@RequestMapping
특정 URL로 Request를 보내면 들어온 요청을 Controller 내부의 특정 Method와 Mapping 하기 위해 사용한다.
Client로부터 요청이 왔을 때 어떤 Controller가 호출될지 Mapping하는것은 단순히 URL로 Mapping 하는것이 아니라 여러가지 요소(URL, Method 등)를 조합하여 Mapping한다.
- URL path
/example만 허용(Mapping)한다./example!=/example/
- 속성값들을 설정할 때 배열 형태로 다중 설정이 가능하다
ex)@RequestMapping**({**”/example”, “/example2”, “/example3”**})** - POST, GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, HEAD 모두 허용한다
- method 속성으로 HTTP 메서드를 지정하면 지정된것만 허용한다.
package com.example.springbasicannotation.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
// 응답 데이터를 반환한다.
@RestController
public class RequestMappingController {
// HTTP Method 는 GET만 허용한다.
@RequestMapping(value = "/v1", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String exampleV1() {
// logic
return "this is sparta!";
}
}@GetMapping
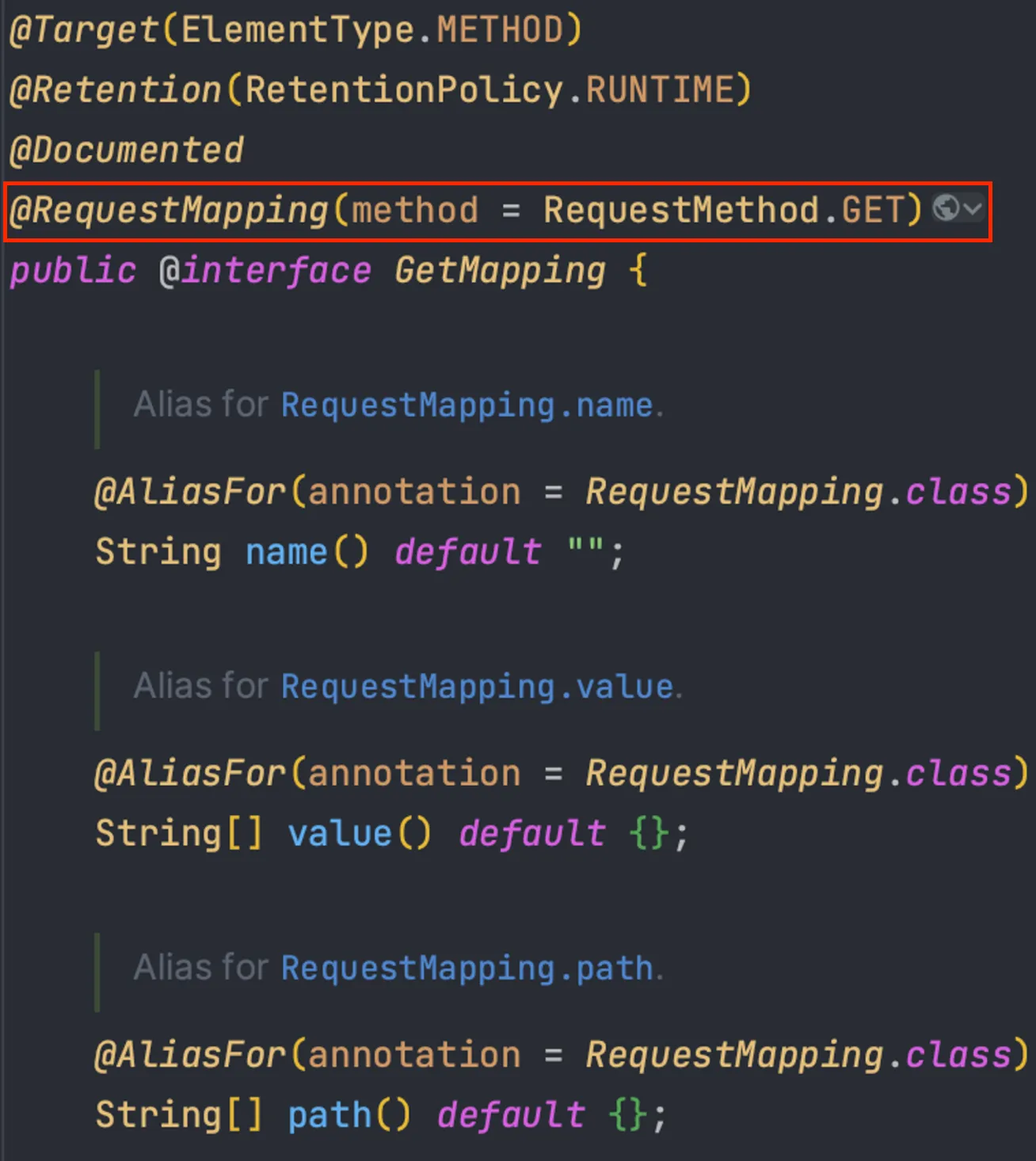
Target(ElementType.METHOD)Method Level에 해당 어노테이션을 적용한다 라는 의미- 내부적으로
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)을 사용하고 있다.
