// sayHello 메소드 호출 (= method call, method invoke)
sayHello("정예경");
sayHello("피카츄");
sayHello("코난");
System.out.println();
sayAge(16);
sayAge(20);
System.out.println();
sayHello2("도라에몽", 100);
sayHello2("노진구", 13);
System.out.println();
sayHello3("토니스타크", 41);
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
// 메소드 정의!
// 메소드이름 : sayHello
// 매개변수 : name
public static void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("안녕하세요.");
System.out.println("제 이름은 " + name + "입니다.");
}
// 메소드이름 : sayAge
// 매개변수 : int 타입의 age
// 리턴타입 : void(리턴값 없다)
public static void sayAge(int age) {
System.out.println("Hi~");
System.out.println("제 나이는 " + age + "입니다");
}
// 메소드 이름: sayHello2
// 매개변수:
// 1) String name
// 2) int age
// 리턴타입: void
public static void sayHello2(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("안녕!");
System.out.println("내 이름은 " + name + " 입니다");
System.out.println("내 나이는 " + age + "살 입니다");
}
// JavaDoc
/**
* 이름과 나이를 출력합니다
* @param name 이름
* @param age 나이
*/
public static void sayHello3(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("**********************************");
sayHello(name);
sayAge(age);
System.out.println("**********************************");
}
} // end class[메인 메소드]
2. 리턴 (return)
return 의 의미
1. 메소드를 호출한 곳으로 값을 리턴한다.
2. 메소드 종료
3. 메소드 정의시 명시한 리턴타입의 값이 '반드시' 리턴되어야 한다
(혹은 리턴타입으로 형변환 가능한 값이)
package com.lec.java.method02;
/* return 의 의미
*
* 1. 메소드를 호출한 곳으로 값을 리턴한다.
* 2. 메소드 종료
* 3. 메소드 정의시 명시한 리턴타입의 값이 '반드시' 리턴되어야 한다
* (혹은 리턴타입으로 형변환 가능한 값이)
*/
public class Method02Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("메소드의 리턴 타입");
int sum = add(110, 220);
System.out.println("sum = " + sum);
int result = sub(100, 200);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
result = multiply(123, 321);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
result = divide(25, 3);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println("결과: " + add(10, add(100, -20)));
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
// 메소드 이름: add
// 매개변수:
// 1) int x
// 2) int y
// 리턴타입: int
public static int add(int x, int y) {
int result = x + y;
return result;
} // end add()
// 메소드 이름: sub
// 매개변수:
// 1) int x
// 2) int y
// 리턴타입: int
public static int sub(int x, int y) {
int result = x - y;
return result;
} // end sub()
// 메소드 이름: multiply
// 매개변수:
// 1) int x
// 2) int y
// 리턴타입: int
public static int multiply(int x, int y) {
int result = x * y;
return result;
} // end multiply()
// 메소드 이름: divide
// 매개변수:
// 1) int x
// 2) int y
// 기능: x를 y로 나눈 몫을 리턴하는 메소드
// 리턴타입: int
public static int divide(int x, int y) {
int result = x / y;
return result;
} // end divide()
// 메소드 이름: divide2
// 매개변수:
// 1) int x
// 2) int y
// 만약에 y 가 0 이면 --> "0으로 나눌수 없습니다"
// y 가 0 이 아니면 --> "몫은 ~~이고 , 나머지는 ~~ 입니다"
// 리턴타입: String ★
} // end class
/*
* Refactor - Inline (ALT + SHIFT + I)
* Refactor - Extract Local Variable (ALT + SHIFT + L)
*
*/[연습문제]
메소드 연습
숫자값을 입력 받아서
위 값을 한변의 길이로 한 정사각형의 넓이를 구하고
위 값을 반지름으로 한 원의 넓이를 구하기
- public static double calcRectArea(double length)
- public static double calcCircleArea(double r)
package com.lec.java.method05;
public class Method05Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("메소드 연습");
double num = 10;
double area;
System.out.println("정사각형의 넓이");
area = calcRectArea(num);
System.out.println("area = " + area);
System.out.println("원의 넓이");
area = calcCircleArea(num);
System.out.println("area = " + area);
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
// method name: calcRectArea
// return: double (정사각형의 넓이)
// arguments: double length (정사각형의 한 변의 길이)
public static double calcRectArea(double length) {
return length * length;
}
// method name: calcCircleArea
// return: double (원의 넓이)
// arguments: double r (원의 반지름)
public static double calcCircleArea(double r) {
return Math.PI * r * r;
}
} // end class3. Method Overloading (메소드 중복 정의) => 면접 多
Method Overloading (메소드 중복 정의)
같은 이름으로 메소드를 매개변수 리스트를 달리하여 중복 정의,
즉, 이름이 같아도 메소드 signature 가 다르면 중복정의 가능.
