11일 실습문제 복습
- 3~7사이의 숫자 하나 출력
- 작은 수, 큰 수를 입력받아 두 수 사이의 랜덤한 숫자 하나 출력
- 1~9까지 정답 수를 랜덤으로 받고 숫자 맞추기 게임
//실습 1번 3 ~ 7 사이의 랜덤한 숫자 하나 출력
int rand_num;
srand(time(NULL));
//입력 (X)
//처리
rand_num = rand() % 5 + 3;
//출력
cout << "3~7사이 랜덤한 숫자 : " << rand_num << endl;
//실습 2번 작은 수와 큰 수를 입력받아 두 수 사이의 랜덤한 숫자 하나 출력
//입력
int input_min_num;
int input_max_num;
cout << "작은 수 : ";
cin >> input_min_num;
cout << "큰 수 : ";
cin >> input_max_num;
//처리
rand_num = rand() % (input_max_num - input_min_num + 1) + input_min_num;
//출력
cout << "사이의 랜덤한 숫자 : " << rand_num << endl;
//실습 3번 프로그램을 실행하면 1 ~ 9 사이의 숫자가 정답으로 정해진다. 유저가 1 ~ 9 사이의 숫자를 입력하면 맞으면 true, 틀리면 false를 출력
//처리
int correct_num = rand() % 9 + 1;
cout << "미리보는 정답 : " << correct_num << endl;
//입력
int input_quiz_num;
cin >> input_quiz_num;
//출력
(input_quiz_num == correct_num) ? cout << "True" << endl : cout << "False" << endl;제어문
제어문 데이터(타입) / 연산자 / <제어구조>
- 조건문 : 특정 조건에 따라서 실행문의 실행여부를 제어 => if문 / switch문
- 반복문 : 특정 조건에 따라서 실행문을 일정 횟수만큼 반복 실행 제어 => for문 / while문
<조건문>
1.1) if 문
if (조건식(참/거짓)) {
실행문;
}
else if (조건식2(참/거짓)) {
실행문2;
}
else {
실행문3;
}- if문 실습
/*
조건문 실습1.
입력받은 숫자가 10보다 크면 "입력된 숫자가 10보다 큽니다." 출력
10이하 9초과 이면 "9보다 큽니다." 출력
9이하 6초과 이면 "6보다 큽니다." 출력
6이하 이면 "6보다 작습니다." 출력
*/
//입력
int input_num;
cout << "숫자 하나를 입력하시오 : ";
cin >> input_num;
//처리, 출력
if (input_num > 10) {
cout << "입력된 숫자는 10보다 큰 수 입니다." << endl;
}
else if (input_num > 9) {
cout << "입력된 숫자는 9보다 큰 수 입니다." << endl;
}
else if (input_num > 6) {
cout << "입력된 숫자는 6보다 큰 수 입니다." << endl;
}
else {
cout << "입력된 숫자는 6보다 작거나 같은 수 입니다." << endl;
}1.2) switch 문
switch(정수형 변수) {
case 정수1 :
실행문1;
break;
.
.
.
case 정수n :
실행문n;
break;
defalut: // 해당하는 정수 값이 없을때
실행문d;
break;
}
- switch문 실습
/*
swtich 문 실습.
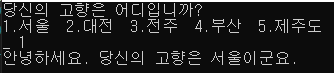
당신의 고향은 어디입니까?
1. 서울 2. 양평 3. 광주 4. 대전 5. 제주도
_ (입력받기)
서울 => 안녕하세요. 당신의 고향은 서울이군요.
제주도 => 안녕하수꽝. 혼저옵서예.
default => 5개 중에 선택해주세요.
