코드파일(.c)을 compile하면 object파일(.o)이 만들어지고, link과정을 통해 object파일들이 합쳐지면 실행파일(.elf)이 된다.
이렇게 만들어진 elf파일의 실행코드는 flash에 저장, 데이터는 RAM에 저장된다.
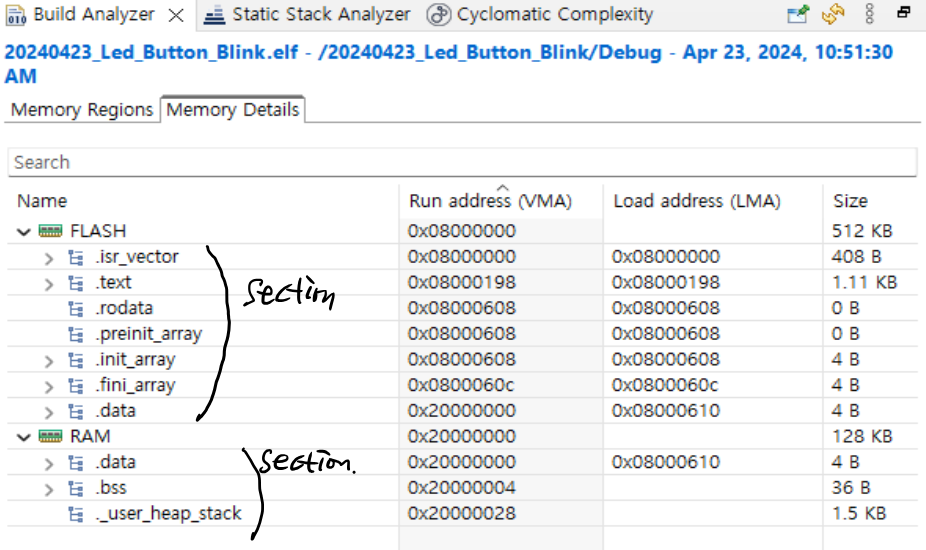
- 실행코드는 section이라고하는 구분단위로 나뉜다.
- complie하면 object file이 생성되고, 이것은 section을 구분해놓은 단위file이다.
Linker Script
linker script : link시 사용되는 파일이며 코드와 데이터가 어디로 저장되는지 주소위치를 지정해준다.

- FLASH.Id는 부팅되기 전 프로그램을 flash에 입력할 때 사용

- RAM.Id는 부팅 후 Flash에 있는 데이터를 RAM으로 불러올 때 사용
/* Entry Point */
ENTRY(Reset_Handler)
/* Highest address of the user mode stack */
_estack = ORIGIN(RAM) + LENGTH(RAM); /* end of "RAM" Ram type memory */ENTRY는 startup의 시작을 나타내고, _estack은 stack의 최상단 주소를 나타내며 stack point이다.
/* Memories definition */
MEMORY
{
RAM (xrw) : ORIGIN = 0x20000000, LENGTH = 128K
FLASH (rx) : ORIGIN = 0x8000000, LENGTH = 512K
}메모리정보에 대한 내용이다. RAM은 실행,읽기,쓰기(xrw) Flash는 읽기,실행(rx)만 가능하다. 각각의 시작주소(ORIGIN)와 크기(LENGTH)를 나타낸다.