// Post, GET, Put, Patch, Delete 모두 가능
@GetMapping(value = "/v2")
public String exampleV2() {
// logic
return "this is sparta!";
}- Spring이 제공하는 Annotation들의 내부에 다 선언되어 있다.
- 대부분의 필요한 기능들이 이미 만들어져 있다.
- 그대로 갖다 쓰면 된다.
@RequestMapping보다는 직관적이고 축약된@GetMapping,@PostMapping등의 형식을 일반적으로 사용한다.
그러면 @RequestMapping은 언제 쓰는데?
- @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping, @PatchMapping의 Target은 Method Level 이다.
- @RequestMapping의 Target은 class, method 레벨에 적용이 가능하다.
- Restful API의 계층 구조
ex)users/{userId}, category/{categoryId}/product/{productId} - prefix로 선언할 URL을 class 레벨에 적용하는 것에 주로 사용된다.
@RequestMapping("/prefix")
@RestController
public class RequestMappingController {
// Post, GET, Put, Patch, Delete 모두 가능
@GetMapping(value = "/v3")
public String exampleV3() {
// logic
return "this is sparta!";
}
}@PathVariable
HTTP 특성 중 하나인 비연결성을 극복하여 데이터를 전달하기 위한 방법 중 하나
URL로 전달된 값을 파라미터로 받아오는 역할을 수행한다.
- 경로 변수를 중괄호 안의 값으로 사용할 수 있다.
ex)user/{id} - 기본적으로
@PathVariable로 설정된 경로 변수는 반드시 값을 가져야 한다.- 값이 없으면
404 Not Found Error발생
- 값이 없으면
- 최근 Restful API를 설계하는 것이 API의 기준이 되며 해당 어노테이션의 사용 빈도가 높아졌다.
@PathVariable의 규칙
1. 파라미터 변수명과 PathVariable 변수명이 같으면 속성 생략 가능
postId로 변수명이 같으므로@PathVariable의 매개변수("postId")생략 가능
@RequestMapping("/posts")
@RestController
public class PathVariableController {
// postId로 된 post 단건 조회
@GetMapping("/{postId}")
// public String pathVariableV1(@PathVariable("postId") Long data) {
// public String pathVariableV2(@PathVariable Long data) {
// logic
String result = "PathvariableV1 결과입니다 : " + data;
return result;
}
}2. @PathVariable 다중 사용 가능
@RestController
public class PathVariableController {
@GetMapping("/{postId}/comments/{commentId}")
public String pathVariableV3(
@PathVariable Long postId,
@PathVariable Long commentId
) {
// logic
String result = "postId : " + postId + "commentsId : " + commentId;
return result;
}
}@RequestMapping("/posts/{postId}")
@RestController
public class PathVariableController {
@GetMapping("/comments/{commentId}")
public String pathVariableV4(
@PathVariable Long postId,
@PathVariable Long commentId
) {
// logic
String result = "postId : " + postId + "commentsId : " + commentId;
return result;
}
}pathVariableV3,pathVariableV4의 차이점- V3
@GetMapping에서 경로 변수를 직접 선언- 요청 예시
GET /123/comments/456
postId = 123,commentId = 456
- V4
@RequestMapping을 사용해 공통 경로prefix분리- 요청 예시
GET /posts/123/commnets/456
postId = 123,commentId = 456
- V3
@RequestMapping에 경로 변수가 들어갈 수 있음
-> 아래에 있는 모든 메소드의prefix를 설정하게 됨- 로직과 기능은 동일함
@RequestMapping을 사용하면 공통된URL prefix를 분리해서 코드 가독성을 높이고 유지보수성을 향상함 !
특정 헤더/파라미터 매핑 방법
속성 설정으로 특정 헤더, 파라미터와 Mapping 할 수 있음
1. 파라미터 추가 매핑
package com.example.springbasicannotation.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class ParameterController {
// parms 속성값 추가
@GetMapping(value = "/users", params = "gender=man")
public String params() {
// logic
String result = "params API가 호출 되었습니다.";
return result;
}
}GET http://localhost:8080/users?gender=man에서gender=man파라미터가 있어야 호출됨- 파라미터가 없으면
400 Bad Request
- 파라미터가 없으면
속성 작성 규칙
params = "gender"- params의 key값은 커스텀이 가능하다
- value는 없어도 된다.
params = "!gender"- gender가 없어야 한다.
params = "gender=man"- gender=man 이어야 한다.
params = "gender!=man"- params의 value값이 man가 아니여야 한다.
params = {"gender=man", "gender=woman"}- 배열로 속성 값을 여러 개 설정이 가능하다.
