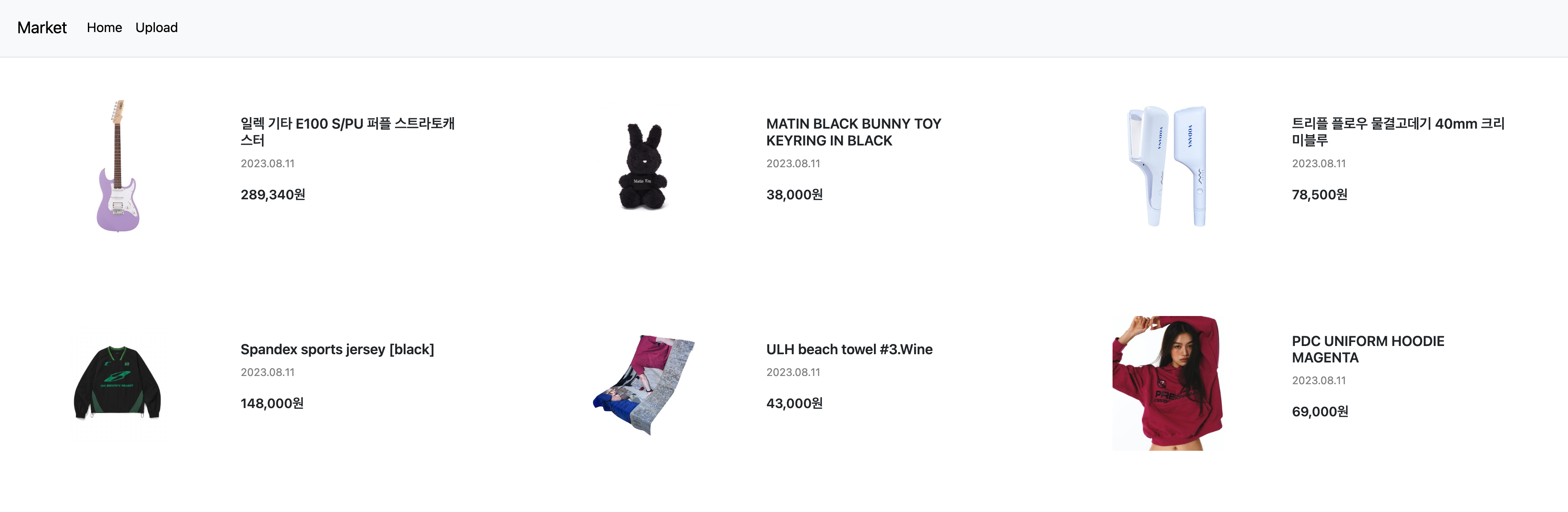
모든 내용은 코딩애플 님의 영상을 보며 배운 내용들이며, firebase 9 버전에 맞게 새로 고쳐 본 코드이다. Next.js 프로젝트로 만들었다.
⚙️ Firebase 설정
Firebase 설치
yarn add firebase
npm install firebaseFirebase CLI 설치
yarn global add firebase-tools
npm install -g firebase-toolsGoogle 로그인
firebase login프로젝트 시작하기
firebase initfirebase init을 하게 되면 이런 선택지를 받게 된다. 우선은 호스팅만 할 거라 Hosting에만 체크해 준 뒤 Enter를 누른다.
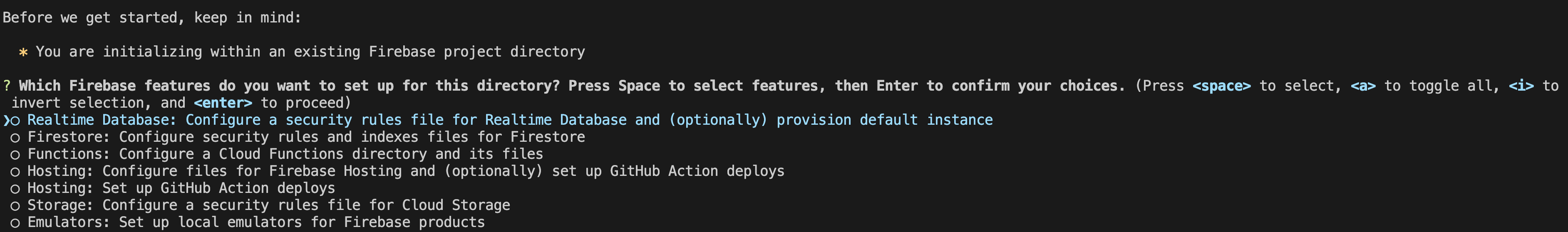
웹 앱 배포 (생략 가능)
firebase deploy- What do you want to use as your public directory?
