수업에서 배운 파일 read와 write 함수를 통해 파일을 복사하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
사용자로 부터 복사할 파일(src_file)과 복사후 생성될 파일(dst_file)을 프로그램 실행시 전달 받아 동작하도록 구현하시오.
예) my_cp src_file dst_file
두 번째 과제는 read 와 write 함수를 통해 파일을 복사하는 프로그램을 작성하는 것이다.
이전 과제에서 작성했던 파일 내용을 읽고 출력하는 프로그램을 참고하여 코드를 작성한다.
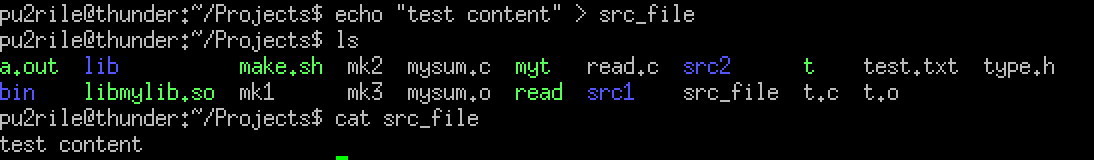
복사할 파일 생성
src_file을 생성한다.
echo "test content" > src_filecat명령어를 통해 잘 생성되었는지 확인한다.
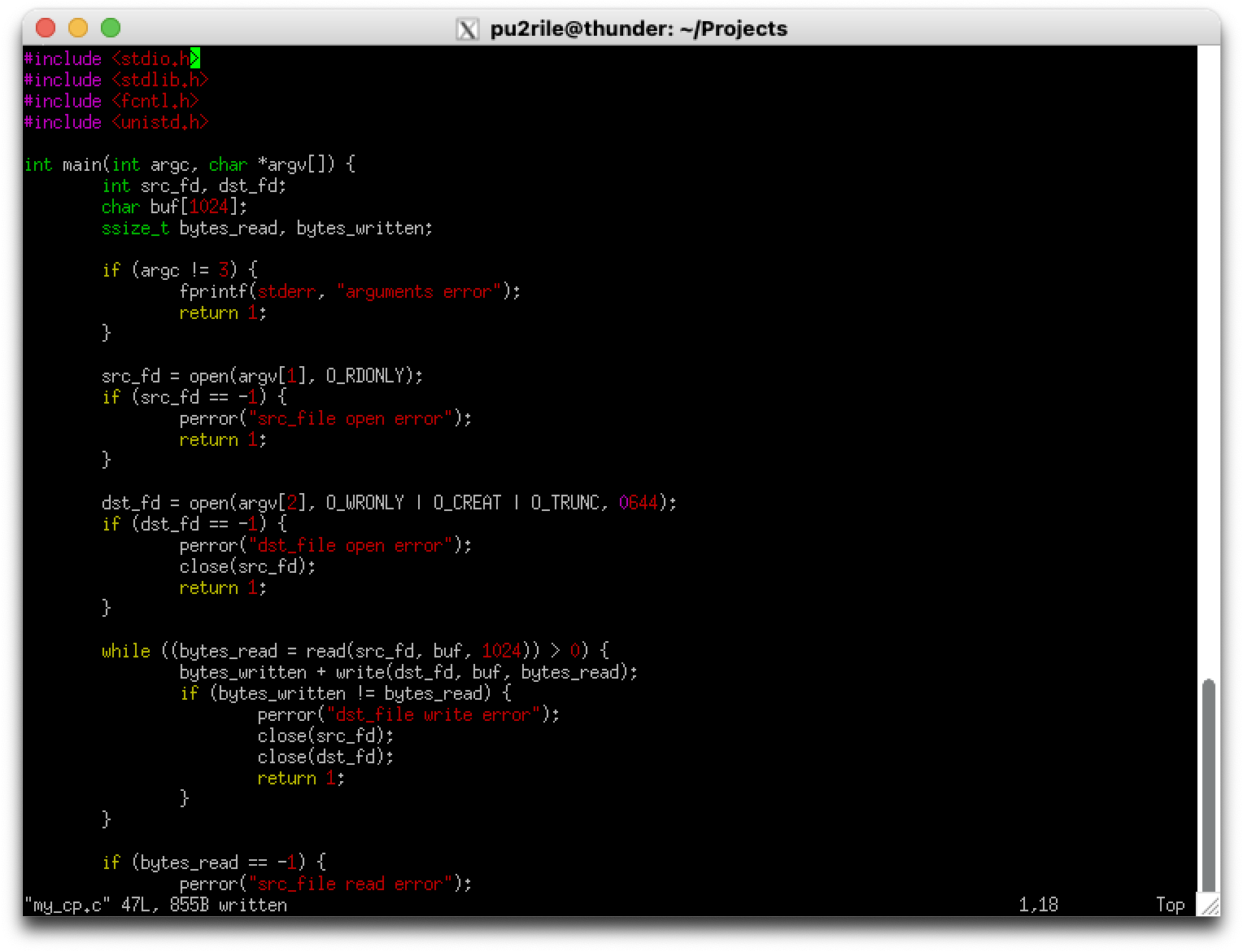
프로그램 소스 코드 작성
사용자가 입력한 복사할 파일(src_file)과 복사 후 생성될 파일(dst_file)을 프로그램 실행 시 전달받아 동작하도록 구현한다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int src_fd, dst_fd;
char buf[1024]; // 버퍼 크기를 1024로 직접 지정
ssize_t bytes_read, bytes_written;
// 인자 확인
if (argc != 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "arguments error\n");
return 1;
}
// 원본 파일 열기
src_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (src_fd == -1) {
perror("src_file open error");
return 1;
}
// 복사할 파일 생성 및 쓰기 가능하도록 열기
dst_fd = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
if (dst_fd == -1) {
perror("dst_file open error");
close(src_fd);
return 1;
}
// 파일 복사 (read/write 사용)
while ((bytes_read = read(src_fd, buf, 1024)) > 0) {
bytes_written = write(dst_fd, buf, bytes_read);
if (bytes_written != bytes_read) {
perror("dst_file write error");
close(src_fd);
close(dst_fd);
return 1;
}
}
if (bytes_read == -1) {
perror("src_file read error");
}
// 파일 닫기
close(src_fd);
close(dst_fd);
return 0;
}
이전 과제처럼 src_fd = open("src_file", O_RDONLY); 이렇게 argv[1] 대신 src_file을 사용하여(파일 이름을 src_file로 하드코딩해서) 복사할 원본 파일을 열려고 했으나,
예) my_cp src_file dst_file