SECTIONS에는 각각 section에 해당하는 정보들이 기술되 있다.
- .isr_vector에는 인터럽트에 사용되는 벡터정보
- .text에는 실행코드에 대한 정보
- .data는 초기화된 전역변수
- .bss는 초기화 안된 전역변수
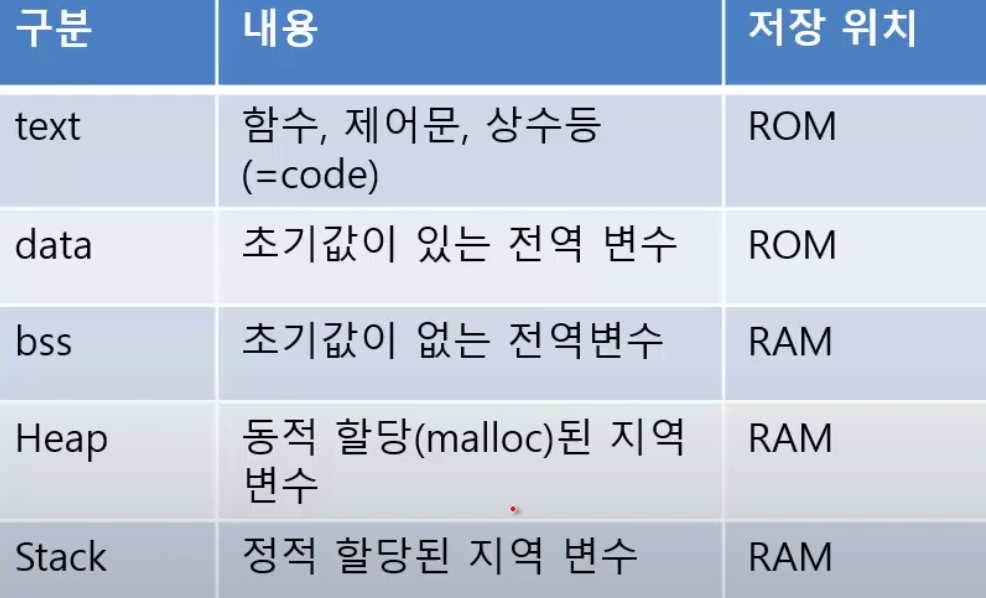
- text, data, bss는 컴파일 시 크기가 결정되고 변하지 않는다.
- heap은 낮은주소에서 높은주소로 올라가고, stack은 LIFO형식으로 stack point에서 낮은주소로 내려간다. (스택오버플로우 발생 주의)
data가 ROM에 있으면 수정이 불가능하므로 부팅 시 RAM으로 복사되 사용된다.
bss는 startup에서 0으로 초기화된다.
Startup Code
MCU는 부팅되고 바로 main함수로 진행하는 것이 아닌, startup code를 제일 먼저 실행하게 된다.
/**
* @brief This is the code that gets called when the processor first
* starts execution following a reset event. Only the absolutely
* necessary set is performed, after which the application
* supplied main() routine is called.
* @param None
* @retval : None
*/
.section .text.Reset_Handler
.weak Reset_Handler
.type Reset_Handler, %function
Reset_Handler:
ldr sp, =_estack /* set stack pointer */
/* Call the clock system initialization function.*/
bl SystemInit
/* Copy the data segment initializers from flash to SRAM */
ldr r0, =_sdata
ldr r1, =_edata
ldr r2, =_sidata
movs r3, #0
b LoopCopyDataInit
CopyDataInit:
ldr r4, [r2, r3]
str r4, [r0, r3]
adds r3, r3, #4
LoopCopyDataInit:
adds r4, r0, r3
cmp r4, r1
bcc CopyDataInit
/* Zero fill the bss segment. */
ldr r2, =_sbss
ldr r4, =_ebss
movs r3, #0
b LoopFillZerobss
FillZerobss:
str r3, [r2]
adds r2, r2, #4
LoopFillZerobss:
cmp r2, r4
bcc FillZerobss
/* Call static constructors */
bl __libc_init_array
/* Call the application's entry point.*/
bl main
bx lr
.size Reset_Handler, .-Reset_Handler
/**
* @brief This is the code that gets called when the processor receives an
* unexpected interrupt. This simply enters an infinite loop, preserving
* the system state for examination by a debugger.
* @param None
* @retval None
*/
.section .text.Default_Handler,"ax",%progbits
Default_Handler:
Infinite_Loop:
b Infinite_Loop
.size Default_Handler, .-Default_Handler부팅과정을 보면 우선 stack point를 RAM의 최상단 주소로 맞추고, fpu, exRAM, 벡터테이블을 초기화 한다. data를 flash에서 가져오고, bss를 0으로 초기화 한다. 이후 main함수를 호출하게 된다.