: 배포할 정적 파일(html이나 js)이 저장되어 있는 디렉토리의 상대 경로를 입력하면 된다. 아무것도 입력하지 않고 Enter를 누르면 기본값인 public으로 지정된다. 만약 build라는 디렉토리에 위치한다면 build라고 입력해야 한다. 나는 Next.js 프로젝트이기 때문에 out으로 설정해 주었다. - Configure as a single-page-app (rewrite all urls to /index.html)?
: 404 오류로 처리되는 URL이 index.html을 대신 제공하도록 rewrite 된다. - Set up automatic build and deploys with GitHub?
: GitHub로의 자동 배포는 필요 없으니 N 입력!
함수 import
이 데이터를 프로젝트에서 읽고 쓰기 위해서는 다음의 함수가 필요하므로 export 해 준다.
// firebase.config.js
import { initializeApp } from 'firebase/app'
import { doc, collection, getFirestore, getDocs, setDoc } from 'firebase/firestore'
import { ref, getStorage, getDownloadURL, uploadBytes } from 'firebase/storage'
const config = {
apiKey: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_APIKEY,
authDomain: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_AUTHDOMAIN,
projectId: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_PROJECTID,
storageBucket: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_STORAGEBUCKET,
messagingSenderId: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_MESSAGINGSENDERID,
appId: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_APPID,
measurementId: process.env.NEXT_PUBLIC_MEASUREMENTID
}
let app, db
if (!app) {
app = initializeApp(config)
db = getFirestore(app)
}
export { app, db, doc, ref, getStorage, getDownloadURL, uploadBytes, collection, getDocs, setDoc }사전 설정
마지막으로 Firebase에서 Storage와 Firestore 항목을 각각 생성한 후 Rules로 가 설정을 바꿔 주어야 한다. 쓰고 읽기 위해 권한을 public으로 바꿔 주는 작업이다.
rules_version = '2';
service firebase.storage {
match /b/{bucket}/o {
match /{allPaths=**} {
// if false를 true로 변경
allow read, write: if true;
}
}
}✏️ 데이터 읽어 오기 (getDocs)
우선 Firestore에 여러 개의 데이터를 만들어 보자. 나는 상품 세 개를 만들어 보았다.
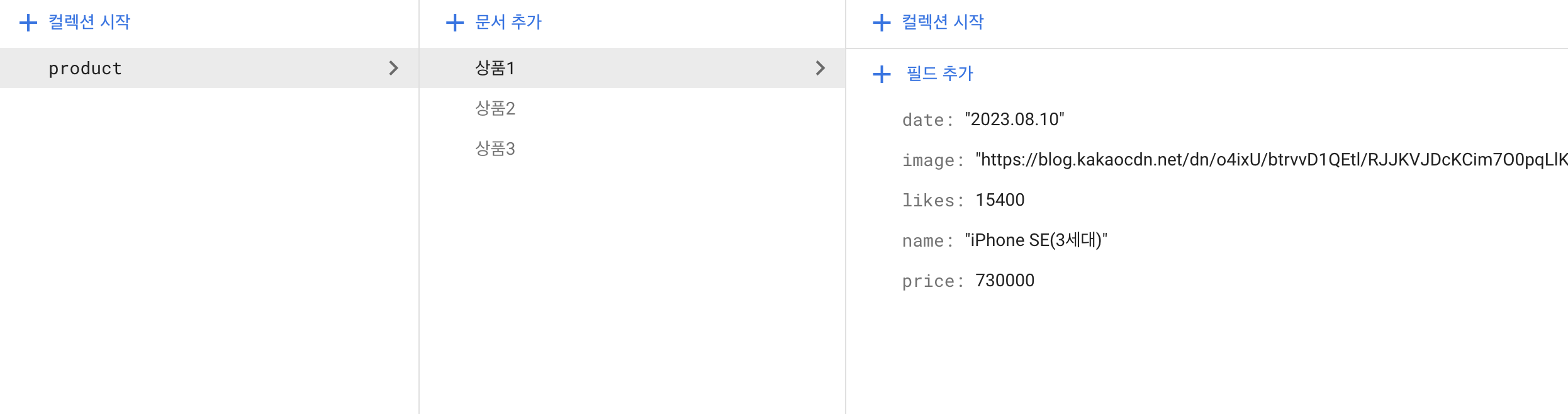
Firestore의 데이터를 읽어 오기 위해서는 getDocs()함수가 필요하다. 코드의 흐름은 이렇다.
