24/12/02 람다식
람다표현식
함수를 간략하게 표현하는 것
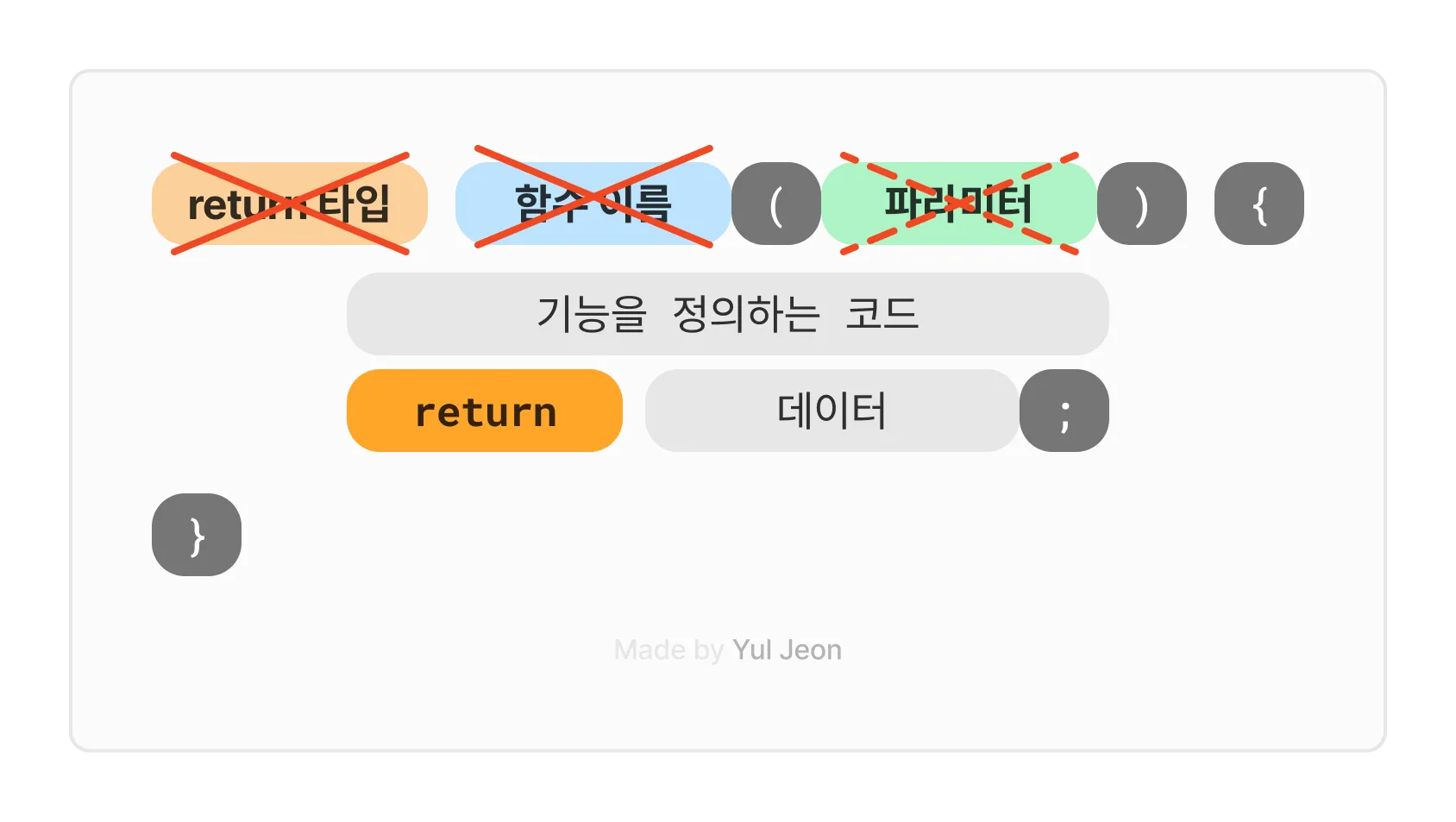

🤖코드의 구조
함수의 기본 구조에서 return 타입, 함수이름, 파라미터를 없애고, 변수이름과 기능을 정의하는 코드로만 구성된다.
(n) -> { }streamAPI
Stream API는 원본 데이터를 조회하여 별도의 Stream 객체로 생성하여 변형할 수 있는 역할
distinct()
중복제거
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<>(); names.add("박효신"); names.add("이지은"); names.add("이지은"); names.add("하현우"); names.add("하현우"); names.add("하현우"); List<String> uniqueNames = names.stream() .distinct() // 중복 제거 .toList(); System.out.println(uniqueNames);
sorted()
정렬
ArrayList<String> 한글 = new ArrayList<>(); 한글.add("다"); 한글.add("가"); 한글.add("나"); List<String> 정렬된한글 = 한글.stream() .sorted() .toList(); assertThat(정렬된한글).containsExactly("가", "나", "다"); List<String> 거꾸로정렬된한글 = 한글.stream() .sorted(Comparator.reverseOrder())//함수는 함수도 받는다. .toList(); assertThat(거꾸로정렬된한글).containsExactly("다", "나", "가");
⚡map()
변환
void mapSquareTest() { List<Integer> numbers = List.of(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); List<Integer> squaredNumbers = numbers.stream() .map(n -> n * n) .toList(); assertThat(squaredNumbers).isEqualTo(List.of(1, 4, 9, 16, 25)); }
⚡filter()
필터링(조건?일때 주로 사용하는 것 같음)
ArrayList<Integer> prices = new ArrayList<>(); prices.add(100); prices.add(150); prices.add(160); prices.add(200); prices.add(800); List<Integer> 이백원미만상품가격들 = prices.stream() .filter((장바구니상품가격) -> 장바구니상품가격 < 200) .toList();
📌 Stream API의 메서드들은 List를 Stream으로 바꿔서 작업하기 때문에
다시 List로 되돌려야 함 ( List → Stream → List )
// Java 16 이상
.toList()
// Java 16 미만
.collect(Collectors.toList())🧐람다식을 사용할 때는 먼저 구조를 잡고 시작해야한다.
() -> {} 하고 변수가 필요하다면 변수를 먼저 집어넣고 생각하면 된다.
😐 느낀점
쉬운데 어려운...
일단 개념자체는 쉬워서 알기는 편하다
map, filter는 많이 사용되니까 잘 알아두어야한다.