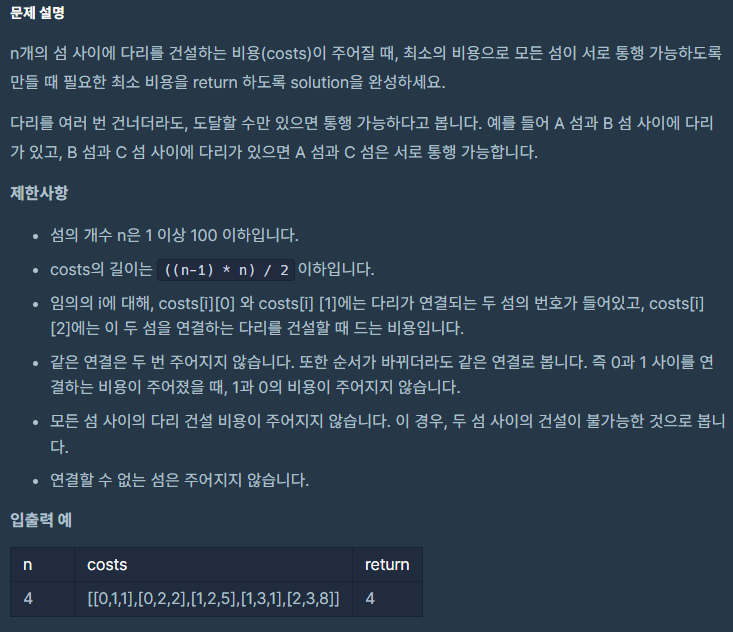
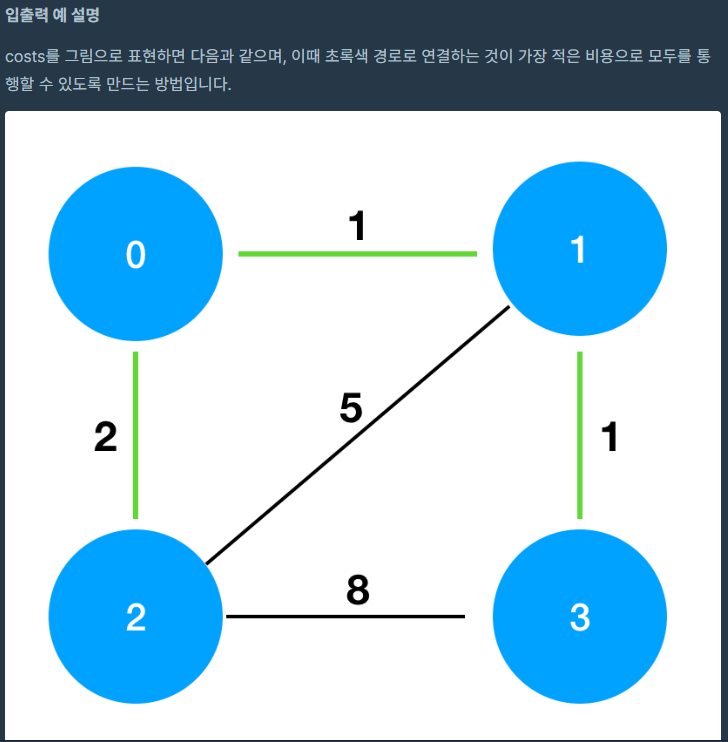
문제
첫 번째 접근 방법
비용마다 섬들을 저장하고 비용을 올려가며 섬들을 연결했음을 표시하면 어떨까 싶었다.
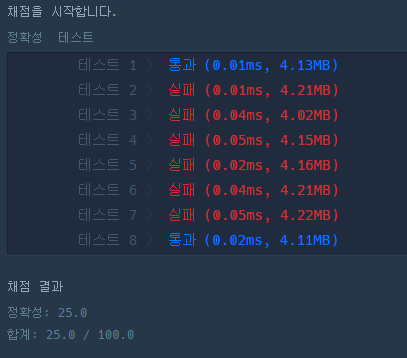
첫 번째 실패
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
bool isConnect[101] = {};
int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> costs)
{
int answer = 0, c = n;
map<int, unordered_set<int>> lowCost;
for (vector<int> cost : costs)
{
lowCost[cost[2]].insert(cost[0]);
lowCost[cost[2]].insert(cost[1]);
}
for (auto i : lowCost)
{
for (int j : i.second)
{
if (!isConnect[j])
{
if (c != n)
answer += i.first;
isConnect[j] = true;
c--;
if (c == 0)
return answer;
}
}
}
}그래프의 정점마다 값을 더해줘서 문제가 발생한 것 같다.
그래프 탐색으로 가야겠다고 생각했다. 찾아보니 최소 비용연결은 프림 알고리즘, 최단 거리는 다익스트라 알고리즘이라는 글을 봤다. 최소 비용연결이므로 프림 알고리즘을 찾아서 적용해야겠다.
두 번째 접근 방법
프림 알고리즘을 찾아보니 문제에서 요구하는 바를 충족시키는 것 같았다. 그대로 적용하면 될 것 같다.
코드
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> costs)
{
vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> v;
bool visit[101] = {};
int answer = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 101; ++i)
{
v.push_back(vector<pair<int, int>>());
}
for (vector<int> cost : costs)
{
v[cost[0]].push_back({cost[1], cost[2]});
v[cost[1]].push_back({cost[0], cost[2]});
}
visit[0] = true;
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> pq;
for (int i = 0; i < v[0].size(); ++i)
{
pq.push({v[0][i].second, v[0][i].first});
}
while (!pq.empty())
{
int cost = pq.top().first;
int node = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if (visit[node])
continue;
visit[node] = true;
answer += cost;
for (int i = 0; i < v[node].size(); ++i)
{
pq.push({v[node][i].second, v[node][i].first});
}
}
return answer;
}풀이
정점에 연결된 최소 비용인 간선을 선택해가며 탐색하는 방식이다.
최소 비용으로 가는 것만 생각해서 예시 문제에서 1->0->2 방식으로 이동하면 2->3이 비싸진다고 생각하여 구상만 하고 구현을 못 했는데, 우선순위 큐를 활용하여 최소 비용인 노드들만 계속 탐색하니 좋은 방법 같다.
프림 알고리즘과 같은 방식은 알아두면 좋을 것 같다.