*/
//입력
int hometown_num;
cout << "당신의 고향은 어디입니까?" << endl << "1.서울 2.대전 3.전주 4.부산 5.제주도" << endl << "_ ";
cin >> hometown_num;
//처리, 출력
switch (hometown_num) {
case 1:
cout << "안녕하세요. 당신의 고향은 서울이군요." << endl;
break;
case 2:
cout << "안녕하세유. 당신 고향 대전이군요." << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "안녕하시랑께. 당신의 고향은 전주군요." << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "안녕하시꽝. 당신의 고향은 부산이군요." << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "혼저옵서예. 제주도 사람인?" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "5개 중에 하나를 선택하세요." << endl;
break;
}반복문
<반복문>
2.1.1) while문 => 조건식이 참이면 실행문 실행
while (조건식){
실행문;
조건식을 바꾸는 실행문; // while문을 중단시키는 첫번째 방법
if(조건식){
break; // while문을 중단시키는 두번째 방법
}
}2.1.2) do-while문 => 조건식이 거짓이어도 한번은 실행한다.
do {
실행문;
}
while (조건식);- while, do-while문 실습
/*
while문 실습
Hello World를 5번 출력하는 프로그램
*/
int repeat_count = 0;
//while문 조건식 변경탈출
while (repeat_count < 5) {
cout << "1. Hello World!" << endl;
repeat_count++;
}
//while문 실행문 안에서 if문으로 break 탈출
while (1) {
cout << "2. Hello World!" << endl;
repeat_count++;
if (repeat_count >= 5) {
break;
}
}
//do-while문
do {
cout << "3. Hello World!" << endl;
repeat_count++;
} while (repeat_count < 5);
// 실습3. 정답 맞추는 문제를 정답 맞출 때 까지 반복되는 프로그램으로 수정
int correct_num = rand() % 9 + 1;
int input_quiz_num = 0;
while (input_quiz_num != correct_num) {
cout << "정답 일 것 같은 숫자 하나를 입력하시오 : _ ";
cin >> input_quiz_num;
(input_quiz_num == correct_num) ? cout << "정답! 프로그램 종료" << endl : cout << "오답!" << endl;
}2.2) for문
for((1)초기식; (2)조건식; (3)증감식){
(4)실행문;
}=> 순서 : (1) -> (2) -> (4) -> (3) -> (2) -> (4) -> (3) -> ... 조건식의 결과값이 0이 나올 때 까지
- for문 실습
/*
for문
실습1. 10부터 1까지 차례대로 출력되는 코드를 작성해보자.
실습2. 100미만의 3의 배수를 차례대로 출력되는 코드 작성해보자
실습3. 1000미만의 2의 승수를 차례대로 출력
*/
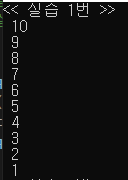
cout << "<< 실습 1번 >>" << endl;
int question1_num = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cout << " " << question1_num<< endl ;
question1_num--;
}
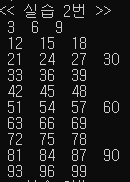
cout << "<< 실습 2번 >>" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
if ((i % 3) == 0) {
cout << " " << i << endl;
}
}
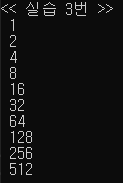
cout << "<< 실습 3번 >>" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i*=2) {
cout << " " << i << endl;
}전체 실습
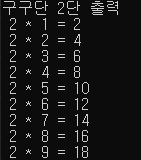
실습4. 구구단을 출력해보자.
4.1) 구구단 2단을 출력해보자.
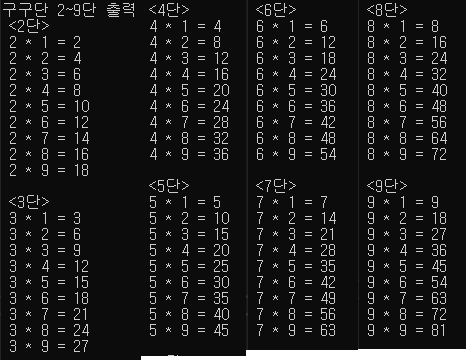
4.2) 구구단 2단 ~ 9단을 차례대로 출력해보자
2단
3단
4단
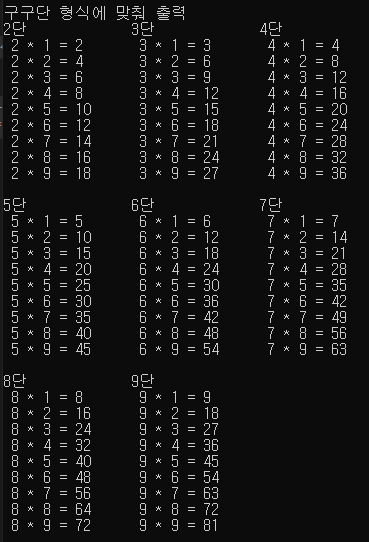
4.3) 구구단 2단 ~ 9단을 다음과 같은 형태로 출력해보자
2단 3단 4단
5단 6단 7단
8단 9단
//4.1) 구구단 2단을 출력해보자.
