전략 패턴이란
- 여러 유사한 알고리즘을 캡슐화 하여 실행(런타임)중에 알고리즘 전략을 선택하여 객체의 행위를 동적으로 변경 가능하게 만드는 패턴이다.
전략패턴의 구조
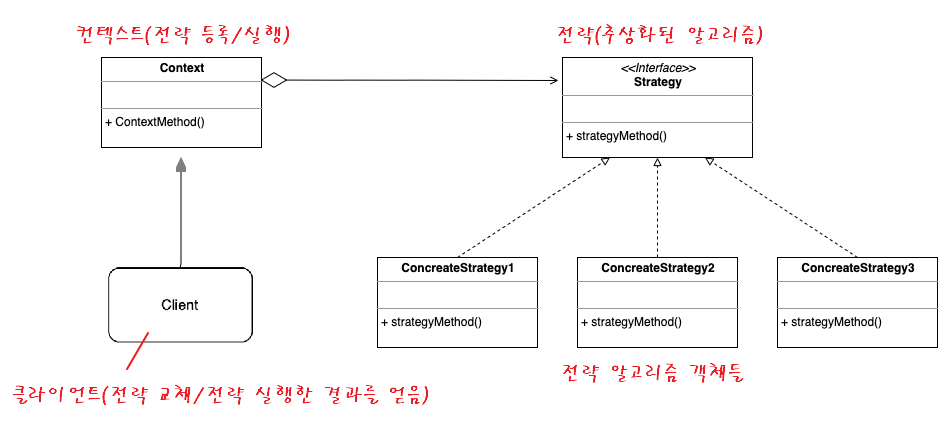
- 전략 알고리즘 객체들 : 알고리즘 , 행위 , 동작을 객체로 정의한 구현체
- 전략 인터페이스 : 모든 전략 구현체에 대한 공용 인터페이스
- 컨텍스트(Context) : 알고리즘을 실행해야 할 때마다 해당 알고리즘과 연결된 전략 객체의 메소드를 호출.
- 클라이언트 : 특정 전략 객체를 컨텍스트에 전달 함으로써 전략을 등록하거나 변경하여 전략 알고리즘을 실행한 결과를 누린다.
전략패턴의 장단점
장점
- 가독성 , 유지보수성이 좋아진다.
- 런타임에 한 객체 내부에서 사용되는 알고리즘을 교환할 수 있다.
- OCP( 개방 폐쇄의 원칙 ) : 변경에 닫혀있고 확장엔 열려있는 객체지향 원칙이 실현된다.
- 다른 행동 및 전략이 추가된다고 해도 기존의 코드는 변경하지 않고 확장이 가능하다.
- 상속 대신 위임을 사용할 수 있다.
- 상속의 단점
- 상속은 단 한개의 클래스만 상속할 수 있기에, 나중에 진짜 상속해야할 클래스가 생길때 상속을 못한다.
- 상위 클래스가 바뀌면 하위 클래스들도 모조리 영향을 받기에, 종속성 측면에서의 단점이 있다.
- 위임의 장점
- 해당 Context 클래스가 변경되더라도, 전략 영역은 영향을 받지 않는다.
단점
- 알고리즘이 많아질수록 관리해야할 객체의 수가 늘어난다는 단점이 있다. ( 복잡도 상승 )
- 어플리케이션의 알고리즘이 많지않고 자주 변경되지 않는다면, 새로운 클래스와 인터페이스를 만들어 프로그램을 복잡하게 만들 이유가 없다.
- 개발자는 적절한 전략을 선택하기 위해 전략간의 차이점을 파악하고 있어야 한다. ( 복잡도 상승 )
전략패턴 예제코드 ( 로봇 설계 )
// 로봇
public class Robot {
private MoveStrategy moveStrategy;
private EmotionStrategy emotionStrategy;
public Robot(MoveStrategy moveStrategy, EmotionStrategy emotionStrategy) {
this.moveStrategy = moveStrategy;
this.emotionStrategy = emotionStrategy;
}
public void robotExplain() {
moveStrategy.move();
emotionStrategy.emotion();
System.out.println("로봇");
}
public void changeMoveStrategy(MoveStrategy moveStrategy) {
this.moveStrategy = moveStrategy;
}
public void changeEmotionStrategy(EmotionStrategy emotionStrategy) {
this.emotionStrategy = emotionStrategy;
}
}
// 행동 영역 설정
public interface MoveStrategy {
void move();
}
// 감정 영역 설정
public interface EmotionStrategy {
void emotion();
}// 서있는 행동 객체
public class Stand implements MoveStrategy {
@Override
public void move() {
System.out.print("서있는 ");
}
}
// 걷고있는 행동 객체
public class Walking implements MoveStrategy {
@Override
public void move() {
System.out.print("걷고있는 ");
}
}
// 달리는 행동 객체
public class Running implements MoveStrategy {
@Override
public void move() {
System.out.print("달리는 ");
}
}// 화난 감정 객체
public class Angry implements EmotionStrategy {
@Override
public void emotion() {
System.out.print("화난 ");
}
}
// 행복한 감정 객체
public class Happy implements EmotionStrategy {
@Override
public void emotion() {
System.out.print("행복한 ");
}
}// 메인 메서드
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Robot robot = new Robot(new Walking(), new Angry()); // 걷고 있는, 화난 객체 설정
robot.robotExplain(); // 출력
robot.changeMoveStrategy(new Running()); // 걷고 있는 -> 달리는 교체
robot.robotExplain(); // 출력
robot.changeEmotionStrategy(new Happy()); // 화난 -> 행복한 교체
robot.changeMoveStrategy(new Stand()); // 달리는 -> 서있는 교체
robot.robotExplain(); // 출력
}
}
// 출력 결과
// 걷고있는 화난 로봇
// 달리는 화난 로봇
// 서있는 행복한 로봇JDK에서 사용되는 전략 패턴
- 대표적으로 많이 사용되는 전략패턴의 예제는 sort()정렬 메서드에 사용되는 Comparator 인터페이스 이다.
class Scratch {
void run () throws IOException {
Integer[] arr = {4, 7, 100, 2, 6, 33523, 6345, 423, 342, 324, 652, 4};
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr) + "\n");
Arrays.sort(arr); // 오름차순 정렬
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr) + "\n");
Arrays.sort(arr, Comparator.reverseOrder()); // reverseOrder() : 내림차순 정렬 알고리즘 부여
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr) + "\n");
Arrays.sort(arr, Comparator.naturalOrder()); // naturalOrder() : 오름차순 정렬 알고리즘 부여
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr) + "\n");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
new Scratch().run();
}
}
// 출력 결과
// [4, 7, 100, 2, 6, 33523, 6345, 423, 342, 324, 652, 4]
//
// [2, 4, 4, 6, 7, 100, 324, 342, 423, 652, 6345, 33523]
//
// [33523, 6345, 652, 423, 342, 324, 100, 7, 6, 4, 4, 2]
//
// [2, 4, 4, 6, 7, 100, 324, 342, 423, 652, 6345, 33523]- 전략 객체를 교체함으로써 알고리즘과 행동 방식이 변경되는 모습을 볼 수 있다.
출처
https://brightstarit.tistory.com/39
https://tjdtls690.github.io/studycontents/java/2022-09-13-strategy_pattern01/