과제에서 위처럼 명령줄 인자로 파일 이름을 받으라고 제시되어 있으므로 argv[1]과 argv[2]를 사용하여 인자를 처리했다.
컴파일 및 실행
gcc -o my_cp my_cp.c→ my_cp.c 파일을 컴파일하여 my_cp라는 실행 파일 생성
./my_cp src_file dst_file→ src_file을 dst_file로 복사
🔍 네? 오류라고요? 복사는 됐는데?
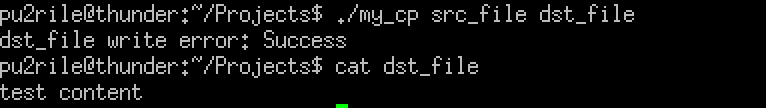
아니 error: Success 가 무슨 말이지요...
GPT 선생님께 물어보니, 오류가 난 것처럼 보이지만 실제로 오류가 없는 상태임에도 불구하고 perror() 함수가 호출되었기 때문에 발생한 현상 이라고 한다.
다시 말해 perror()는 시스템 호출이 실패했을 때만 사용해야 하는데 내가 작성한 위 코드에서는 부분 쓰기 여부를 처리할 때도 perror()가 호출되어 오류 메시지로 "Success"가 출력된 것이다.
write() 함수가 실제로 오류를 반환할 때만 perror()를 호출하도록 수정
while ((bytes_read = read(src_fd, buf, 1024)) > 0) {
bytes_written = write(dst_fd, buf, bytes_read);
if (bytes_written == -1) { // write가 오류를 반환했을 때만 perror 호출
perror("dst_file write error");
close(src_fd);
close(dst_fd);
return 1;
}
}
최종 결과
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int src_fd, dst_fd;
char buf[1024];
ssize_t bytes_read, bytes_written;
if (argc != 3) {
fprintf(stderr, "arguments error");
return 1;
}
src_fd = open(argv[1], O_RDONLY);
if (src_fd == -1) {
perror("src_file open error");
return 1;
}
dst_fd = open(argv[2], O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
if (dst_fd == -1) {
perror("dst_file open error");
close(src_fd);
return 1;
}
while ((bytes_read = read(src_fd, buf, 1024)) > 0) {
bytes_written = write(dst_fd, buf, bytes_read);
if (bytes_written == -1) {
perror("dst_file write error");
close(src_fd);
close(dst_fd);
return 1;
}
}
if (bytes_read == -1) {
perror("src_file read error");
}
close(src_fd);
close(dst_fd);
return 0;
}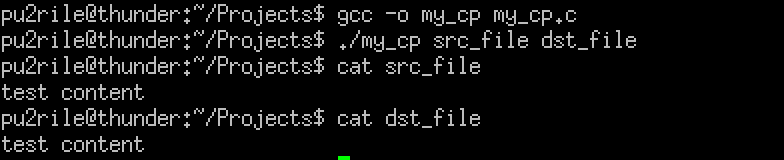
컴파일 및 실행 후 src_file과 dst_file 모두 같은 내용이 출력되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
끝.