Method Signature 란
메소드 이름 + 매개변수 리스트 (parameter list)
1. 매개변수의 개수가 다르거나
2. 매개변수의 자료형이 다르거나
3. 매개변수의 순서가 다를 때
위 3개를 '매개변수 리스트' 라 한다
-> 메소드의 리턴 타입만 다른 경우는 중복 정의할 수 없다!!
메소드 오버로딩의 장점:
동일한 동작을 하는 메소드에 대해 매개변수만 달리하여 중복정의 하면
이 메소드를 사용하는 입장에선 여러타입의 이름을 익힐 필요가 없다.
package com.lec.java.method06;
public class Method06Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Method Overloading (메소드 중복 정의)");
sayHello();
sayHello("이수현");
sayHello(20);
sayHello("이재우", 20);
// sayHello("상배, "기석"); // The method sayHello(String, int) in the type Method06Main is not applicable for the arguments(String, String)
sayHello(32, "기석");
sayHello('A'); // char -> int 자동형변환 가능
// sayHello(10L); // long -> int 자동형변환 불가
byte b = 10;
sayHello(b); // short 타입으로 받음
// 메소드 오버로딩의 장점? -> 동일한 동작에 대해 동일한 이름의 메소드를 다양한 타입을 받아서 수행할 수 있게 해줌
System.out.println(10);
System.out.println(3.14);
System.out.println("hello");
// printInt()
// printDouble()
// printString()
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
// 1
public static void sayHello() {
System.out.println("sayHello() 호출");
System.out.println("안녕하세요~");
}
// 리터타입만 다르다고 하여 오버로딩이 인정되지 않는다.
// public static int sayHello() {
// return 0;
// }
// 2
public static void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("sayHello(String) 호출");
System.out.println("Hi~");
System.out.println("제 이름은 " + name + "이에요~");
}
// 3-1
public static void sayHello(int age) {
System.out.println("sayHello(int) 호출");
System.out.println("My Age is " + age);
}
// 3-2
public static void sayHello(short age) {
System.out.println("sayHello(short) 호출");
System.out.println("My Age is " + age);
}
// 4
public static void sayHello(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("sayHello(String, int) 호출");
System.out.println("하이~ 헬로~");
System.out.println("이름: " + name);
System.out.println("나이: " + age);
}
// 5
public static void sayHello(int age, String name) {
System.out.println("sayHello(int, String) 호출");
System.out.println("하이~ 헬로~");
System.out.println("이름: " + name);
System.out.println("나이: " + age);
}
} // end class4. Math 클래스의 메소드
package com.lec.java.method07;
import java.util.Random;
/* Math 클래스의 메소드 (import 호출 없이도 사용 가능)
*/
public class Method07Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Math 객체의 메소드");
// Math.random() : 0.0 <= r < 1.0 사이의 난수 발생(double)
double r;
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i ++) {
r = Math.random();
System.out.println(r);
}
System.out.println();
// double Math.floor(num): num을 넘지 않는 가장 큰 정수(바닥)
// double Math.ceil(num): num보다 큰 가장 작은 정수(천장)
// long Math.round(num): num에서 소수점 사사오입 (반올림)
r = 2.7;
System.out.println(Math.floor(r));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(r));
System.out.println(Math.round(r));
r = -1.2;
System.out.println(Math.floor(r));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(r));
System.out.println(Math.round(r));
System.out.println();
r = -2.8;
System.out.println(Math.floor(r));
System.out.println(Math.ceil(r));
System.out.println(Math.round(r));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("1,2,3 범위중 난수 발생시키기");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
r = Math.random(); // 0.0 <= r < 1.0
r = r * 3; // 0.0 <= r < 3.0
r = Math.floor(r); // 0.0 1.0 2.0
r = r + 1; // 1.0 2.0 3.0
System.out.println((int)r); // 1 2 3
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("로또: 1 ~ 45 숫자중에서 랜덤으로 6개 출력");
// TODO
System.out.println();
System.out.println("Random 객체 사용하여 난수 출력");
Random rand = new Random(); // ctrl + shift + o => import
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.print(rand.nextInt(3) + ", "); // 0 ~ 2, 사이의 정수 난수 발생
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
// TODO
} // end class[연습문제]
메소드 연습 : 컴퓨터 생각 맞추기 게임
1. 메뉴를 보여주고
2. 사용자로부터의 입력을 받고
3. 컴퓨터의 생각(난수)와 비교 판정 내기
4. 사용자가 메뉴에서 '종료' 누르면 종료 시키기
package com.lec.java.method08;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Method08Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("컴퓨터 생각 맞추기 게임");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true) {