1. collection()으로 참조할 컬렉션을 지정한다. 두 번째 매개변수에 컬렉션의 이름을 작성하면 된다.
2. getDocs()에 참조할 컬렉션을 담아 호출한다.
3. 성공할 경우 productsData에 각각의 데이터를 forEach 문을 통해 담아 준다.
4. 데이터의 개수만큼 컴포넌트가 렌더링될 수 있도록 Product 컴포넌트를 따로 만들어 준다.
5. 따로 작성하지는 않았지만 아래에서 Product를 map 돌리면 개수만큼 렌더링된다.
const [products, setProducts] = useState<any[]>([])
const Product = ({ productData }) => {
return (
<Box>
<Thumbnail style={{ background: `url(${productData.image}) no-repeat center / contain` }} />
<Detail>
<h5>{productData.name}</h5>
<p className='date'>{productData.date}</p>
<p className='price'>{productData.price?.toLocaleString()}원</p>
</Detail>
</Box>
)
}
useEffect(() => {
const productCollection = collection(db, 'product')
getDocs(productCollection)
.then(snapshot => {
const productsData = []
snapshot.forEach(doc => {
productsData.push(doc.data())
})
setProducts(productsData)
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error)
})
}, [])✏️ 데이터 쓰기 (setDoc)
- 문서 이름 지정
: 지정한 이름(상품4) 안에 필드가 추가됐다.
const productCollection = doc(db, 'product/상품4')
setDoc(productCollection, { name: '상품' }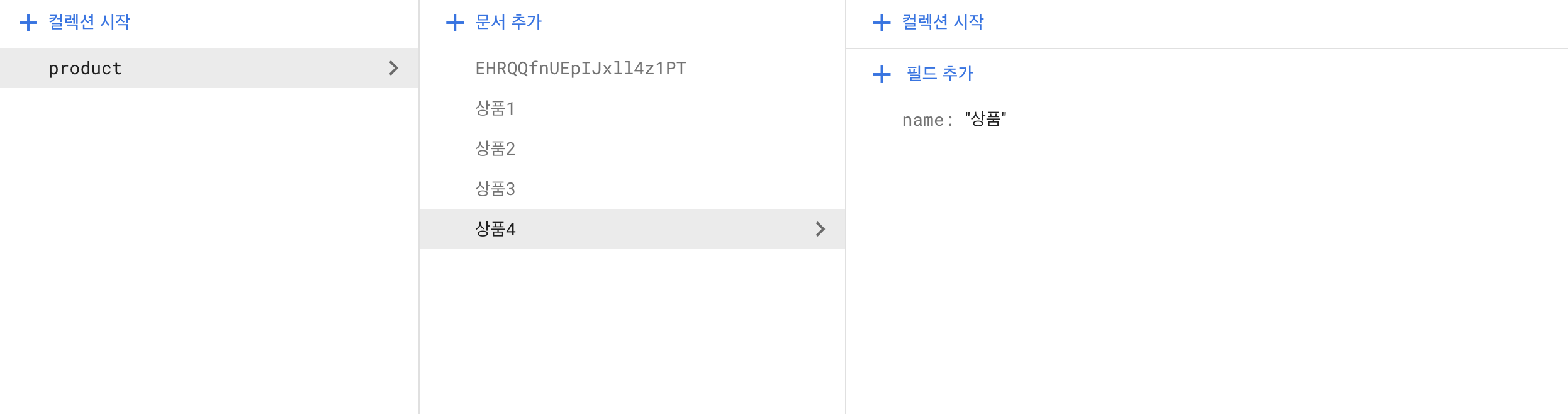
- 임의의 문서 이름으로 추가
: 문서 이름을 지정하지 않았기 때문에 문서 이름은 Hash 값으로 생성된다. 보통은 이 방법을 많이 쓴다. 유저가 많아지게 되면 일일히 하나씩 이름을 붙여 주기가 어렵기 때문이다.
