
이중 연결 리스트
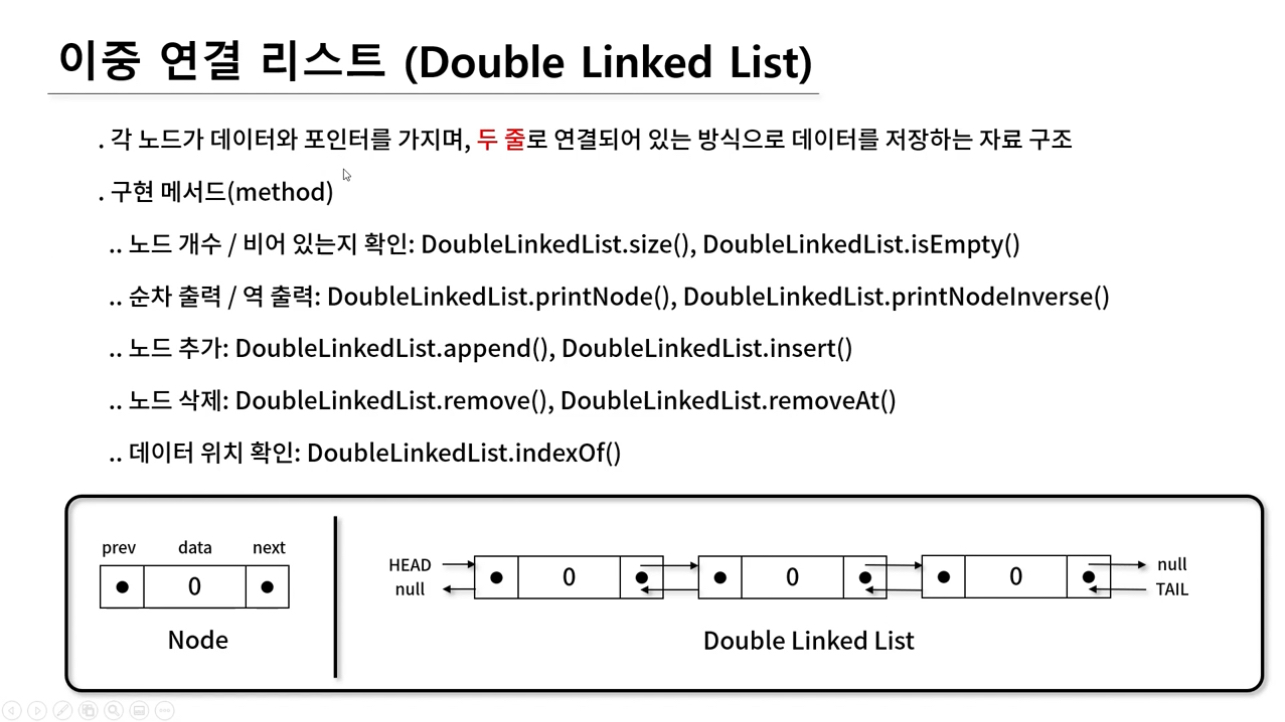
- 두 줄로 연결되어 있어서 pointer가 prev, next 두 개 존재한다.
- 리스트 뒤에서부터 노드에 접근할 수 있어 편하다.
- 리스트를 조작하는 경우엔 업데이트해야 하는 값이 늘어나서 주의해야 한다.
// 기본 코드
function Node(data){
this.prev = null;
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
function DoubleLinkedList(){
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.size = function(){
return this.length;
}
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.isEmpty = function(){
return this.length === 0;
}📌 append
// append(): 연결 리스트 가장 끝 부분에 노드 새로 생성 후 추가
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.append = function(data){
let node = new Node(data);
if(this.head === null){
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}else{
this.tail.next = node;
node.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = node;
}
this.length++;
}
let dll = new DoubleLinkedList();
dll.append(1);
dll.append(10);
dll.append(100);✅ 연결 리스트와 다른점?
똑같이 리스트 끝에 노드를 추가하더라도 이중연결 리스트는 끝에 tail과의 연결도 신경써야 한다.
- 리스트가 비어있는 경우: this.head, this.tail 모두 node를 가리킴
- 노드가 1개 이상 있는 경우:
this.tail.next = node -> 원래 연결됐던 노드에 새 node 연결
node.prev = this.tail -> node.prev로 원래 노드 가리킴(연결)
this.tail = node -> this.tail랑 새 node 연결
📌 printNode, printNodeInverse
// printNode(): 연결 리스트 내에 노드 모두 출력
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.printNode = function(){
process.stdout.write('head -> ');
for(let node = this.head; node != null; node = node.next){
process.stdout.write(`${node.data} -> `);
}
console.log('null');
}
// printNodeInverse(): 연결 리스트 노드를 뒤에서부터 모두 출력
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.printNodeInverse = function(){
let temp = [];
process.stdout.write('null <- ');
for(let node = this.tail; node != null; node = node.prev){
temp.push(node.data);
}
for(let i = temp.length-1; i >= 0; i--){
process.stdout.write(`${temp[i]} <- `);
}
console.log('tail');
}
dll.printNode();
dll.printNodeInverse();head -> 1 -> 10 -> 100 -> null // printNode null <- 1 <- 10 <- 100 <- tail // printNodeInverse두 결과는 거의 비슷하기 때문에 printNode 메서드를 이용한 트릭으로 tail
리스트를 출력할 수도 있지만 tail과 prev 포인터를 적극 이용해서 노드를 출력 했다.
- 빈 배열 temp를 만든다.
- 가장 마지막 값인 null을 문자열로 출력한다.
- this.tail부터 시작 -> node.prev로 업데이트 하면서 노드에 접근한다.