showMenu();
int userChoice = inputChoice(sc);
if(userChoice == 0) break;
int com = new Random().nextInt(3) + 1; // 1, 2, 3
if(com == userChoice) {
System.out.println("맞췄습니다");
} else {
System.out.println("틀렸습니다. (com: " + com + ")");
}
}
sc.close();
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main
private static int inputChoice(Scanner sc) {
int choice;
while (true) {
choice = sc.nextInt();
if(0 <= choice && choice <= 3) {
return choice;
}
System.out.println("다시 입력하세요");
}
}
// 메뉴 보여주기
// 메소드 이름 : showMenu()
public static void showMenu() {
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.println("COM의 생각을 맞춰보세요");
System.out.println("1]");
System.out.println("2]");
System.out.println("3]");
System.out.println("0] 종료");
System.out.println("-------------");
System.out.print("선택:");
}
// 메소드 이름 : inputChoice
// 매개변수 : Scanner sc
// 리턴타입 : int
// 0 ~ 3 까지의 정수를 Scanner 로부터 입력받아 리턴
// 범위 밖의 수일때는 재입력받는다
// TODO
} // end class5. 메소드와 배열
package com.lec.java.method10;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
/* 메소드와 배열
* 매개변수가 배열, 리턴타입이 배열
*/
public class Method10Main {
public static final int NUM_STUDENT = 10;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("메소드와 배열");
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 점수를 저장할 배열 선언
int [] score = new int[NUM_STUDENT];
displayScore(score);
// 점수 입력 -> score 배열 저장
inputScore(sc, score);
displayScore(score);
// 총점 계산
int total = calcTotal(score);
System.out.println("총점: " + total);
// 평균 계산
double average = (double) total / NUM_STUDENT;
System.out.println("평균: " + average);
// 최댓값 계산
int max = findMax(score);
System.out.println("최댓값: " + max);
// 최솟값 계산
int min = findMin(score);
System.out.println("최솟값: " + min);
sc.close();
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
// method name: inputScore
// return: void
// arguments:
// 1) Scanner sc - 입력장치
// 2) int[] score: 점수를 입력받아서 저장할 배열
public static void inputScore(Scanner sc, int [] score) {
System.out.println("length : " + score.length);
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) { // ctrl + space : use index on array
System.out.println("점수" + (i + 1) + " 입력: ");
score[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
// method name: displayScore
// return: void
// arguments: int[] score - 출력할 점수가 저장된 배열
public static void displayScore(int [] score) {
System.out.println("점수");
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
for(int x : score ) {
System.out.print(x + ", ");
}
System.out.println();
System.out.println("-----------------------------------");
}
// method name: calcTotal
// return: int (계산된 총점을 리턴)
// arguments: int[] score (점수들을 저장한 배열)
public static int calcTotal(int [] score) {
int total = 0;
for(int x : score) {
total += x;
}
return total;
}
// method name: findMax
// return: int (최대값)
// arguments: int[] score (점수들 저장된 배열)
public static int findMax(int [] score) {
int max = score[0];
for(int i = 1; i < score.length; i++) {
if(max < score[i])
max = score[i];
}
return max;
}
// method name: findMin()
// return: int (최소값)
// arguments: int[] score
public static int findMin(int [] score) {
int min = score[0];
for(int i = 1; i < score.length; i++) {
if(min > score[i])
min = score[i];
}
return min;
}
// method name: genRandom()
// return: double[] (생성된 난수 배열)
// arguments: n 생성할 난수 개수
// TODO
} // end class Method09Main6. 재귀호출
재귀 호출 (recursive call)
메소드(혹은 함수) 내부에서 메소드가 자기 자신을 또다시 호출하는 것.
- 장점:
복잡한 문제를 간단하고 논리적으로 기술 가능.- 단점 & 주의 :
메모리 부담 발생
무한히 재귀호출 할 수 없다. --> Stack Overflow 발생
-> 따라서 재귀호출은 '종료조건'이 반드시 필요하다.
[재귀호출 - 팩토리얼 예시]
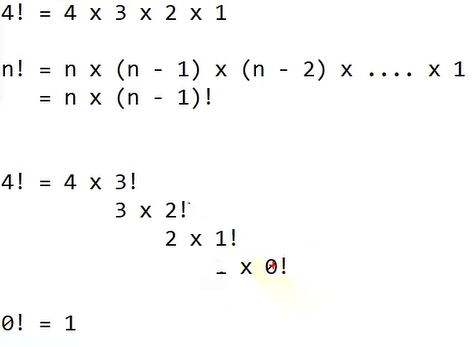
package com.lec.java.method11;
public class Method11Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("재귀 호출 (recursive call)");
System.out.println("재귀 메소드(recursive method)");
// Stack 메모리 용량 초과 : StackOverFlowError
// showNumber(1); // 무한히 재귀호출 불가!