const productCollection = collection(db, 'product')
setDoc(doc(productCollection), { name: '상품' })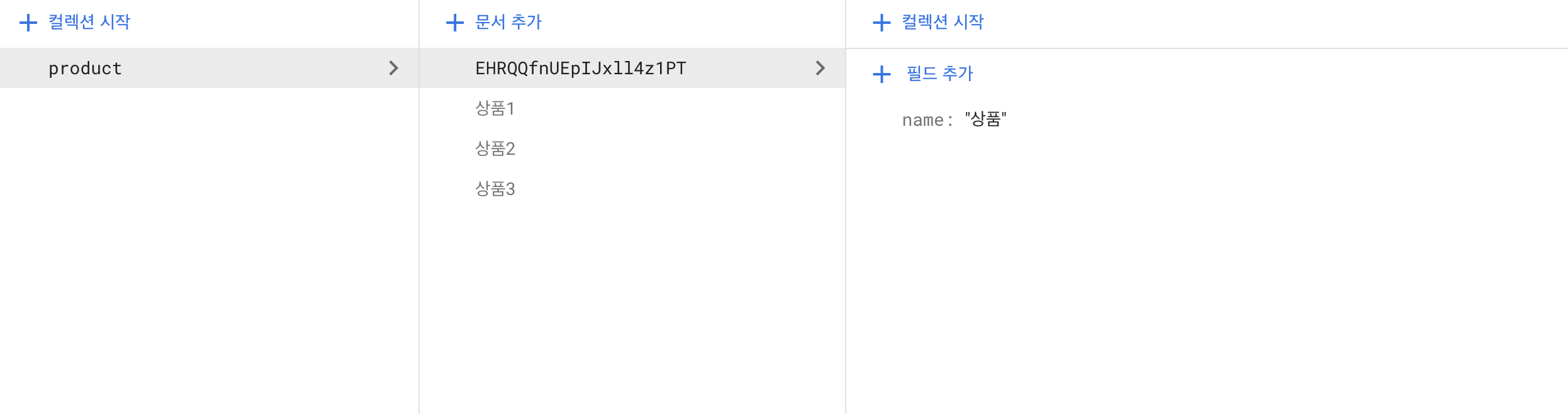
그러면 이제 input 값을 받아 Firestore에 저장될 수 있도록 해 보자. 폼은 이런 형식으로 만들어 뒀다.