int two_num = 2;
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
cout << " " << two_num << " * " << i << " = " << two_num * i << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//4.2) 구구단 2단 ~ 9단을 차례대로 출력해보자
int gugudan1_num = 2;
while (gugudan1_num != 10) {
cout <<" <" << gugudan1_num << "단>" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
cout << " " << gugudan1_num << " * " << i << " = " << gugudan1_num * i << endl;
}
gugudan1_num++;
cout << endl;
}
/*4.3) 구구단 2단 ~ 9단을 다음과 같은 형태로 출력해보자
2단 3단 4단
5단 6단 7단
8단 9단
*/
int mutiple_num = 1;
cout << "2단\t\t" << "3단\t\t" << "4단\t\t" << endl;
while (1) {
for (int i = 2; i <= 4; i++) {
cout << " " << i << " * " << mutiple_num << " = " << i * mutiple_num << "\t";
}
if (mutiple_num < 10) {
mutiple_num++;
cout << endl;
}
if (mutiple_num == 10) {
break;
}
}
cout << endl;
cout << "5단\t\t" << "6단\t\t" << "7단\t\t" << endl;
mutiple_num = 1;
while (1) {
for (int i = 5; i <= 7; i++) {
cout << " " << i << " * " << mutiple_num << " = " << i * mutiple_num << "\t";
}
if (mutiple_num < 10) {
mutiple_num++;
cout << endl;
}
if (mutiple_num == 10) {
break;
}
}
cout << endl;
cout << "8단\t\t" << "9단\t\t" << endl;
mutiple_num = 1;
while (1) {
for (int i = 8; i <= 9; i++) {
cout << " " << i << " * " << mutiple_num << " = " << i * mutiple_num << "\t";
}
if (mutiple_num < 10) {
mutiple_num++;
cout << endl;
}
if (mutiple_num == 10) {
break;
}
}
숙제(별찍기)
//숙제 : 별찍기 7개
/*
1)
*
**
***
****
*****
*/
cout << endl << "1번";
for (int i1 = 0; i1 <= 5; i1++) {
for (int j1 = 0; j1 < i1; j1++) {
cout << "*";
}
for (int k1 = 5; k1 > i1; k1--) {
cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
2)
*
**
***
****
*****
*/
cout << endl << "2번";
for (int i2 = 0; i2 <= 5; i2++) {
for (int j2 = 5; j2 > i2; j2--) {
cout << " ";
}
for (int k2 = 0; k2 < i2; k2++) {
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
3)
*****
****
***
**
*
*/
cout << endl << "3번" << endl;
for (int i3 = 0; i3 <= 5; i3++) {
for (int j3 = 5; j3 > i3; j3--) {
cout << "*";
}
for (int k3 = 0; k3 < i3; k3++) {
cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
4)
*****
****
***
**
*
*/
cout << endl << "4번" << endl;
for (int i4 = 0; i4 <= 5; i4++) {
for (int j4 = 0; j4 < i4; j4++) {
cout << " ";
}
for (int k4 = 5; k4 > i4; k4--) {
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
5)
*
***
*****
*******
*********
*/
cout << endl << "5번" << endl;
for (int i5 = 0; i5 < 5; i5++) { //칸수