- 접근한 노드의 값을 빈 배열에 인덱스 0부터 차례로 push한다.
- prev가 가리키는 노드가 빈 경우 반복문을 끝낸다.
- 출력 순서는 printNode와 같지만 화살표 방향과 시작 끝이 다르게 출력하기 위해 배열을 거꾸로 출력한다.
- 시작점인 tail을 문자열로 출력한다.
📌 insert
//insert(): position 위치에 노드 추가
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.insert = function(value,position = 0){
if(position < 0 || position > this.length){
return false;
}
let node = new Node(value),
current = this.head,
count = 0,
prev;
if(position === 0){
if(this.head === null){
this.head = node;
this.tail = node;
}else{
node.next = current;
current.prev = node;
this.head = node;
}
this.length++;
}else{
if(position === this.length){
current = this.tail;
current.next = node;
node.prev = current;
this.tail = node;
}else{
while(count++ < position){
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
prev.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = prev;
}
this.length++;
}
}
let dll = new DoubleLinkedList();
dll.insert(1);
dll.insert(10);
dll.insert(100);
dll.printNode(); // head -> 100 -> 10 -> 1 -> null
dll.printNodeInverse(); // null <- 100 <- 10 <- 1 <- tail
dll.insert(2,1);
dll.insert(3,3);
dll.printNode(); // head -> 100 -> 2 -> 10 -> 3 -> 1 -> null
dll.printNodeInverse(); // null <- 100 <- 2 <- 10 <- 3 <- 1 <- tail✅ 연결 리스트와 다른점?
이중 연결에서는 this.tail의 존재때문에 노드를 넣고 싶은 자리의 조건을 세세하게 나눠야 한다.
(value,position을 인자로 받고 position 값을 받지 못하면 디폴트 값 0)
- position == 0
+ this.head === null : 리스트가 빈경우
+ 노드가 1개 이상 있는 경우- position == this.length
this.tail과 연결 해야함- 위 둘 다 아닌 경우
prev, current 이용해서 노드 중간에 연결
📌 remove
// remove(): value 데이터를 찾아서 노드 삭제
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.remove = function(value){
let current = this.head,
prev;
while(current.data != value && current.next != null){
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
if(current.data != value) return null; //리스트에 없는 경우 null, 리스트가 텅 빈 경우도 current.next == null, current.data != value이므로 캐치
if(current === this.head){
this.head = current.next;
if(this.length == 1) this.tail = null; // if(current.next == null) 보다 명시적임
else this.head.prev = null;
}else if(current === this.tail){ // 이미 위 조건에서 노드가 1개인 경우 캐치,
this.tail = current.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
}else{
prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = prev;
}
this.length--;
return current.data;
}
let dll = new DoubleLinkedList();
dll.insert(1);
dll.insert(10);
dll.insert(100);
dll.insert(2,1);
dll.insert(3,3);
console.log(dll.remove(1000));
dll.printNode();
dll.printNodeInverse();
console.log(dll.remove(1));
dll.printNode();
dll.printNodeInverse();
console.log(dll.remove(2));
dll.printNode();
dll.printNodeInverse();
console.log(dll.remove(100));
dll.printNode();
dll.printNodeInverse();- 지우고 싶은 노드를 current에 저장하기 위해서 while문 이용
- 리스트를 모두 돌았는데 current.data != value면 null 반환
- 지우고 싶은 노드가 첫 노드인 경우 current.next 값을 this.head에 할당한다.
+ 노드가 1개만 있는 경우 -> this.tail = null
+2개 이상 있는 경우 -> this.head.prev = null
this.head 는 지운 노드의 다음 값이고 이제는 첫 노드가 된다.
첫 노드의 경우 prev 값이 null 이니까 this.head.prev = null 초기화- 지우고 싶은 노드가 마지막인 경우 this.tail에 current.prev값을 연결한다.
첫 번째 조건에서 노드가 1개인 경우는 이미 해결 했으니까 this.tail은
2개 이상인 경우만 신경쓴다.- 지우고 싶은 노드가 노드 중간에 있는 경우엔 while문으로 찾아낸 prev, current값을 이용해서 연결해준다.
📌 removeAt
// removeAt(): position 위치 노드 삭제
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.removeAt = function(position = 0){
if( position < 0 || position >= this.length) return null;
let current = this.head,
count = 0,
prev;
if(position === 0){
this.head = current.next;
if(this.length == 1) this.tail = null;
else this.head.prev = null;
}else if(position === this.length-1){
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
this.tail.next = null;
}else{
while(count++ < position){
prev = current;
current = current.next;
}
prev.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = prev;
}
this.length--;
return current.data;
}- remove 메서드에서는 value값과 일치하는 노드를 지웠다면 removeAt은
position으로 위치를 찾는다. - 지울 노드가 this.head,this.tail과 연결되는 경우
- 지울 노드가 노드 중간에 있는 경우
# 📌 indexOf, remove2
// indexOf() : value 값과 일치하는 노드의 인덱스를 반환
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function(value){
let current = this.head,
count = 0;
while(current != null){
if(current.data === value) return count;
current = current.next;
count++
}
return -1;
}
// remove2 (): indexOf() + removeAt() = remove2()
DoubleLinkedList.prototype.remove2 = function(value){
let index = this.indexOf(value);
return this.removeAt(index);
}- current != null로 리스트가 비어있는 경우와 모든 노드를 돌고도
찾는 값이 없는 경우 모두를 캐치할 수 있다. - while 문에서 리턴이 되지 않으면 무조건 -1
- remove2는 indexOf로 해당 값의 인덱스를 받아서 removeAt으로 인덱스의 노드를 삭제하고 삭제한 노드를 반환하는 메서드.
