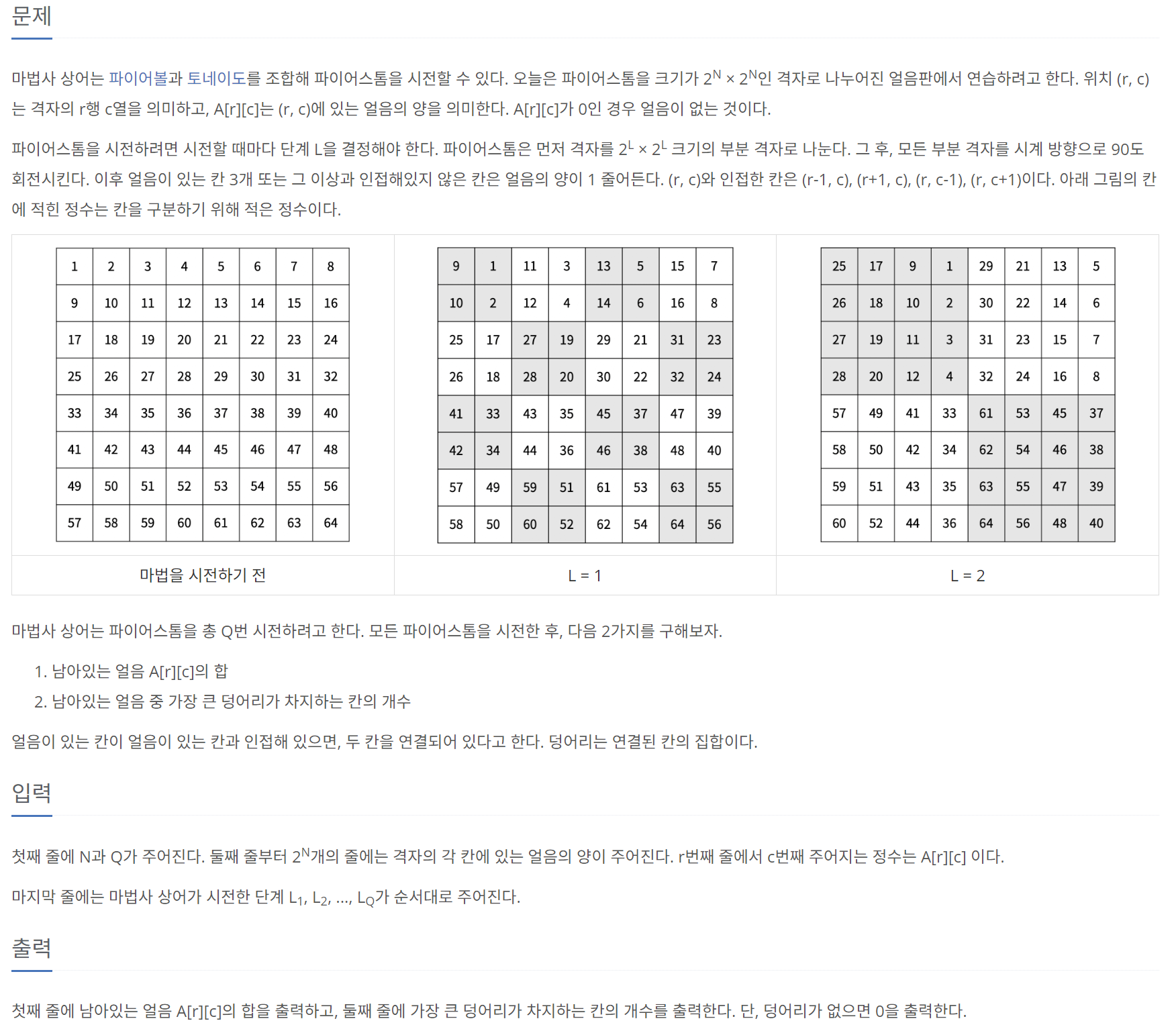
문제
접근 방법
각각의 영역을 회전 후 인접한 얼음의 개수를 세어준다.
3개를 못 넘으면 감소해 준다.
감소할 때 다른 얼음의 영향을 안 받게 감소한 값을 저장해 주는 공간을 따로 만들어 주면 된다.
코드
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
vector<vector<int>> graph, buffer;
int dy[] = {0, 0, -1, 1}, dx[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
int N, Q, L, iceSum, maxArea;
bool isOut(int ny, int nx)
{
return ny < 0 || nx < 0 || ny >= N || nx >= N || !graph[ny][nx];
}
bool isCorrect(int y, int x)
{
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
int ny = y + dy[i], nx = x + dx[i];
if (isOut(ny, nx))
continue;
++cnt;
}
return cnt >= 3;
}
void step()
{
int len = (1 << L);
// 회전
for (int i = 0; i < N; i += len)
for (int j = 0; j < N; j += len)
for (int k = 0; k < len; ++k)
for (int l = 0; l < len; ++l)
buffer[i + k][j + l] = graph[i + len - 1 - l][j + k];
graph = buffer;
// 인접한 얼음 확인
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
if (graph[i][j] && !isCorrect(i, j))
buffer[i][j] = graph[i][j] - 1;
graph = buffer;
}
void bfs(int y, int x)
{
int cnt = 0;
queue<pii> q;
q.push({y, x});
iceSum += graph[y][x];
graph[y][x] = 0;
while (!q.empty())
{
pii cur = q.front();
q.pop();
++cnt;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; ++i)
{
int ny = cur.first + dy[i];
int nx = cur.second + dx[i];
if (isOut(ny, nx))
continue;
iceSum += graph[ny][nx];
graph[ny][nx] = 0;
q.push({ny, nx});
}
}
maxArea = max(maxArea, cnt);
}
void input()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0);
cin >> N >> Q;
N = (1 << N);
graph = buffer = vector<vector<int>>(N, vector<int>(N));
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
cin >> graph[i][j];
}
void solve()
{
while (Q--)
{
cin >> L;
step();
}
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j)
if (graph[i][j])
bfs(i, j);
cout << iceSum << "\n"
<< maxArea;
}
int main()
{
input();
solve();
return 0;
}풀이
범위의 회전, 전체의 인접한 얼음 확인을 반복하다가 마지막에 출력할 값을 확인해 주면 된다.
출력할 값의 경우 탐색을 통해 구할 수 있다.
BFS를 활용하여 이미 탐색한 부분, 얼음이 아닌 부분은 넘어간다. 그렇게 되면 덩어리를 구할 수 있다.

