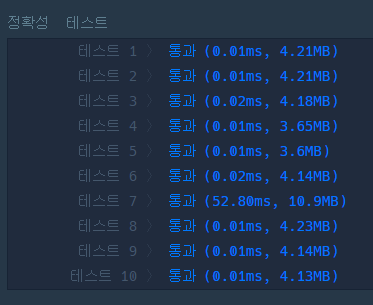
문제 풀기 : https://school.programmers.co.kr/learn/courses/30/lessons/42628

CPP 연습에 의의가 있다.
문제 접근
문제해석
- 아주 노골적으로 우선순위 큐가 있고, 그것이 이중으로 있다는 점에 착안한 문제이다.
- 따라서, 최댓값이나 최소값을 찾아서
- 멸령어 해석에 있어서 cpp언어라면 주의를 요한다!
Heap 과 우선순위 큐 의 개념
우선순위 큐
- 나오는데 순서가 있는 큐를 의미한다.
- 이는 보통 힙으로 구현한다.
Heap의 속성
- 힙은 tree에서 파생하여 나온 자료구조이다.
- 이는 특정한 방식에 의해 위계를 갖추고, 자식이 2개이하인 tree를 의미한다.
- 포화 이진트리의 경우 node수는 2^(n-1)개의 node를 가지고 있다. (n = 층계)
그러므로. 완전탐색으로 역값을 찾을 필요는 없다.
최솟값을 찾으려면, node/2까지만 탐색해도 된다. - 왜나하면, 최대 heap에 의하면 가장 최대값은 leaf가까이 있기 때문이다.
문제 풀이
Cpp String 처리
#include <string>을 도입해주어야 사용가능하다!
stoi-> string to intsubstr(begin,size)-> begin~size 까지의 인덱스로 string을 자른다.
CPP에서의 Heap
#include <algorithm>을 도입해주어야 사용가능하다!
push/pop
둘다 사용패턴은 아래와 같다.
somevector.push_back(...);
somevector.push_heap(somevector.begin(),somevector.end());
pop_heap(heap.begin(),heap.end());
heap.pop_back();- push_heap(it begin, it end) : begin~end 까지의 heap에 값을 삽입한다.
- pop_heap ... : begin~end 까지의 heap에 맨 위값을 맨 뒤로 뺀다.
sort_heap 과 make_heap의 차이
make_heap: vector 자체를 힙으로 만든다. (기본값 최대힙)sort_heap: 힙 자체를 재정렬하는데, 이때 어떤 연산자를 주지 않는다면 최소힙을 만든다partial_sort: 힙기반 정렬. > 3개를 받는데 중간을 잘라서 정렬하는 함수이다.
결합.
- I로 시작하는 모든 명령어는 최대힙으로 삽입한다.
D 1은 최댓값을 찾아 제거한다.
D -1은 최솟값을 찾아서 제거하는데...최솟값을 찾기 위해서는, 위에서 최대 길이의 n/2까지만 돌아도 충분함을 보였으므로,
그 범위내에서 가장 최솟값을 찾으면 된다.
- 이후 다시 정리를 하고, 값을 돌려주면 된다.
코드
// 살짝 난잡하니 나중에 코드 정리하자...
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
vector<int> solution(vector<string> operations) {
vector<int> heap = {};
for(auto now = operations.begin(); now != operations.end(); now++)
{
string st = (*now);
int val = stoi(st.substr(2,st.size()-2));
if(st.at(0) == 'I')
{
heap.push_back(val);
push_heap(heap.begin(),heap.end());
}
else if (st.at(0) != 'D') continue;
else if (val == -1)
{
if(heap.size() == 0)
continue;
else if(heap.size() == 1)
{
heap.erase(heap.begin());
continue;
}
int min_check = *(heap.rbegin());
int min_idx = heap.size()-1;
for(int now = heap.size()-1; now >= heap.size()/2 ; now-- )
{
if(heap.at(now) < min_check)
{
min_check = heap.at(now);
min_idx = now;
}
}
heap.erase(heap.begin() + min_idx);
make_heap(heap.begin(),heap.end());
}
else if (val == 1)
{
if(heap.size() == 0) continue;
pop_heap(heap.begin(),heap.end());
heap.pop_back();
}
}
vector<int> answer = {0,0};
if(heap.size() == 0)
return answer;
sort_heap(heap.begin(),heap.end());
pop_heap(heap.begin(),heap.end());
int min_check = *(heap.rbegin());
int min_idx = heap.size()-1;
int max_check = *(heap.begin());
int max_idx = 0;
if(heap.size() > 1)
{
for(int now = heap.size()-1; now >= heap.size()/2 ; now-- )
{
if(heap.at(now) < min_check)
{
min_check = heap.at(now);
min_idx = now;
}
}
for(int now = 0 ; now >= 2 ; now ++ )
if(heap.at(now) > max_check)
{
max_check = heap.at(now);
max_idx = now;
}
}
answer[0] = heap.at(max_idx);
answer[1] = heap.at(min_idx);
return answer;
}결과