for (int empty1 = 4; empty1 > i5; empty1--) { //공백
cout << " ";
}
for (int star1 = 0; star1 < 2 * i5 + 1; star1++) { //별
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
6)
*********
*******
*****
***
*
*/
cout << endl << "6번" << endl;
for (int i6 = 0; i6 < 5; i6++) { //칸수
for (int empty2 = 0; empty2 < i6; empty2++) { //공백
cout << " ";
}
for (int star2 = 9; star2 > 2 * i6; star2--) { //별
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
7)
*
***
*****
*******
*********
*******
*****
***
*
*/
cout << endl << "7번" << endl;
int i7, empty3, star3;
for (i7 = 0; i7 < 5; i7++) { //칸수
for (empty3 = 4; empty3 > i7; empty3--) { //공백
cout << " ";
}
for (star3 = 0; star3 < 2 * i7 + 1; star3++) { //별
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
for (i7 = 1; i7 < 5; i7++) { //칸수
for (empty3 = 0; empty3 < i7; empty3++) { //공백
cout << " ";
}
for (star3 = 9; star3 > 2 * i7; star3--) { //별
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}Visual Studio 학습 내용
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <ctime>
#include <Windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
srand(time(NULL));
//실습 1번 3 ~ 7 사이의 랜덤한 숫자 하나 출력
int rand_num;
//입력 (X)
//처리
rand_num = rand() % 5 + 3;
//출력
cout << "3~7사이 랜덤한 숫자 : " << rand_num << endl;
//실습 2번 작은 수와 큰 수를 입력받아 두 수 사이의 랜덤한 숫자 하나 출력
//입력
int input_min_num;
int input_max_num;
cout << "작은 수 : ";
cin >> input_min_num;
cout << "큰 수 : ";
cin >> input_max_num;
//처리
rand_num = rand() % (input_max_num - input_min_num + 1) + input_min_num;
//출력
cout << "사이의 랜덤한 숫자 : " << rand_num << endl;
//실습 3번 프로그램을 실행하면 1 ~ 9 사이의 숫자가 정답으로 정해진다. 유저가 1 ~ 9 사이의 숫자를 입력하면 맞으면 true, 틀리면 false를 출력
//처리
int correct_num = rand() % 9 + 1;
cout << "미리보는 정답 : " << correct_num << endl;
//입력
int input_quiz_num;
cin >> input_quiz_num;
//출력
(input_quiz_num == correct_num) ? cout << "True" << endl : cout << "False" << endl;
/*
if 문 실습.
입력받은 숫자가 10보다 크면 "입력된 숫자가 10보다 큽니다." 출력
10이하 9초과 이면 "9보다 큽니다." 출력
9이하 6초과 이면 "6보다 큽니다." 출력
6이하 이면 "6보다 작습니다." 출력
*/
//입력
int input_num;
cout << "숫자 하나를 입력하시오 : ";
cin >> input_num;
//처리, 출력
if (input_num > 10) {
cout << "입력된 숫자는 10보다 큰 수 입니다." << endl;
}
else if (input_num > 9) {
cout << "입력된 숫자는 9보다 큰 수 입니다." << endl;
}
else if (input_num > 6) {
cout << "입력된 숫자는 6보다 큰 수 입니다." << endl;
}
else {
cout << "입력된 숫자는 6보다 작거나 같은 수 입니다." << endl;
}
/*
swtich 문 실습.
당신의 고향은 어디입니까?
1. 서울 2. 양평 3. 광주 4. 대전 5. 제주도
_ (입력받기)
서울 => 안녕하세요. 당신의 고향은 서울이군요.
제주도 => 안녕하수꽝. 혼저옵서예.
5개 중에 선택해주세요.