// Heap 메모리 용량 초과 : OutOfMemoryError
// int n = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // 21억 정도
// double [] arr = new double[n];
for(int i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
System.out.println(i + "! = " + calcFactorial(i));
}
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
public static void showNumber(int n) {
System.out.println(n);
showNumber(n + 1); // 재귀호출
System.out.println("리턴");
}
// method name: calcFactorial
// return: long (num의 팩토리얼을 계산해서 리턴)
// arguments: long num
// 기능:
// if n == 0, 0! = 1
// if n > 0, n! = n * (n - 1)!
// if n < 0, 계산 불가
public static long calcFactorial(long num) {
long result = 0L;
if(num == 0) { // 0! = 1 재귀호출 종료조건
result = 1L;
} else if (num > 0) {
result = num * calcFactorial(num -1);
} else {
System.out.println("음수 팩토리얼은 없어요");
}
return result;
}
// 대부분의 recursive call 은 for/while 등의 순환문으로 전환 가능하다
// 실습: calcFactorial 오버로딩 하여, for/while 문으로 구현해보기
// TODO
// method name: pow
// return: double (n의 e승을 계산해서 리턴)
// arguments: int n, int e
// 기능:
// if e == 0, n^0 = 1
// if e > 0, n^e = n x n^(e-1)
// TODO
// method name: powerOfTwo
// return: double (2의 n승을 계산해서 리턴)
// arguments: int n
// 기능:
// if n == 0, 2^0 = 1
// if n > 0, 2^n = 2 x 2^(n-1)
// if n < 0, 2^n = 1 / 2^(-n)
// TODO
} // end class7. Call by Value / Call by Reference
Call By Value : 값에 의한 호출
Call By Reference : 참조에 의한 호출
