이전 시간까지는 제네릭의 기본적인 사용에 대해 알아보았습니다.
Generic 파트의 마지막으로, 이번 시간에는 조금 더 복잡한 제네릭의 사용 예시에 대해 살펴보겠습니다!
Reculsive Type Bound
reculsive type bound는 type parameter가 자신을 상한으로 하는 bounded type parameter로 사용되는 것을 말합니다.
class Box<T extends Comparable<T>> implements Comparable<Box<T>> {
private T value;
public Box(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
public T getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Box<T> other) {
return this.value.compareTo(other.getValue());
}
}위 코드에서 formal type parameter T는 Comparable<T>로 upper bounded 됩니다.
따라서 actual type parameter로는 Comparable<T>를 구현하고 있는 클래스만 가능하고, value의 compareTo()를 호출할 수 있습니다.
이와 같이 자신을 포함하는 수식으로 bounded 되는 type parameter를 사용하는 것을 reculsive type bound라 합니다.
Box<Integer> box1 = new Box<>(10);
Box<Integer> box2 = new Box<>(7);
Box<Integer> box3 = new Box<>(16);
List<Box<Integer>> list = Arrays.asList(box1, box2, box3);
list.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());
list.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getValue()));
// 출력
7
10
16Java의 Integer의 경우, Comparable<Integer>를 구현하고 있으므로 actual type parameter로 사용 가능합니다.
만약 Comparable을 구현하지 않는 클래스를 actual type parameter로 넣게 되면, 에러가 발생합니다.
Box<Object> objectBox = new Box<>(10); // error!
복수의 Type Parameter 사용
class ListBox<T extends Number, U extends List<T>> {
private U list;
public ListBox(U list) {
this.list = list;
}
public double sum() {
double result = 0.0;
for (T element : list) {
result += element.doubleValue();
}
return result;
}
}
psvm {
ListBox<Integer, List<Integer>> listBox = new ListBox<>(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3));
System.out.println(listBox.sum());
// 출력
6.0
}위 코드와 같이 type parameter를 여러개 사용할 수 있습니다.
각각의 type parameter에 대해 bound를 정의할 수 있으며, wildcard type 또한 개별적으로 정의할 수 있습니다.
private static void test1(ListBox<?, List<?>> listBox) {} // 가능!
private static void test2(ListBox<?, List<Integer>> listBox) {} // 가능!위 테스트는 U가 List<T>로의 bound가 존재하기 때문에, 개별적인 wildcard type 테스트를 제약없이 하기 위하여 단순한 클래스를 생성하여 테스트해보겠습니다.
class A<T, E> {
private T tVal;
private E eVal;
}위 클래스에 대해 다음과 같은 wildcard type 사용이 가능합니다.
private static void test3(A<?, ?> a) {}
private static void test4(A<Integer, ?> a) {}
private static void test5(A<?, Integer> a) {}
private static void test6(A<Integer, String> a) {}즉, type parmeter를 여러개 사용하는 것이 가능하며 각 type parameter는 별개로 사용되어 bound 혹은 wildcard type를 개별적으로 자유롭게 사용할 수 있습니다.
Bounded Type Parameter 사용시 Bound 여러개 사용
class Box<T extends Number & Comparable<T>> implements Comparable<Box<T>> {
private T value;
public Box(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
public T getValue() {
return value;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Box<T> o) {
return value.compareTo(o.getValue());
}
}bounded type parameter 사용시 '&' 연산자를 통하여 명시된 클래스들의 Sub에 해당되는 클래스만 actual type parameter로 제한할 수 있습니다.
위의 예시의 경우 Number, Comparable<T>를 모두 상속하는 Integer, Double과 같은 클래스들이 후보로 추려집니다.
public static <E extends Comparable<? super E>> E max(List<? extends E> list)
public static <E extends Comparable<? super E>> E max(List<? extends E> list)는 이펙티브 자바에서 소개된 예시입니다.
recursive type bound를 사용한 public static <E extends Comparable<E>> E max(List<E> list)의 경우 List<ScheduledFuture<?>> scheduledFutures를 인자로 받을 수 없기 때문에 위와 같이 변형했다고 소개하고 있습니다.
그렇다면, 그 이유에 대해 파헤쳐보겠습니다.
변경 전 메소드
public static <E extends Comparable<E>> E max(List<E> list) {
if(list.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("empty list!");
}
E result = null;
for(E e : list) {
if(result == null || e.compareTo(result) > 0) {
result = Objects.requireNonNull(e);
}
}
return result;
}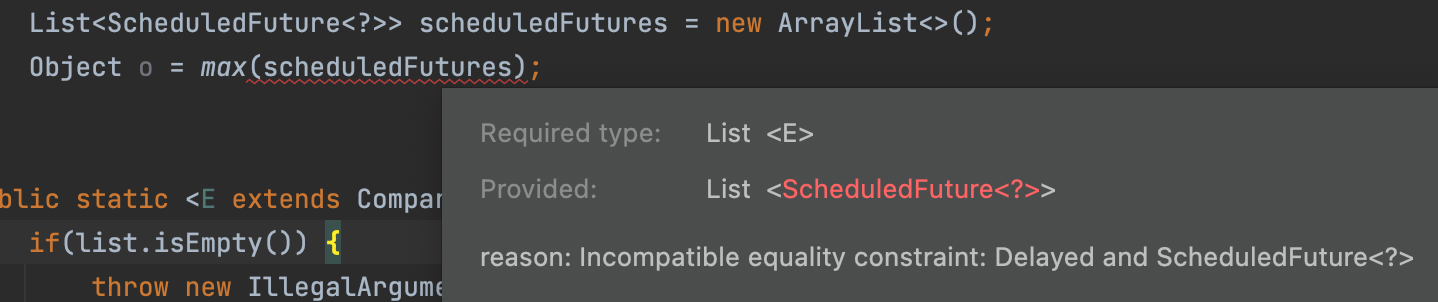
변경 전 메소드에서는 List<ScheduledFuture<?>> 를 인자로 넣으면 에러가 발생합니다.
ScheduledFuture는 Delayed의 하위 인터페이스이고, Delayed가 Comparable<Delayed>를 구현했기 때문에 ScheduledFuture는 해당 인스턴스 뿐만이 아닌, Delayed의 인스턴스와도 비교할 수 있기 때문입니다.
그렇다면 변경된 메소드를 확인해보겠습니다.
public static <E extends Comparable<? super E>> E max(List<? extends E> list) {
if(list.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("empty list!");
}
E result = null;
for(E e : list) {
if(result == null || e.compareTo(result) > 0) {
result = Objects.requireNonNull(e);
}
}
return result;
}
이제 에러가 발생하지 않고 List<ScheduledFuture<?>> 를 인자로 받을 수 있는 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
E는 Comparable 구현한 객체 타입으로 제한되고, 리스트의 요소들이 E의 하위 클래스이기 때문에,
public interface Comparable<E>public interface Delayed extends Comparable<Delayed>public interface ScheduledFuture<V> extends Delayed, Future<V>
의 상속 관계에서 Comparable<Delayed>를 구현한 Delayed를 상속받는 ScheduledFuture List를 받을 수 있는 것입니다.