2. 특정 헤더 매핑
@RestController
public class ParameterController {
// headers 속성값 추가
@PostMapping(value = "/users", headers = "Content-Type=application/json")
public String headers() {
// logic
String result = "headers API가 호출 되었습니다.";
return result;
}
}속성 작성 규칙
params 규칙과 같다.
3. MediaType 매핑, consume (수용)
- HTTP Header Content-Type(요청)과 Mapping 됨
@RestController
public class ParameterController {
// consumes 속성값 추가
@PostMapping(value = "/users", consumes = "application/json") // MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE
public String consumes() {
// logic
String result = "consumes API가 호출 되었습니다.";
return result;
}
}consumes의 value는MediaType.*형태로 사용됨
파라미터가 없거나 다르면
405 Unsupported Media Type Exception 발생
속성 작성 방법
consumes=”application/json”- application/json 미디어 타입 허용
consumes=”!application/json”- application/json 제외 미디어 타입 허용
consumes=”application/*”- application/ 으로 시작하는 모든 미디어 타입 허용
consumes=”*\/*”- 모두 허용
4. MediaType 매핑, produces (제공)
- 요청 헤더의 Accept 값에 따라 제공하는 값이 변함
@RestController
public class ParameterController {
// produces 속성값 추가
@GetMapping(value = "/users", produces = "text/plain")
public String produces() {
// logic
String result = "text/plain 데이터 응답";
return result;
}
}consumes의 value는MediaType.*형태로 사용됨- HTTP 요청 Accept Header에 Media Type이 있어야 함
속성 작성 방법
consumes 규칙과 같다.
Spring이 지원하는 Parameter
1. HTTP 헤더 조회
- 요청 Header에 쉽게 접근할 수 있음
- HttpservletRequest와 같이 파라미터로 다룰 수 있음
// 로깅
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class RequestHeaderController {
@GetMapping("/request/headers")
public String headers(
HttpServletRequest request, // Servlet에서 사용한 것과 같음
HttpServletResponse response, // Servlet에서 사용한 것과 같음
@RequestHeader MultiValueMap<String, String> headerMap,
@RequestHeader("host") String host,
@CookieValue(value = "cookie", required = false) String cookie,
HttpMethod httpMethod,
Locale locale
) {
// Servlet
log.info("request={}", request);
log.info("response={}", response);
// @RequestHeader
log.info("headerMap={}", headerMap);
log.info("host={}", host);
// @CookieValue
log.info("cookie={}", cookie);
// HttpMethod
log.info("httpMethod={}", httpMethod);
// Locale
log.info("Locale={}", locale);
return "success";
}
}출력 결과
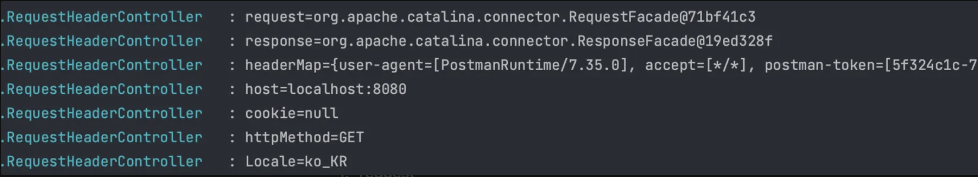
- request
- HttpServletRequest 객체 주소 값
- response
- HttpServletRequest 객체 주소 값
- headerMap
hashMap={
user-agent=[PostmanRuntime/7.35.0],
accept=[*/*],
postman-token=[5f324c1c-7902-4750-9e01-2c4d093e8ad6],
host=[localhost:8080],
accept-encoding=[gzip, deflate, br],
connection=[keep-alive]
}- host
- host 정보
- cookie
- Header의 Cookie 값
- httpMethod
- 호출에 사용한 HttpMethod
- Locale
- 위치 정보를 나타내는 헤더
- 우선순위가 존재한다.
MultiValueMap
Map과 유사하게
Key-Value형식
Map과 다르게 하나의 Key가 여러 개의 Value를 가질 수 있음
HTTP Header, Reqeust Parameter와 같이 하나의 Key에 여러 값을 받을 때 사용한다.ex)
key1=value2&key1=value2
MultiValueMap<String, String> linkedMultiValuemap = new LinkedMultiValueMap();
// key1에 value1 저장
linkedMultiValuemap.add("key1", "value1");
// key1에 value2 저장
linkedMultiValuemap.add("key1", "value2");
// key1에 저장된 모든 value get
List<String> values = linkedMultiValuemap.get("key1");참고자료
Spring 입문 - 4주차
- Request Mapping 1강
- Request Mapping 2강