메소드 호출시 매개변수에 넘겨주는 값의 '복사' 가 발생.
자바에선,
- primitive type 이 매개변수 인 경우 Call By Value
: '값' 이 복사된다
: 메소드에서 매개변수 값을 변경해도 호출한 원본 쪽은 변화 없슴- reference type 이 매개변수 인 경우 Call By Reference 발생
: '주소' 가 복사된다.
: 메소드에서 매개변수 를 통해 변경하면 호출한 원본 쪽도 변화 발생
package com.lec.java.method09;
public class Method09Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Call By Value : 값에 의한 호출");
System.out.println("Call By Reference : 참조에 의한 호출");
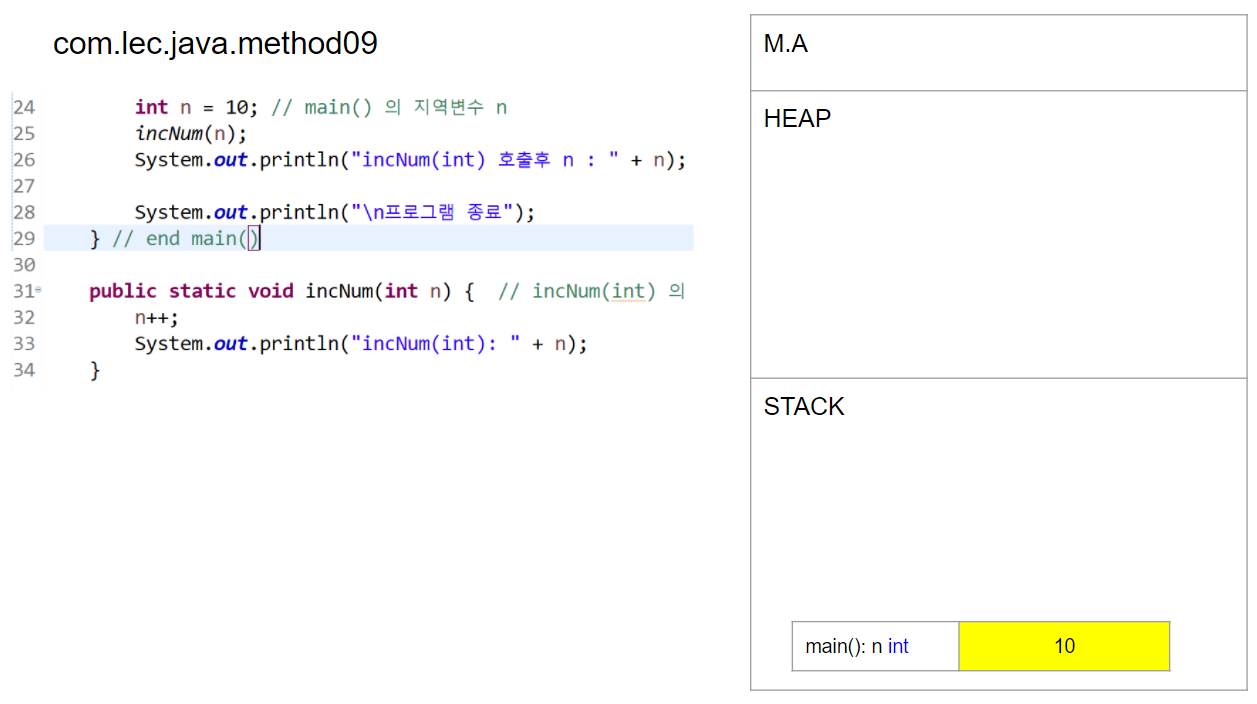
int n = 10;
incNum(n);
System.out.println("incNum(n) 호출후 n:" + n); // n값 : 10
System.out.println();
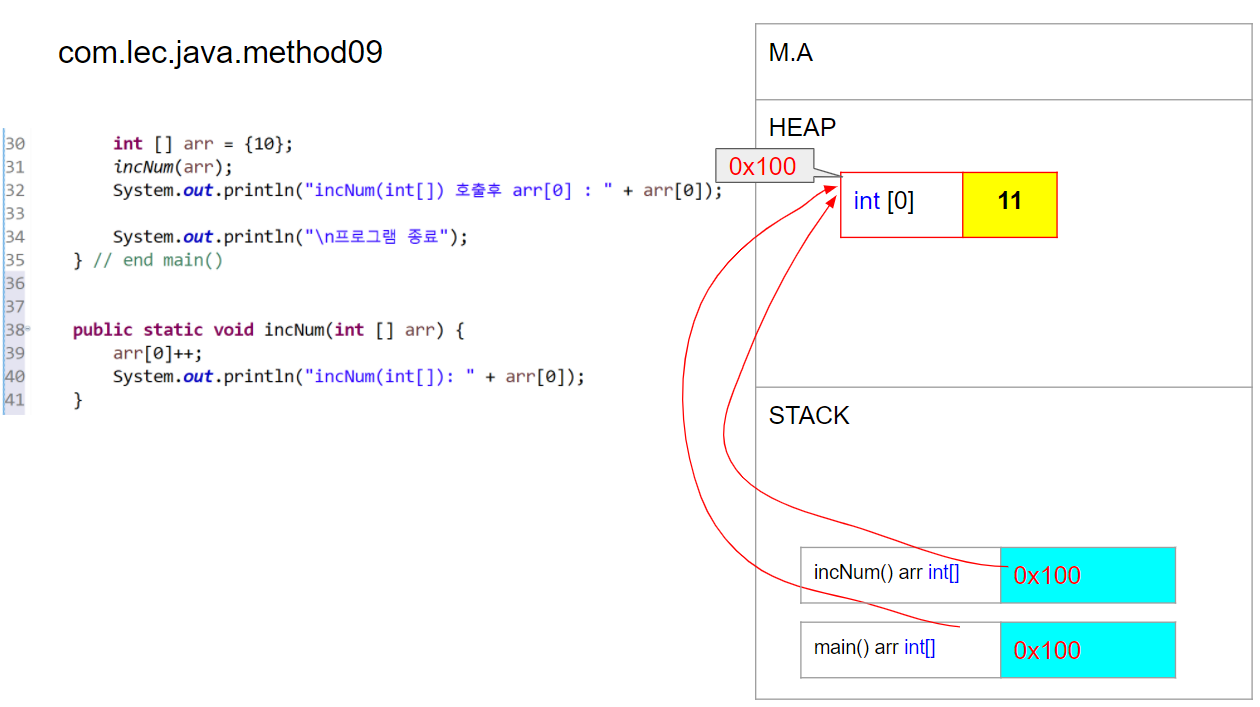
int [] arr = {10};
incNum(arr);
System.out.println("incNum(int[]) 호출후 arr[0]: " + arr[0]); // n값 : 11
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
public static void incNum(int n) {
n++;
System.out.println("incNum(n): " + n); // n값 : 11
}
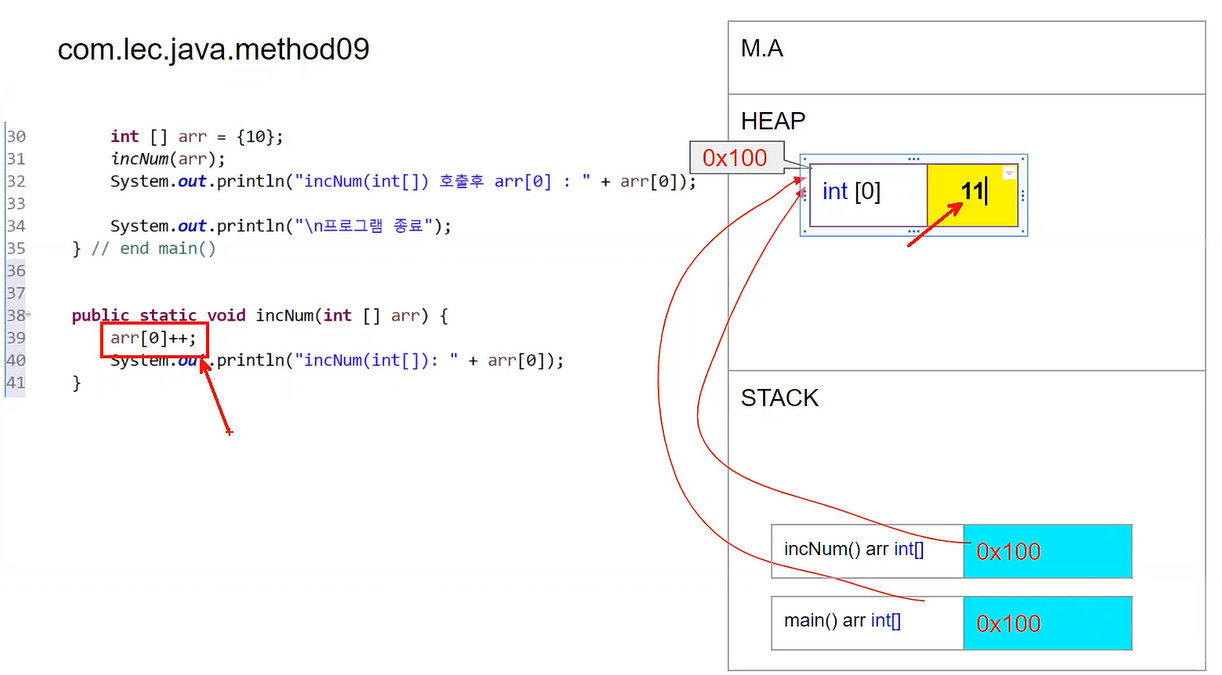
public static void incNum(int [] arr) {
arr[0]++;
System.out.println("incNum(arr[]): " + arr[0]); // n값 : 11
}
} // end class[Call By Value 설명]
- 메서드 호출시 매개변수 값의 복사가 발생함
- 메서드의 값이 11이 됨
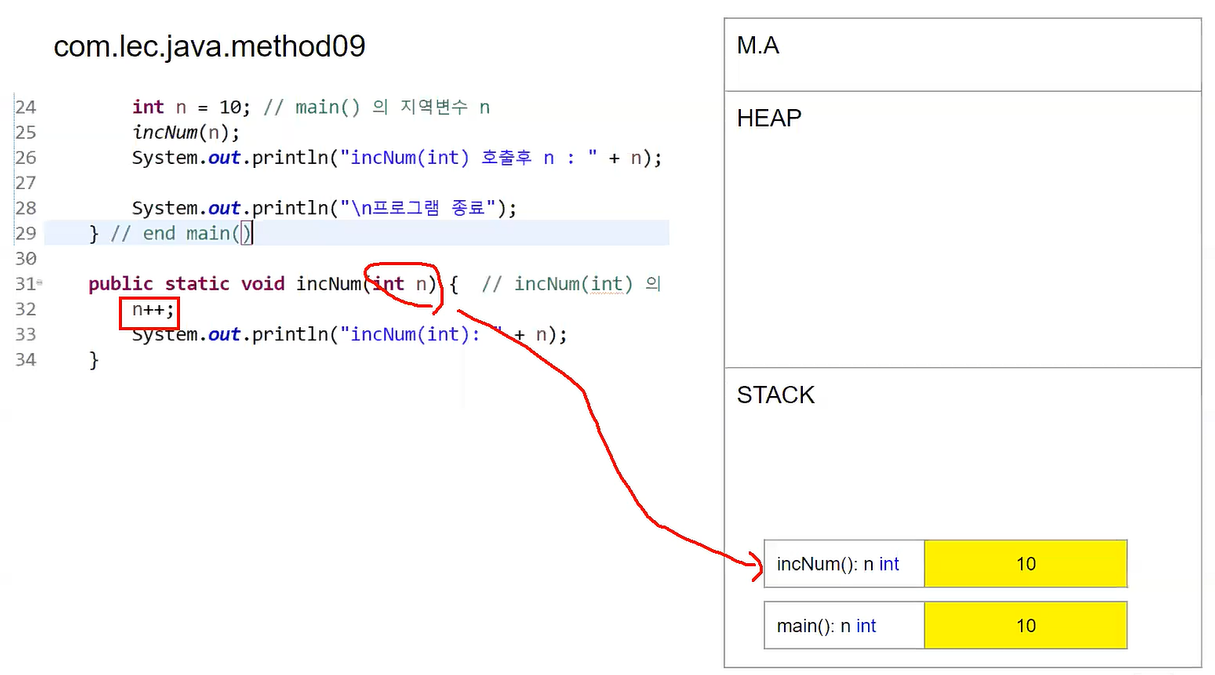
- 메서드가 끝나면 stack에서 사용된 메서드가 사라짐
- main에서 n을 출력하면, 10이 출력됨
[Call By Reference 설명]
- 메서드 호출시 매개변수 주소값의 복사가 발생함
- 주소값에 있는 값이 10 -> 11로 변경
- 메서드가 끝나면 stack에서 사용된 메서드가 사라짐
[연습문제]


package practice.stddev;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