*/
//입력
int hometown_num;
cout << "당신의 고향은 어디입니까?" << endl << "1.서울 2.대전 3.전주 4.부산 5.제주도" << endl << "_ ";
cin >> hometown_num;
//처리, 출력
switch (hometown_num) {
case 1:
cout << "안녕하세요. 당신의 고향은 서울이군요." << endl;
break;
case 2:
cout << "안녕하세유. 당신 고향 대전이군요." << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "안녕하시랑께. 당신의 고향은 전주군요." << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "안녕하시꽝. 당신의 고향은 부산이군요." << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "혼저옵서예. 제주도 사람인?" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "5개 중에 하나를 선택하세요." << endl;
break;
}
// 위 switch 문 if문으로 변경
if (hometown_num == 1) {
cout << "안녕하세요. 당신의 고향은 서울이군요." << endl;
}
else if (hometown_num == 2) {
cout << "안녕하세유. 당신 고향 대전이군요." << endl;
}
else if (hometown_num == 3) {
cout << "안녕하시랑께. 당신의 고향은 전주군요." << endl;
}
else if (hometown_num == 4) {
cout << "안녕하시꽝. 당신의 고향은 부산이군요." << endl;
}
else if (hometown_num == 5) {
cout << "혼저옵서예. 제주도 사람인?" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "5개 중에 하나를 선택하세요." << endl;
}
/*
while문 실습
Hello World를 5번 출력하는 프로그램
*/
int repeat_count = 0;
//while문 조건식 변경탈출
while (repeat_count < 5) {
cout << "1. Hello World!" << endl;
repeat_count++;
}
//while문 실행문 안에서 if문으로 break 탈출
cout << endl;
repeat_count = 0;
while (1) {
cout << "2. Hello World!" << endl;
repeat_count++;
if (repeat_count >= 5) {
break;
}
}
//do-while문
cout << endl;
repeat_count = 0;
do {
cout << "3. Hello World!" << endl;
repeat_count++;
} while (repeat_count < 5);
// 실습3. 정답 맞추는 문제를 정답 맞출 때 까지 반복되는 프로그램으로 수정
cout << endl;
int correct_num = rand() % 9 + 1;
int input_quiz_num = 0;
while (input_quiz_num != correct_num) {
cout << "정답 일 것 같은 숫자 하나를 입력하시오 : _ ";
cin >> input_quiz_num;
(input_quiz_num == correct_num) ? cout << "정답! 프로그램 종료" << endl : cout << "오답!" << endl;
}
/*
for문
실습1. 10부터 1까지 차례대로 출력되는 코드를 작성해보자.
실습2. 100미만의 3의 배수를 차례대로 출력되는 코드 작성해보자
실습3. 1000미만의 2의 승수를 차례대로 출력
실습4. 구구단을 출력해보자.
4.1) 구구단 2단을 출력해보자.
4.2) 구구단 2단 ~ 9단을 차례대로 출력해보자
2단
3단
4단
4.3) 구구단 2단 ~ 9단을 다음과 같은 형태로 출력해보자
2단 3단 4단
5단 6단 7단
8단 9단
*/
cout << "<< 실습 1번 >>" << endl;
int question1_num = 10;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cout << " " << question1_num<< endl ;
question1_num--;
}
cout << "<< 실습 2번 >>" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < 100; i++) {
if ((i % 3) == 0) {
cout << " " << i << " ";
}
}
cout << "<< 실습 3번 >>" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i < 1000; i*=2) {
cout << " " << i << endl;
}
//4.1) 구구단 2단을 출력해보자.