<Container>
<h1>상품 등록</h1>
<input
type='text'
className='form-control mt-4'
id='name'
placeholder='상품 이름'
onChange={e => setProductName(e.target.value)}
/>
<textarea className='form-control mt-4' id='content' placeholder='내용' />
<input
type='number'
className='form-control mt-4'
id='price'
placeholder='가격'
onChange={e => setProductPrice(parseInt(e.target.value))}
/>
<input type='file' className='form-control mt-4' id='image' accept='image/*' onChange={onImageChange} />
<button
className='btn btn-secondary mt-4'
id='upload'
onClick={onClickUpload}
disabled={!productName || !productPrice || !productImage ? true : false} >
업로드
</button>
</Container>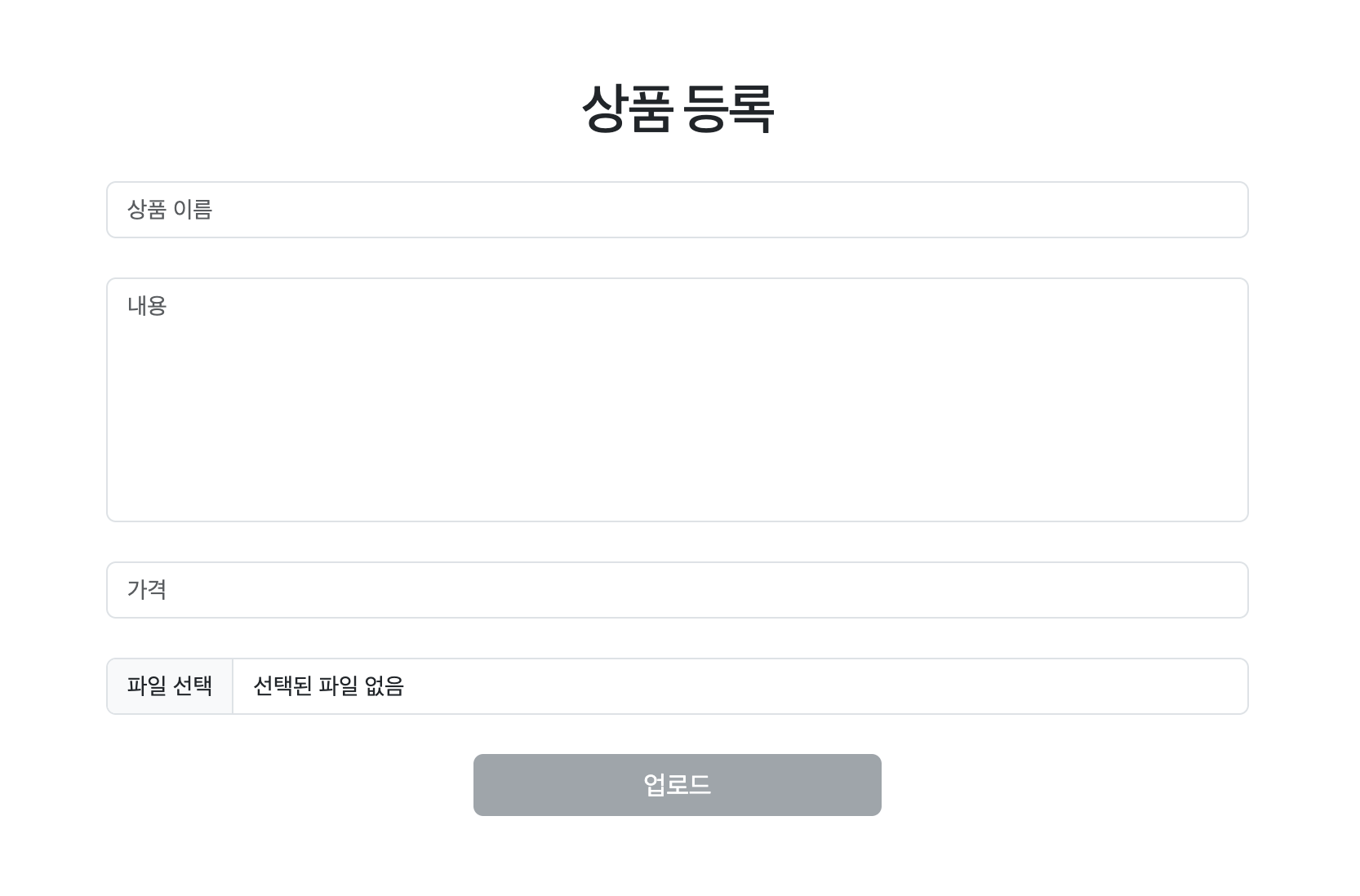
useForm을 이용해서 폼에 작성된 데이터를 한 번에 담는 방법도 있지만, 가볍게 만들 것이기 때문에 useState를 사용해서 각각의 값을 담았다. 상품 내용은 렌더링하지 않을 거라 따로 상태값에 담지 않았다.
const [productName, setProductName] = useState<string>('')
const [productPrice, setProductPrice] = useState<number>(0)
const [productImage, setProductImage] = useState<File | null>(null)이제 firestore에 값을 넣고 싶다!!!
1. collection() 함수로 어느 컬렉션에 쓸 것인지 담아 준다.