public class StdDev {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 임의정수 5개로 초기화한 정수로
// 평균, 분산, 표준편차 구하기
double avg = 0;
double var = 0;
double stdDev = 0;
Random rand = new Random();
int [] arr = new int[5];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
arr[i] = rand.nextInt(100) + 1; // 1 ~ 100
}
// 평균, 분산, 표준편차 구하기
avg = calcAvg(arr);
var = calcVariance(arr);
stdDev = calcStdDev(arr);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
System.out.println("평균: " + avg);
System.out.println("분산: " + var);
System.out.println("표준편차: " + stdDev);
} // end main
/**
* 메소드 이름 : calcAvg
* 매개변수 : int []
* 리턴값 : double
*
* 주어진 배열의 '평균값' 리턴
*/
public static double calcAvg(int [] arr) {
double sum = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum += arr[i];
}
return sum / arr.length;
}
/**
* 메소드 이름 : calcVariance
* 매개변수 : int []
* 리턴값 : double
*
* 주어진 배열의 '분산값' 리턴
*/
public static double calcVariance(int [] arr) {
double var = 0.0;
double avg = calcAvg(arr); // 평균
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
var += Math.pow(arr[i] - avg, 2);
}
return var /= arr.length;
}
/**
* 메소드 이름 : calcStdDev
* 매개변수 : int []
* 리턴값 : double
*
* 주어진 배열의 '표준편차' 리턴
*/
public static double calcStdDev(int [] arr) {
return Math.sqrt(calcVariance(arr));
}
} // end class8. 문자열(String) 관련 메소드
문자열 (String) 관련 메소드들
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/lang/String.html