cout << "구구단 2단 출력" << endl;
int two_num = 2;
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
cout << " " << two_num << " * " << i << " = " << two_num * i << endl;
}
cout << endl;
//4.2) 구구단 2단 ~ 9단을 차례대로 출력해보자
cout << "구구단 2~9단 출력" << endl;
int gugudan1_num = 2;
while (gugudan1_num != 10) {
cout <<" <" << gugudan1_num << "단>" << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
cout << " " << gugudan1_num << " * " << i << " = " << gugudan1_num * i << endl;
}
gugudan1_num++;
cout << endl;
}
/*4.3) 구구단 2단 ~ 9단을 다음과 같은 형태로 출력해보자
2단 3단 4단
5단 6단 7단
8단 9단
*/
cout << "구구단 형식에 맞춰 출력" << endl;
int mutiple_num = 1;
int gugu_su = 0;
cout << "2단\t\t" << "3단\t\t" << "4단\t\t" << endl;
while (1) {
for (gugu_su = 2; gugu_su <= 4; gugu_su++) {
cout << " " << gugu_su << " * " << mutiple_num << " = " << gugu_su * mutiple_num << "\t";
}
if (mutiple_num < 10) {
mutiple_num++;
cout << endl;
}
else if (mutiple_num == 10) {
break;
}
}
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "5단\t\t" << "6단\t\t" << "7단\t\t" << endl;
mutiple_num = 1;
while (1) {
for (gugu_su = 5; gugu_su <= 7; gugu_su++) {
cout << " " << gugu_su << " * " << mutiple_num << " = " << gugu_su * mutiple_num << "\t";
}
if (mutiple_num < 10) {
mutiple_num++;
cout << endl;
}
else if (mutiple_num == 10) {
break;
}
}
cout << endl << endl;
cout << "8단\t\t" << "9단\t\t" << endl;
mutiple_num = 1;
while (1) {
for (gugu_su = 8; gugu_su <= 9; gugu_su++) {
cout << " " << gugu_su << " * " << mutiple_num << " = " << gugu_su * mutiple_num << "\t";
}
if (mutiple_num < 10) {
mutiple_num++;
cout << endl;
}
else if (mutiple_num == 10) {
break;
}
}
//숙제 : 별찍기 7개
/*
1)
*
**
***
****
*****
*/
cout << endl << "1번";
for (int i1 = 0; i1 <= 5; i1++) {
for (int j1 = 0; j1 < i1; j1++) {
cout << "*";
}
for (int k1 = 5; k1 > i1; k1--) {
cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
2)
*
**
***
****
*****
*/
cout << endl << "2번";
for (int i2 = 0; i2 <= 5; i2++) {
for (int j2 = 5; j2 > i2; j2--) {
cout << " ";
}
for (int k2 = 0; k2 < i2; k2++) {
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
3)
*****
****
***
**
*
*/
cout << endl << "3번" << endl;
for (int i3 = 0; i3 <= 5; i3++) {
for (int j3 = 5; j3 > i3; j3--) {
cout << "*";
}
for (int k3 = 0; k3 < i3; k3++) {
cout << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
4)
*****
****
***
**
*
*/
cout << endl << "4번" << endl;
for (int i4 = 0; i4 <= 5; i4++) {
for (int j4 = 0; j4 < i4; j4++) {
cout << " ";
}
for (int k4 = 5; k4 > i4; k4--) {
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
5)
*
***
*****
*******
*********
*/
cout << endl << "5번" << endl;
for (int i5 = 0; i5 < 5; i5++) { //칸수
for (int empty1 = 4; empty1 > i5; empty1--) { //공백
cout << " ";
}
for (int star1 = 0; star1 < 2 * i5 + 1; star1++) { //별
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
6)
*********
*******
*****
***
*
*/
cout << endl << "6번" << endl;
for (int i6 = 0; i6 < 5; i6++) { //칸수
for (int empty2 = 0; empty2 < i6; empty2++) { //공백
cout << " ";
}
for (int star2 = 9; star2 > 2 * i6; star2--) { //별
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
/*
7)
*
***
*****
*******
*********
*******
*****
***
*
*/
cout << endl << "7번" << endl;
int i7, empty3, star3;
for (i7 = 0; i7 < 5; i7++) { //칸수
for (empty3 = 4; empty3 > i7; empty3--) { //공백
cout << " ";
}
for (star3 = 0; star3 < 2 * i7 + 1; star3++) { //별
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
for (i7 = 1; i7 < 5; i7++) { //칸수
for (empty3 = 0; empty3 < i7; empty3++) { //공백
cout << " ";
}
for (star3 = 9; star3 > 2 * i7; star3--) { //별
cout << "*";
}
cout << endl;
}
}