BigInteger
BigInteger란?
BigInteger는 자바에서 제공하는 클래스로, 임의 정밀도 정수(arbitrary-precision integers)를 나타내는 데 사용된다.
정수를 표현할 때 일반적으로 사용되는 기본 자료형(int, long 등)은 크기에 제한이 있다. 예를 들어, int는 32비트이므로 최대값은 2의 31승 - 1이 됩니다. 하지만 BigInteger는 이러한 제한이 없습니다. 따라서 매우 큰 정수 값도 표현할 수 있음!!
장점
BigInteger 클래스는 다음과 같은 메서드를 제공하여 정수 연산을 수행할 수 있다
- 더하기, 빼기, 곱하기
- 나누기, 나머지 연산
- 거듭제곱
- 비트 연산
- 비교
예를 들어, 아주 큰 두 정수를 더하고 싶을 때, int나 long으로는 범위를 초과하여 오버플로우가 발생할 수 있지만, BigInteger를 사용하면 이러한 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
즉, 연산 메서드가 내장되어 있다고 볼 수 있음
내장된 메서드 정리
-
add(BigInteger val): 현재 BigInteger와 인수로 전달된 BigInteger를 더한다.
-
subtract(BigInteger val): 현재 BigInteger에서 인수로 전달된 BigInteger를 뺀다.
-
multiply(BigInteger val): 현재 BigInteger에 인수로 전달된 BigInteger를 곱한다.
-
divide(BigInteger val): 현재 BigInteger를 인수로 전달된 BigInteger로 나눈다. 몫을 반환
-
remainder(BigInteger val): 현재 BigInteger를 인수로 전달된 BigInteger로 나눈 나머지를 반환
-
pow(int exponent): 현재 BigInteger를 지수로 제곱
-
abs(): 현재 BigInteger의 절댓값을 반환
-
negate(): 현재 BigInteger의 부호를 바꾼다.
-
compareTo(BigInteger val): 현재 BigInteger를 인수로 전달된 BigInteger와 비교합니다. 값이 같으면 0, 현재 BigInteger가 크면 양수, 작으면 음수를 반환합니다.
-
equals(Object x): 현재 BigInteger와 지정된 객체를 비교하여 같으면 true를 반환합니다.
-
toString(): BigInteger를 문자열로 변환하여 반환합니다.
🤔 왜? 찾아봤는데?
알고리즘 공부하다가

여기서 가장 핵심은
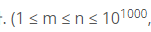
이거임!!
근데 나는 풀이 과정에서 다른 걸 문제 삼고 있었다.
해결과정
1.InputMismatch 런타임에러
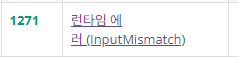
이 런타임에러는 InputMismatchException은 입력 데이터가 예상한 형식과 일치하지 않을 때 발생하는 런타임 예외로, 이 예외는 주로 Scanner 클래스를 사용하여 입력을 파싱할 때 발생한다.
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int m = 0;
int n = 0;
try {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
m = in.nextInt();
n = in.nextInt();
int result = m / n;
int remainder = m % n;
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(remainder);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}여기서 음... int에 문제인가 싶어서 long으로 바꿨음
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long m = 0;
long n = 0;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
m = in.nextLong();
n = in.nextLong();
long result = m / n;
long remainder = m % n;
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(remainder);
}
}그러나.. 똑같았고... 찾아보니 일반 타입으로는 안되었던 것... BigInteger이 필요했다.
2. NoSuchElement 런타임에러
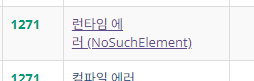
NoSuchElement 런타임에러는 Scanner 객체에서 nextLine() 메서드를 호출했을 때 입력 스트림에서 읽을 요소가 없는 경우에 발생할 수 있는 예외로, 이는 일반적으로 입력이 끝난 후에 또 다시 입력을 요구할 때 발생할 수 있다.
예를 들어, 사용자가 프로그램 실행 중에 엔터키를 누르거나 입력을 마치고 엔터키를 입력하지 않은 경우에 발생할 수 있음!!
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String m;
String n;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
BigInteger number1;
BigInteger number2;
try{
m = in.nextLine();
n = in.nextLine();
number1 = new BigInteger(m);
number2 = new BigInteger(n);
BigInteger result = number1.divide(number2);
BigInteger remainder = number1.remainder(number2);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(remainder);
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("올바른 숫자 형식이 아닙니다.");
}
}
}즉, nextLine으로 받아서 그럼
최종 코드
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String m;
String n;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
BigInteger number1;
BigInteger number2;
try{
m = in.next();
n = in.next();
number1 = new BigInteger(m);
number2 = new BigInteger(n);
BigInteger result = number1.divide(number2);
BigInteger remainder = number1.remainder(number2);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(remainder);
}
catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("올바른 숫자 형식이 아닙니다.");
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
System.out.println("0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.");
}
}
}소감
항상 알고리즘 공부 미뤘는데.. 파이썬으로 하기 전에 회사에서 자바쓰니까 자바로 공부해봐야지