- 문자열 메소드는 꼭 정독하기
- 매개변수의 의미, 동작의 의미, 리턴값의 의미 꼭 숙지하기
- 인스턴스 메소드 인지, 클래스 메소드(static) 인지 구분
package com.lec.java.string01;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class String01Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("String 클래스의 메소드들");
String str1 = "AbCdEfg";
String str2 = "안녕하세요~";
System.out.println();
System.out.println("length()"); // 문자의 개수
System.out.println("str1 길이: " + str1.length());
System.out.println("str2 길이: " + str2.length());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("concat()"); // 문자열 연결 (concatenation)
System.out.println(str1.concat(str2));
System.out.println(str2.concat(str1));
System.out.println(str1.concat(str2).concat(str1));
// ★주의★
// 문자열(String) 은 변경불가(immutable) 이기 때문에
// 메소드 수행했다고 하여 원본이 변경되지 않는다.
str1.concat(str2);
System.out.println(str1); // <-- str1은 변경 안되었다.
str1 = str1.concat(str2); // <-- 변경하려면 이와 같이 덮어쓰기 해야 한다.
System.out.println(str1);
// ★주의★
// empty 문자열과 null 은 다르다
// null 인 경우 메소드 수행하면 NullPointerException 발생!
String str3 = " "; // empty 문자열, 문자열 객체가 존재하나 비어있는 문자열
System.out.println(str3.length());
str3 = null; // null, 문자열 객체가 존재하지 않음.
// System.out.println(str3.length()); // NullPointerException (NPE) (null과 empty의 차이)
System.out.println();
System.out.println("charAt(index)"); // 문자열 안의 특정위치(index)의 문자 리턴, 인덱스 범위 벗어나면 StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
// 문자열 인덱스는 0 부터 시작!