2. getStorage() 함수로 Firebase Storage의 인스턴스를 가져온다. (큰 의미 없음. 그냥 문법임.)
const productCollection = collection(db, 'product')
const storage = getStorage(app)업로드 버튼을 클릭했을 때 동작할 수 있도록 onClickUpload 함수를 만들었다. 데이터를 읽어 올 때는 getDocs를 썼지만 쓸 때는 setDoc을 사용한다. 위에서 만든 productCollection을 doc 안에 첫 번째 매개변수로 넣어 주고, 두 번째 매개변수로 필드와 필드값을 입력해 주면 된다.
Date는 yyyy.MM.dd 형식으로 사용하고 싶어 new Date()의 기본값으로 담지 않고 format으로 형식을 바꾸어 담았다.
const date = new Date()
const formattedDate = format(date, 'yyyy.MM.dd')
const onClickUpload = async () => {
try {
setDoc(doc(productCollection), {
name: productName,
price: productPrice,
date: formattedDate
})
router.push('/home')
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
}
}이제 이미지를 넣을 차례! 이미지는 그냥 업로드는 할 수 있지만, 읽어 오려면 string 형식이어야 한다. 화면에 보이게 하려면 src나 url 같은 속성에 넣어야 하기 때문에 이미지 주소가 더더욱 필요하다. 우선 이미지가 바뀌면 바로 상태값에 들어갈 수 있도록 onChange에 넣을 함수를 만들자. e.target.files가 파일의 목록(Array-like 객체)을 나타내기 때문에 첫 번째 요소만 가지고 오기 위해 e.target.files?.[0]로 작성한다.
간단히 말해 파일을 선택한 경우에는 첫 번째 파일을, 선택하지 않은 경우에는 null 값을 file 변수에 할당하는 역할을 한다.
const onImageChange = async (e: ChangeEvent<HTMLInputElement>) => {
const file = e.target.files?.[0] || null
setProductImage(file)
}ref() 함수는 스토리지 내의 특정 파일 또는 폴더에 대한 참조를 생성하고, uploadBytes()는 파일의 내용을 바이트 단위로 업로드하는 역할을 한다. 흐름은 이렇다.
1. imageRef 이미지를 업로드할 경로를 설정한다. (ref가 참조할 경로)
2. uploadBytes()로 상품의 이미지 정보를 업로드한다.
3. getDownloadURL()로 설정한 경로에 업로드된 파일의 다운로드 URL을 가지고 온다.
4. 필드값으로 넣는다.
const onClickUpload = async () => {
const imageRef = ref(storage, `images/${productName}/${productImage.name}`)
await uploadBytes(fileRef, productImage)
const imageURL = await getDownloadURL(imageRef)
try {
setDoc(doc(productCollection), {
name: productName,
price: productPrice,
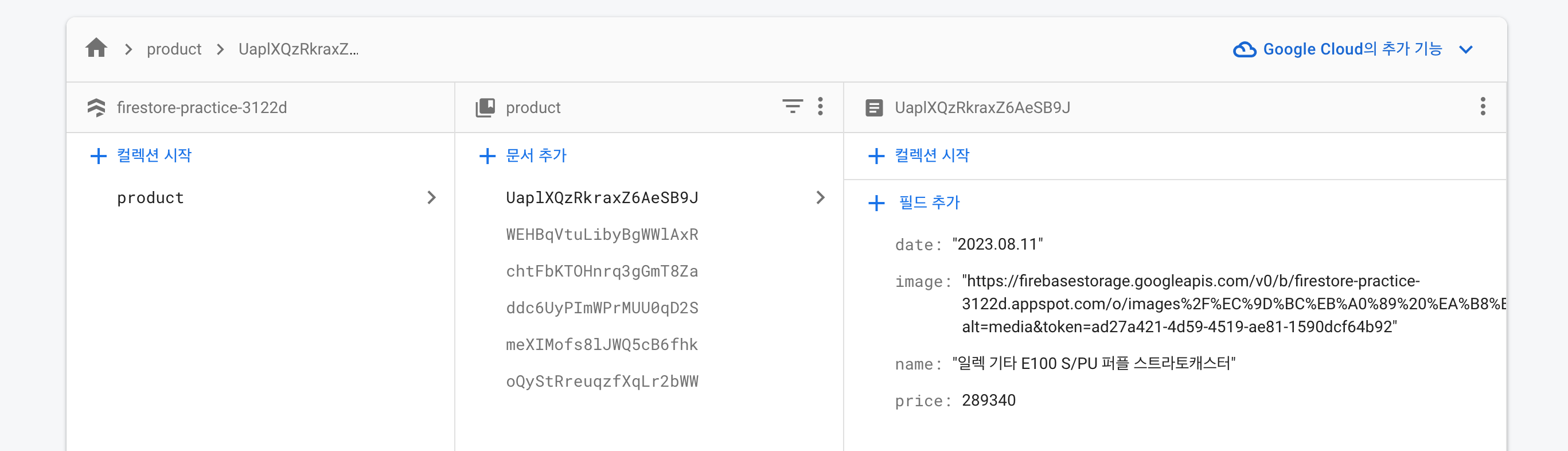
image: imageURL,
date: formattedDate
})
router.push('/home')
} catch (error) {
console.error(error)
}
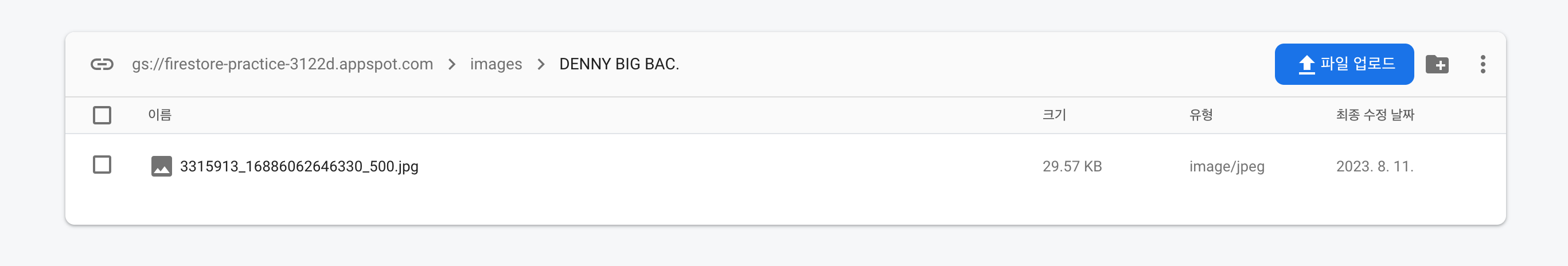
}업로드 버튼을 클릭해 함수를 실행시키면 Storage와 Firestore에 각각 이렇게 담긴다.
Storage
- images/
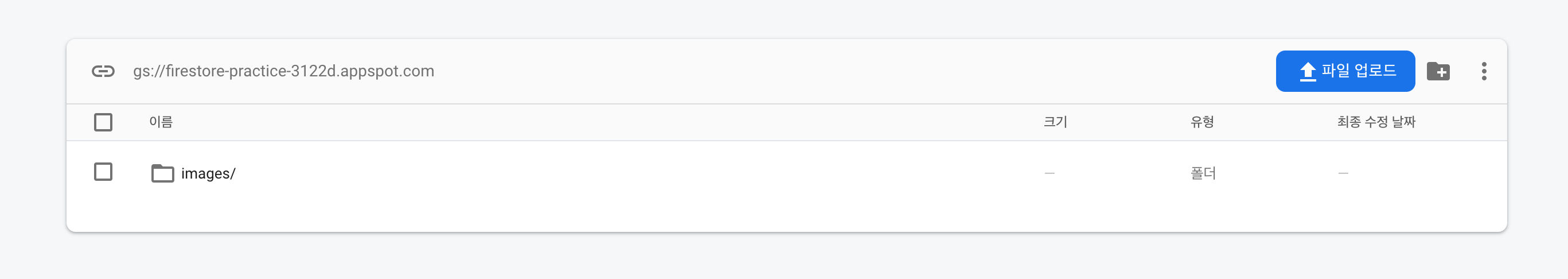
- images/productName
- images/productName/productImage.name
Firestore
🖥️ 결과 화면