System.out.println(str1.charAt(0));
System.out.println(str1.charAt(1));
// System.out.println(str1.charAt(20)); // StringIndexOutOfBoundsException
System.out.println();
System.out.println("indexOf(char), indexOf(String)"); // 문자열 안에서 특정 문자(char) 혹은 문자열(String)의 위치(index), 발견 못하면 -1 리턴
System.out.println(str1.indexOf('C'));
System.out.println(str1.indexOf('c'));
System.out.println(str2.indexOf('요'));
System.out.println(str2.indexOf("하세"));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("toUpperCase(), toLowerCase"); // 대문자 변환, 소문자 변환
System.out.println(str1.toUpperCase());
System.out.println(str1.toLowerCase());
System.out.println();
System.out.println("startWith()"); // 문자열이 주어진 prefix문자열로 시작하는지 여부 true/false 리턴
String prefix = "http://";
String url = "www.google.com";
System.out.println(url.startsWith(prefix));
if(!url.startsWith(prefix)) {
String newUrl = prefix.concat(url);
System.out.println(newUrl);
}
// endsWith(postfix)
System.out.println();
System.out.println("split(regex)"); // 문자열을 주어진 문자열로 쪼개어 String[] 리턴
String str4 = "HH:MM:SS";
String [] strings = str4.split(":");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings));
// 공백기준으로 쪼갤때는 정규표현식의 \\s+ 사용하기 : 공백, 탭, 줄바꿈
str4= " Hello\t \n \t My \n \n World";
strings = str4.split("\\s+");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings));
// 단! "|" 을 할경우는 주의, ※ split(정규표현식) 을 사용하는 메소드임
String str5 = "HH|MM|SS";
// strings = str5.split("|") // <--- 이렇게 하면 결과 이상해진다. (// <-- 이렇게 하면 결과 이상해진다. (내부적으로 "|" 정규표현식에서 boolean (OR)와 같은 동작함. 따라서 아래와 같이 escaping 해야 함)
strings = str5.split("\\|");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(strings));
// String.join()
// 문자열들, 문자열 배열 --> 하나의 문자열로 합하기 split() 과 반대
System.out.println();
System.out.println("String.join(delimeter, elements ...)");
String[] str7 = {"Alice", "Bob", "Carol"};
System.out.println(String.join("-", str7));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("substring(beginIndex, endIndex)"); // 문자열의 일부분 추출 beginIndex ~ endIndex직전 까지, 인덱스 범위 벗어나면 IndexOutOfBoundsException
String str8 = "Hello Java";
System.out.println(str8.substring(2, 5)); // 2 부터 5 전까지
System.out.println(str8.substring(6)); // 6 부터 끝까지
System.out.println();
System.out.println("trim()"); // 좌우의 여백 제거
String str9 = " 김동후 ";
System.out.println("[" + str9 + "]");
System.out.println("[" + str9.trim() + "]");
System.out.println();
System.out.println("replace(target, replacement)"); // 문자열 치환 target → replacement
String str10 = "Hello Language My Language";
System.out.println(str10.replace("My", "Our"));
System.out.println(str10.replace("Language", "Java")); // 매칭되는 것 모두 치환
System.out.println();
System.out.println("replaceAll(regex, replacement), replaceFirst(regex, replacement)"); // 정규표현식 사용버젼 , replaceAll() 매칭되는것 전부 치환, replaceFirst() 첫매칭만 치환
System.out.println(str10.replaceAll("Language", "자바")); // 매칭되는 것 전부를 치환
System.out.println(str10.replaceFirst("Language", "자바")); // 첫번째 매칭만 치환
System.out.println();
System.out.println("equals(), equalsIgnoreCase()"); // 문자열 비교
String str11 = "Java";
String str12 = "java";
System.out.println(str11.equals("Java"));
System.out.println(str11.equals("str12")); // 대소문자 구분
System.out.println(str11.equalsIgnoreCase(str12)); // 대소문자 구분없이 비교
System.out.println();
System.out.println("String.format()");
// TODO
// 연습 : id /pw 입력받고요
// 로그인 성공 여부를 출력해주세요
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// TODO
sc.close();
System.out.println("\n프로그램 종료");
} // end main()
} // end class[연습문제]

LetterCapitalize
문장을 입력하고, 단어의 앞 문자를 대문자로 만들어 출력하기를 반복하다가 quit 을 입력 받으면 종료하기
[입력예]
hello my world
[출력예]
Hello My World
package practice.capitalize;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class LetterCapitalize {
// TODO : 필요한 메소드 있으면 추가 작성
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String str;
String [] words;
while(true) {
str = sc.nextLine();
if(str.trim().equalsIgnoreCase("quit")) break;
str = str.toLowerCase(); // 일단 소문자로 변환
words = str.split("\\s+"); // 공백기준으로 단어 쪼개기
for(String word : words) {
String firstLetter = word.substring(0, 1).toUpperCase();
String rest = word.substring(1); // 나머지 문자열
System.out.print(firstLetter + rest + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
sc.close();
} // end main()
} // end class✨Tips!
1. 메소드 단축키
- F3 : 정의한 메소드로 이동
- ctrl + alt + h (마우스 오른쪽 -> Open Call Hierarchy 클릭) : 메소드 사용 위치 찾기
- 호출관게 확인 가능 ex) Call stack
- stack은 메모리에 차곡차곡 쌓이며, 위에서 부터 사라짐

- JavaDoc
- 도움말 기능 텍스트 지정


- 재귀호출 함수 문제 모음
http://www.jungol.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=pbank&sca=2080
(웹개발하면서 재귀호출을 많이 보진 않지만, 상식적으로 알아두기!)
